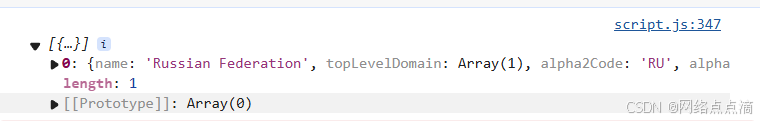
Promise.race
Promise.race是一个用于处理多个异步操作的静态方法,它只会返回首先完成的结果,无论这个结果是resolved或者rejected,其他的未完成的就会被忽略;
(async function () {
const res = await Promise.race([
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/italy`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/egypt`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/china`),
]);
console.log(res[0]);
});
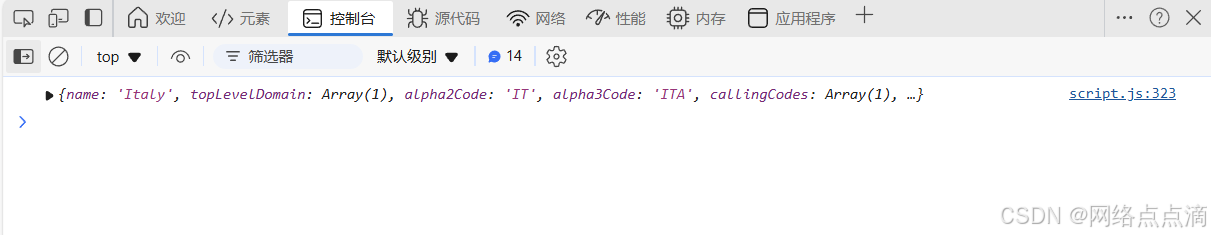
多刷新几次可能会出现不通的结果;
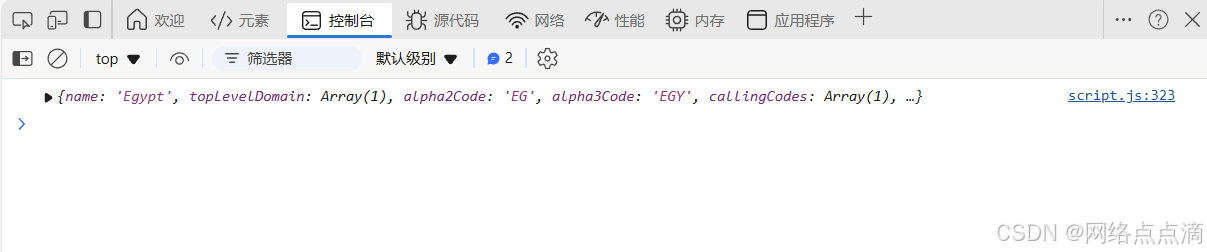
Promise.race在实际中的样例
比如在前端开发中,网络请求可能因为各种原因,比如服务器响应缓慢,网络中断,网络缓慢等原因请求不成功,这时候我们应该自动终止并报错响应的操作;
const timeout = function (sec) {
return new Promise(function (_, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
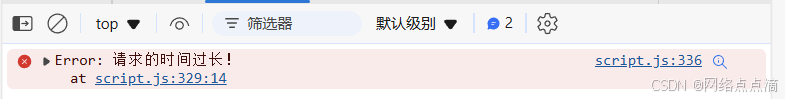
reject(new Error('请求的时间过长!'));
}, timeout);
}, sec);
};
Promise.race([getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/china`), timeout(100)])
.then(res => console.log(res[0]))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
实际生活中,Promise.all和Promise.race是最常用的Promise组合器,但是还有其他的组合器我们也来简单的学习一下;
Promise.allSettled
Promise.allSettled和Promise.all相似,他们都接受多个异步参数,但是Promise.allSettled返回一个数组,其次呢,Promise.all如果多个异步参数中其中一个参数出现reject,那么其他的异步参数也会被短路,但是Promise.allSettled不会被短路,无论你是resolved还是rejected,都会被返回
Promise.allSettled([
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/italy`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/不存在的国家`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/china`),
]).then(res => console.log(res));

Promise.any
Promise.any和Promise.race相似,也是接受一个数组中的多个异步参数,但是他只返回第一个成功的,而在这个成功之前的rejected会被自动忽略;
Promise.any([
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/不存在的国家1`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/不存在的国家2`),
getJSON(`https://restcountries.com/v2/name/Russia`),
]).then(res => console.log(res));