本期我们将深入学习C++中关于STL容器的容器类型:stack(栈)和deque(队列)
作者本人的gitee:楼田莉子 (riko-lou-tian) - Gitee.com
目录
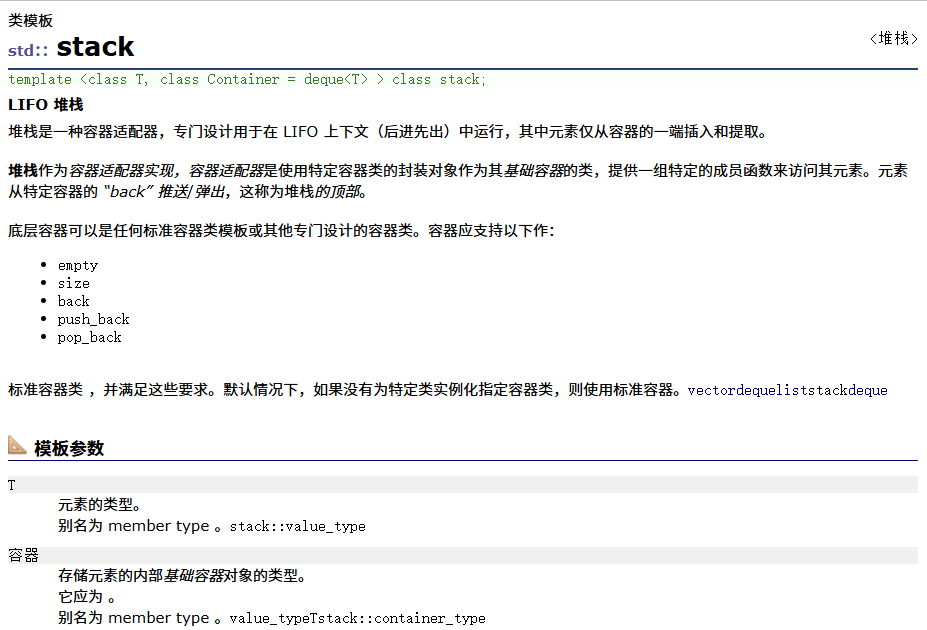
stack的介绍和官方文档
官方文档: stack - C++ 参考
stack的介绍
stack的构造函数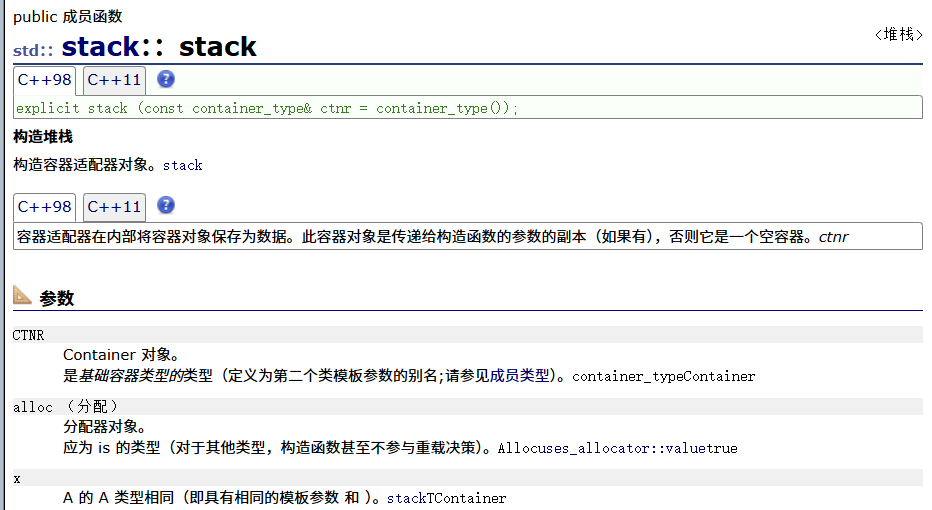
stack不支持迭代器遍历,因此stack也不支持范围for。
stack相关的函数
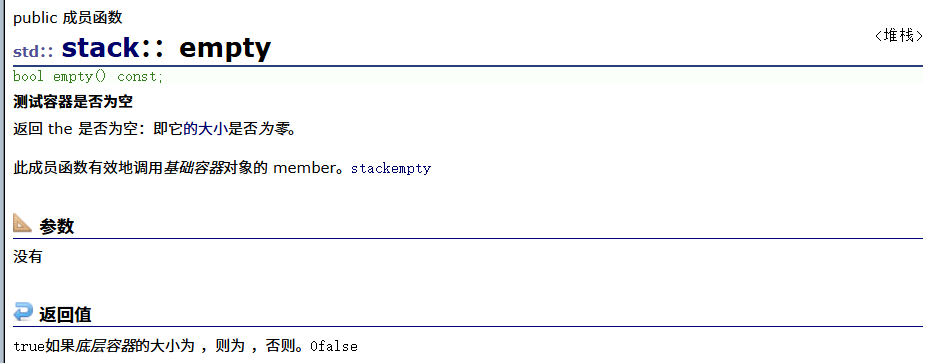
empty(判空)
push(入栈)
pop(出栈)
top(取栈顶元素 )
测试:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
stack<int> s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}结果为:
![]()
size
emplace
swap
stack的模拟实现
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
namespace Boogiepop
{
//适配器/配接器 //用缺省值可以不传递第二个模板参数
template<class T, class container=deque<T>>
//适配器是用来实现转换的
//本质上是容器适配器
//用容器适配转换出来的
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con.back();
}
private:
container _con;
};stack相关题目
1、最小栈

题目中“在常数时间内获取最小栈”意思是getmin()函数的时间复杂度是O(1).
答案:
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack()
{
}
void push(int val)
{
_st.push(val);
if(_minst.empty()||val<=_minst.top())
{
_minst.push(val);
}
}
void pop()
{
if(_st.top()==_minst.top())
{
_minst.pop();
}
_st.pop();
}
int top()
{
return _st.top();
}
int getMin()
{
return _minst.top();
}
private:
stack<int> _st;
stack<int> _minst;
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(val);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/2、栈的压入弹出序列
本题中从大小关系入手是没有意义的。
思路是模拟出入栈顺序跟出栈顺序匹配
思路如下:
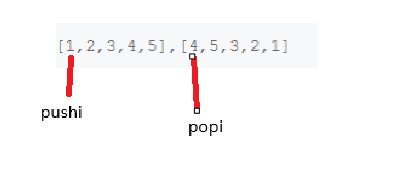
1、pushi指向的数据入栈
2、持续地让栈中数据与popi比较。如果想等则popi++,出栈顶数据,直到为空或者不匹配。
3、重复1、2 步
核心原则:持续比较
结束条件:pushi走到尾部
class Solution
{
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pushV int整型vector
* @param popV int整型vector
* @return bool布尔型
*/
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV)
{
// write code here
stack<int> st;
size_t pushi=0,popi=0;
while(pushi<pushV.size())
{
//先入栈
st.push(pushV[pushi++]);
//尝试与出栈序列匹配
while(!st.empty()&&st.top()==popV[popi])
{
popi++;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
};3、逆波兰表达式求值


逆波兰表达式的解释和扩展:【数据结构】你知道波兰表达式和逆波兰表达式吗?我才知道原来栈在表达式求值中还能这样使用……-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 简单来说,计算机的运算表达式有三种:
中缀表达式(最常用的):运算数+运算符+运算数
前缀表达式:运算符+运算数+运算数
后缀表达式:运算数+运算数+运算符
所以本质上逆波兰表达式就是后缀表达式
后缀表达式运算符按优先级排列,而且要挨着要运算的运算数。
思路:
1、运算数入栈
2、如果是运算符,则出栈顶的两个数据,然后继续入栈
这里额外科普一个string的应用:将string转化为整数
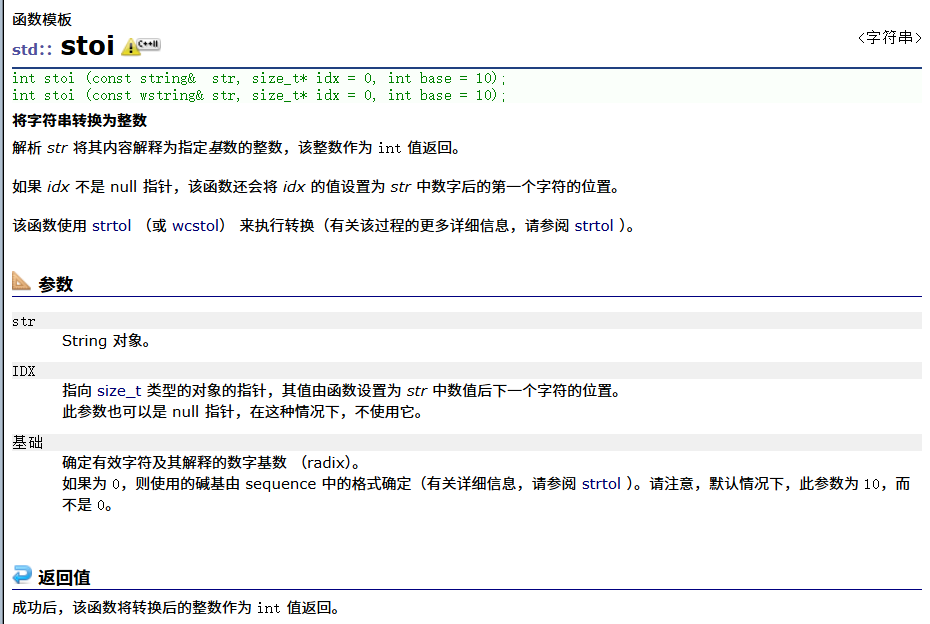
答案:
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens)
{
stack<int> st;
for(auto& str:tokens)
{
if(str=="+"||str=="-"||str=="*"||str=="/")
{
//遇到运算符要出栈两个运算数然后运算后入栈
int right=st.top();
st.pop();
int left=st.top();
st.pop();
switch(str[0])
{
case '+':
st.push(left+right);
break;
case '-':
st.push(left-right);
break;
case '*':
st.push(left*right);
break;
case '/':
st.push(left/right);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
//运算数入栈
st.push(stoi(str));
}
}
return st.top();
}
};4、用栈实现队列


5、二叉树层序遍历
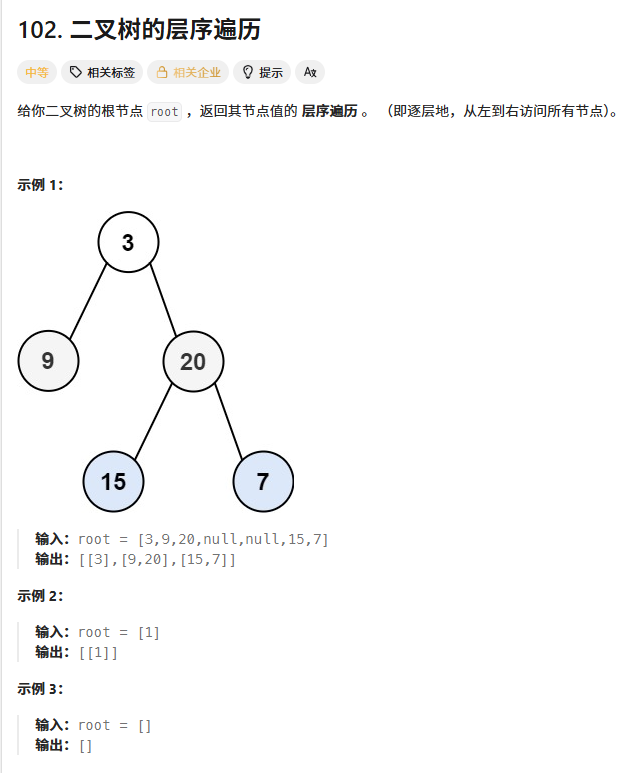
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
queue<TreeNode*>q;
int levelsize=0;//记录当前层数多少个数据
if(root)
{
q.push(root);
levelsize=1;
}
vector<vector<int>>vv;
//层序遍历
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int>v;
//控制一层一层出
while(levelsize--)
{
TreeNode*front=q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(v);
//当前层出完了下一层节点都进队列,队列数据个数就是下一次节点个数
levelsize=q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};这段代码的时间复杂度不是O(N^2)。因为队列进入和出只用了N次。所以实际上时间复杂度是O(N)
queue的介绍和官方文档
官方文档:
queue(单端队列)的介绍
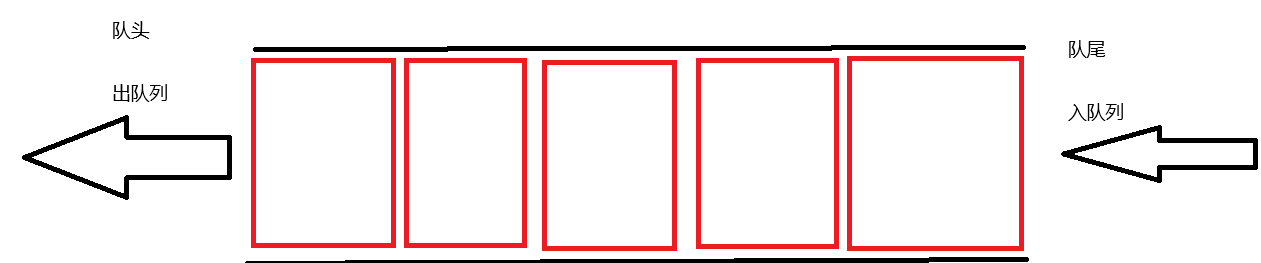
queue构造函数
queue相关的函数
empty

size
front
back
push(入队列)
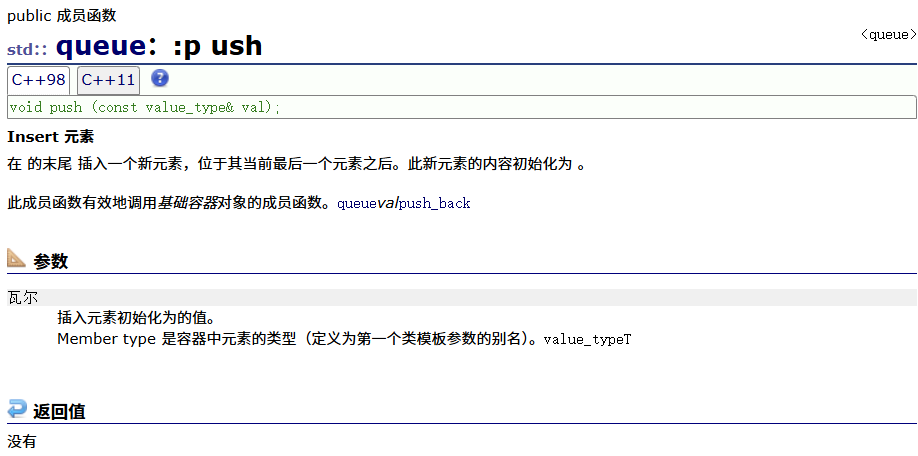
pop(出队列)
emplace
 swap
swap
测试:
void test1()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
cout << q.front() << endl;
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}答案:
queue的模拟实现
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
namespace Boogiepop
{
//适配器/配接器 //用缺省值可以不传递第二个模板参数
template<class T, class container = deque<T>>
//适配器是用来实现转换的
//本质上是容器适配器
//用容器适配转换出来的
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
//_con.erase(_con.begin());效率比较低
_con.pop_front();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con.back();
}
private:
container _con;
};
}
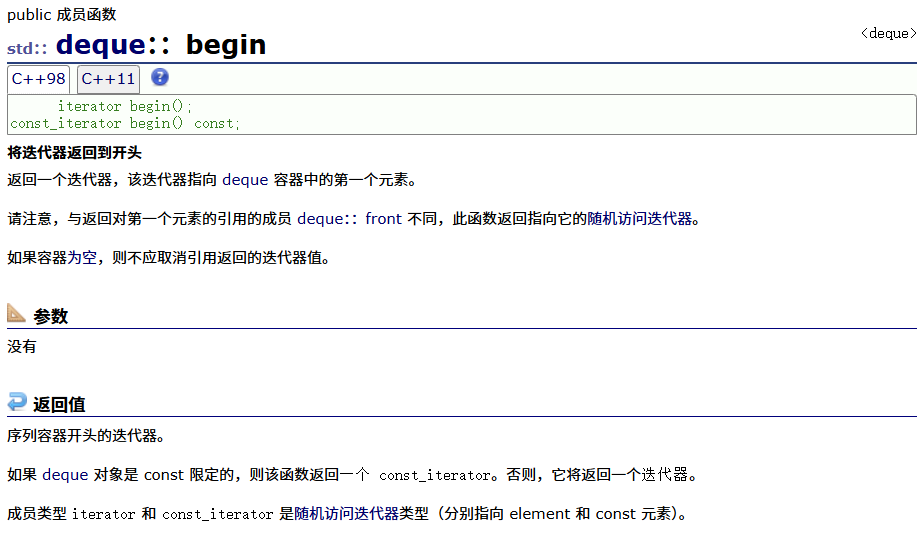
deque的介绍和官方文档
官方文档:deque - C++ 参考
std::d eque - cppreference.com
deque(双端队列)的介绍

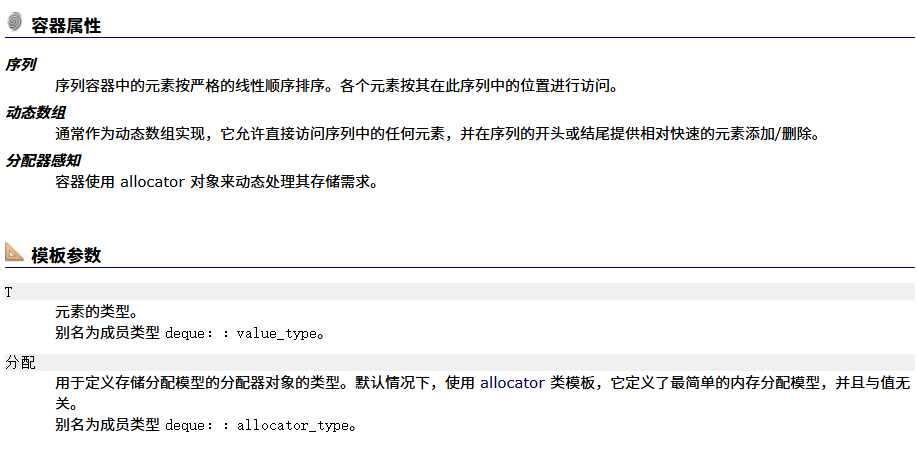
deque的结构图
deque的特殊之处:为什么模拟实现用deque
如上图所示,deque在功能上拥有vector和list的结合。
但是deque遍历的性能并不高效
vector
优点:
1下标随机访问,快;
2尾插尾删效率高
3、CPU高速缓存命中率高
缺点:
1头部、中间插入删除效率低下;
2插入空间不够要扩容,扩容有一定性能消耗,倍数扩容有一定空间浪费
list
优点:
1、任意位置均为O(1)复杂度的插入删除
2、按需申请释放内存
缺点:
1、不支持下标随机访问
2、CPU高速缓存命中率低,还存在缓存污染。
deque
优点:适合头尾插入删除,效率高;下标随机访问效率还不错(大量数据处理不如vector)
缺点:中间位置插入删除效率低,需要大量挪动数据。
相比于vector和list,性能都不够极致
[]下标随机访问的效率:
list<<deque<vector
那是否存在一种数据结构将两者的优点结合起来呢?deque。那么deque的底层结构是怎么样的呢?
我们可以创建一个buffer数组,每个数组由10个,然后创建一个指针数组
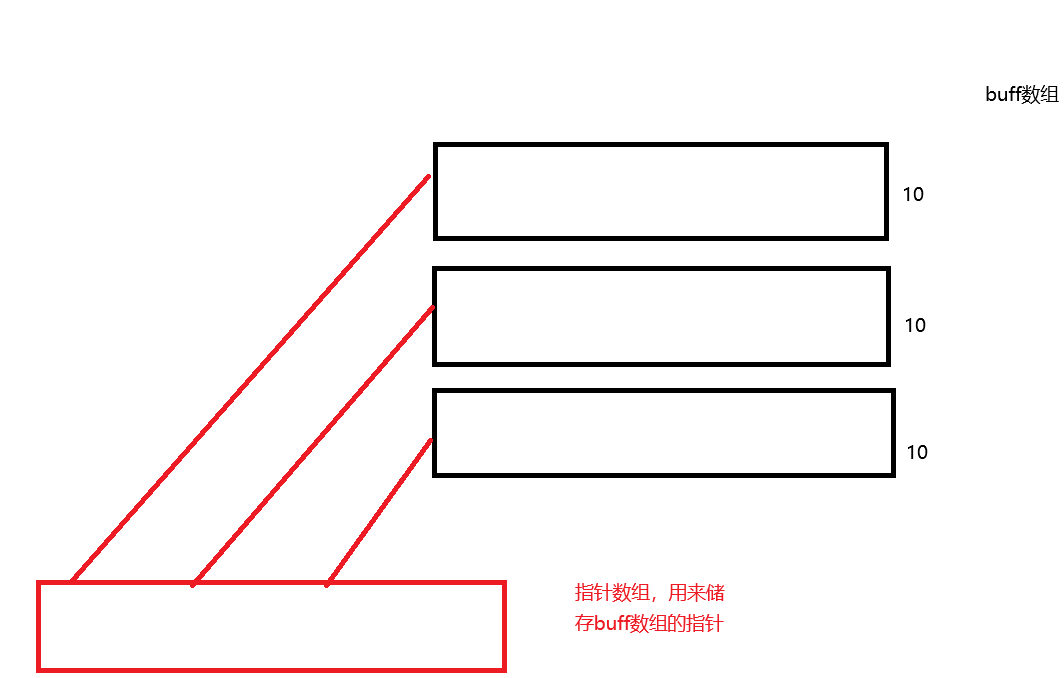
buffer数组的迭代器
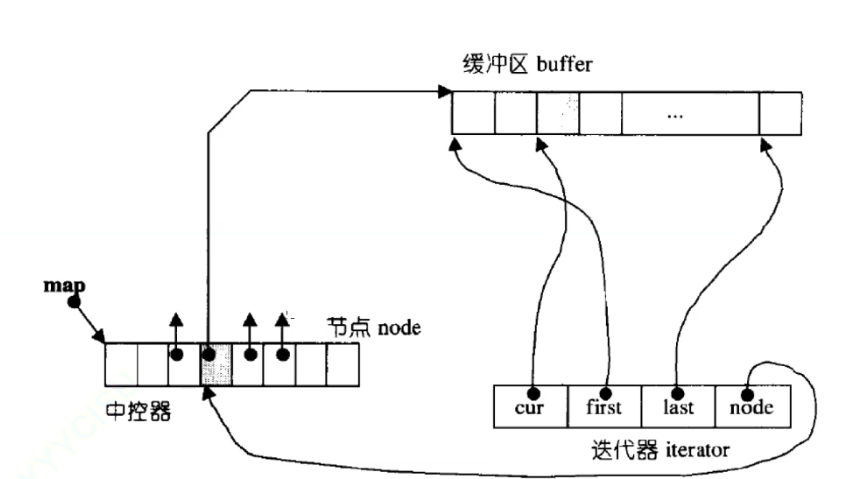
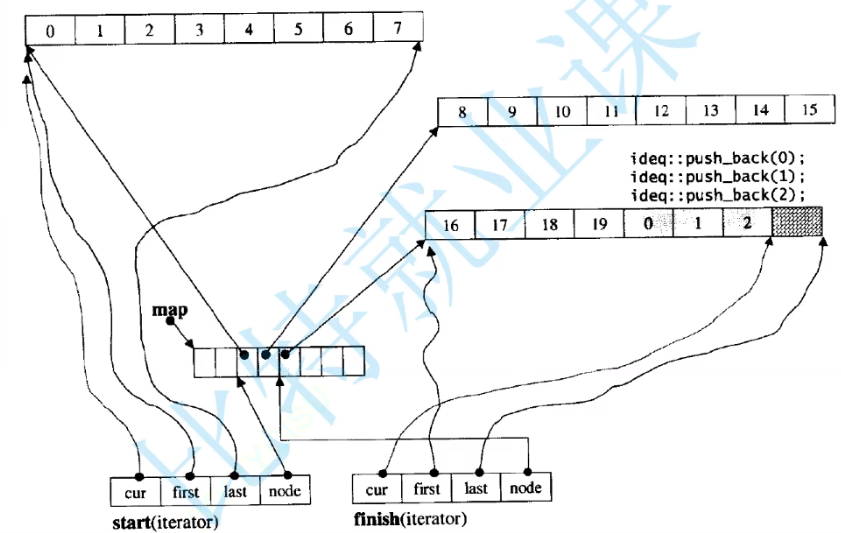
以下是deque的功能介绍,了解即可。
deque初始
构造
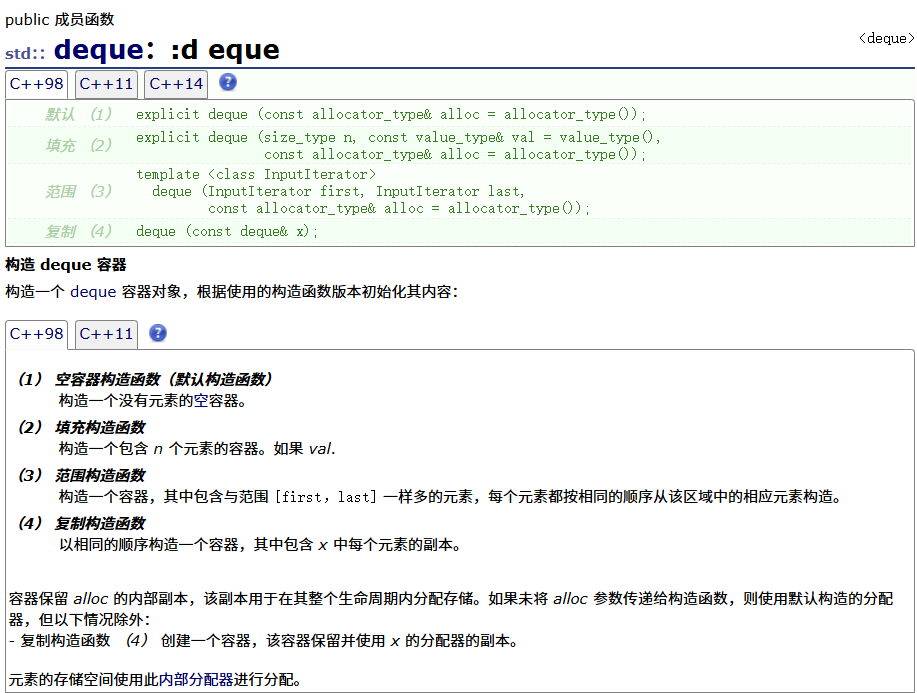
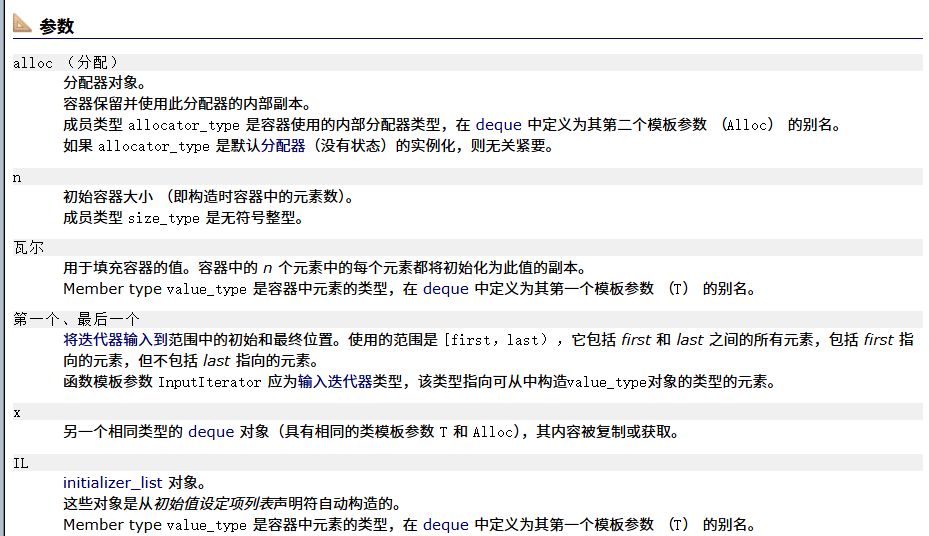
析构
=运算符重载
迭代器
正向
反向

const正向
const反向
容器
size
max_size
resize
empty
shrink_to_fit
访问队列
[]运算符重载
at
front
back

deque的成员函数
push_back
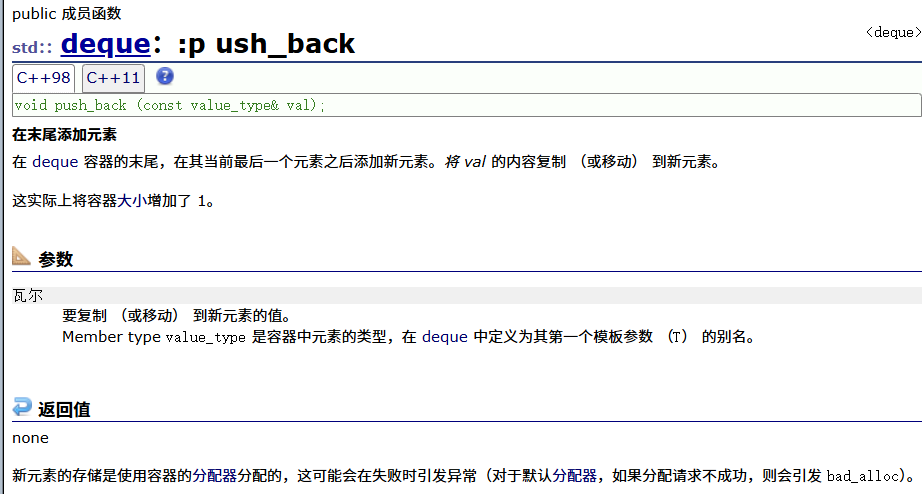
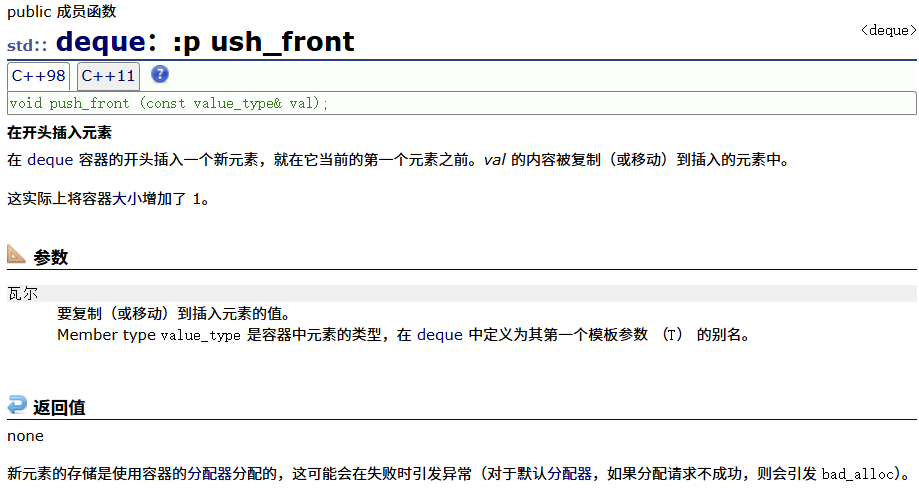
push_front
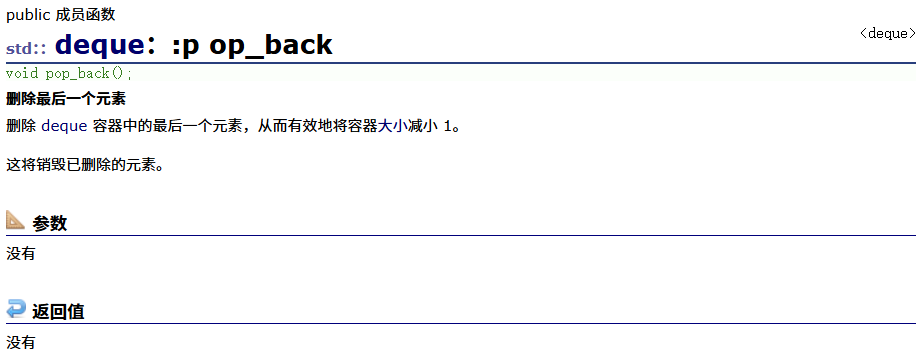
pop_back
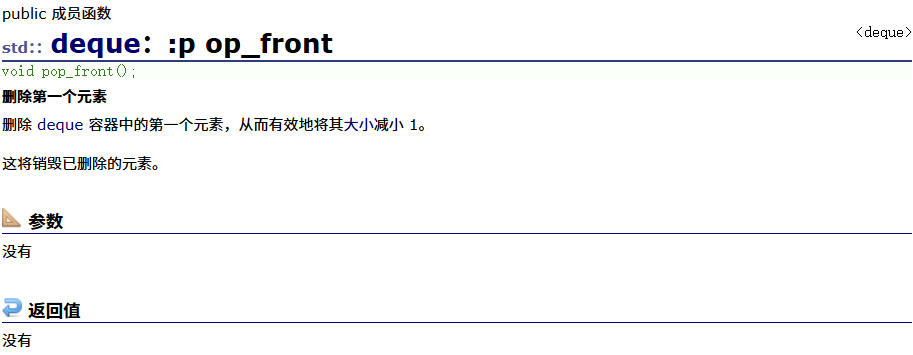
pop_front
insert
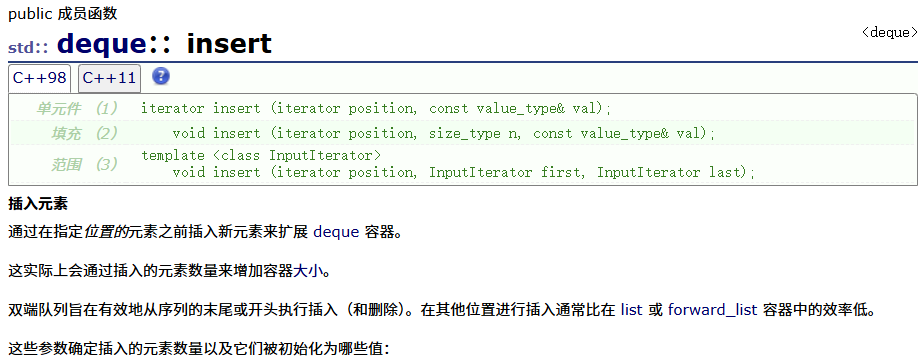
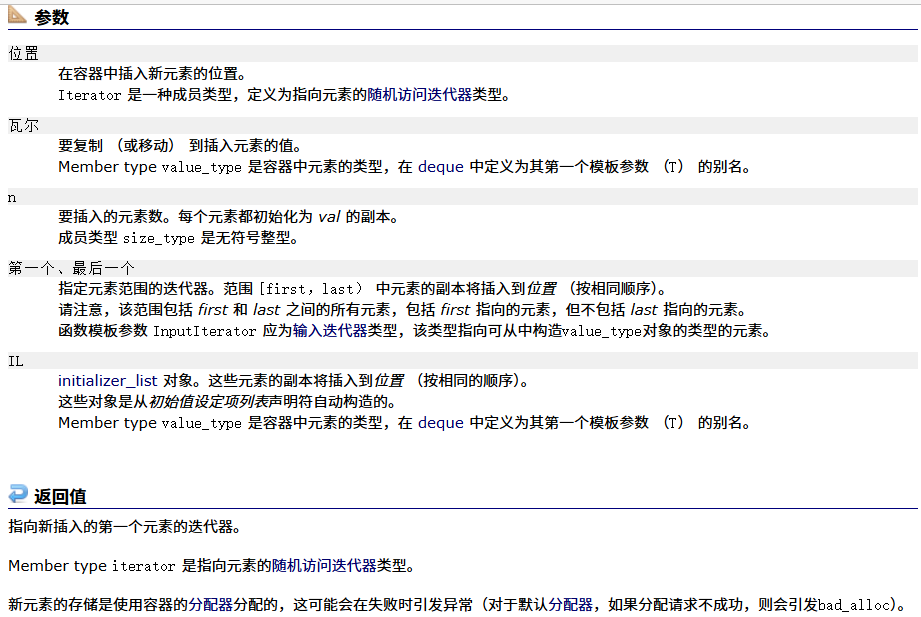
erase
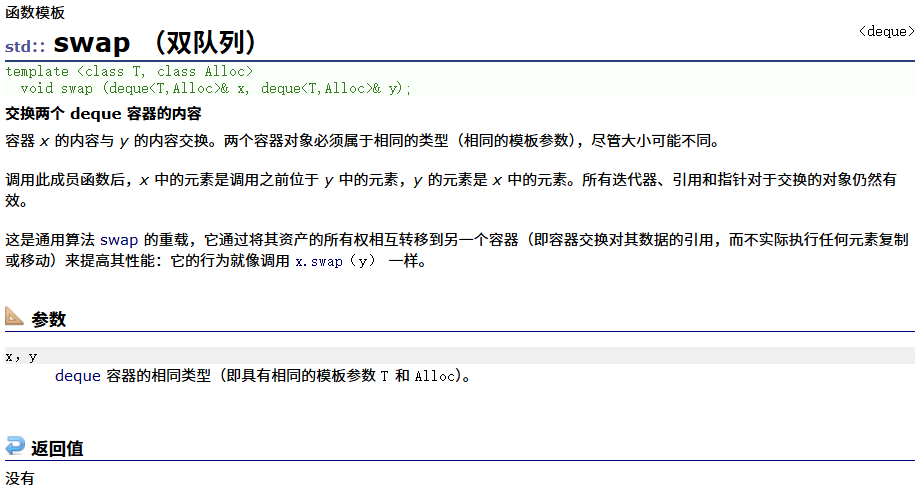
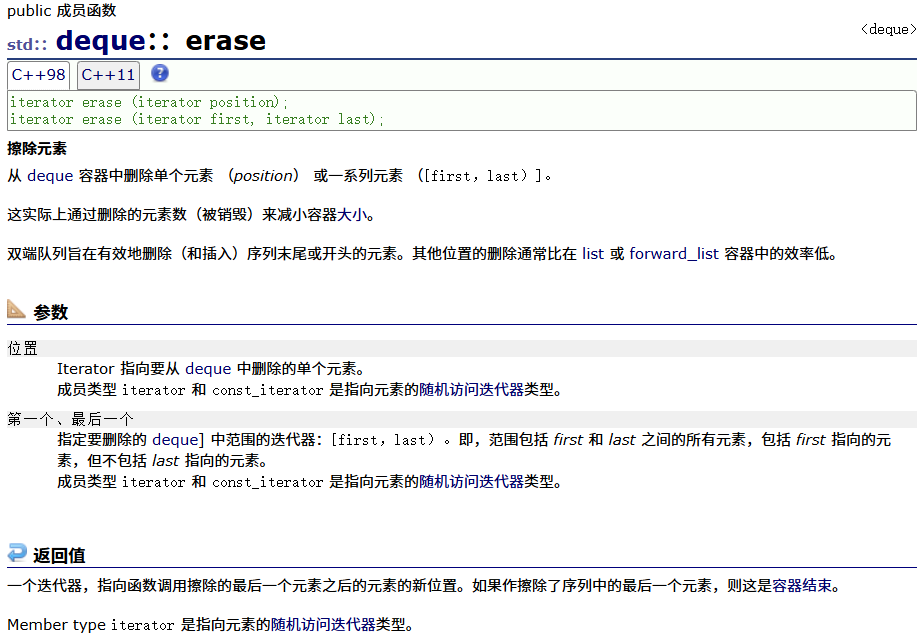 swap
swap

clear
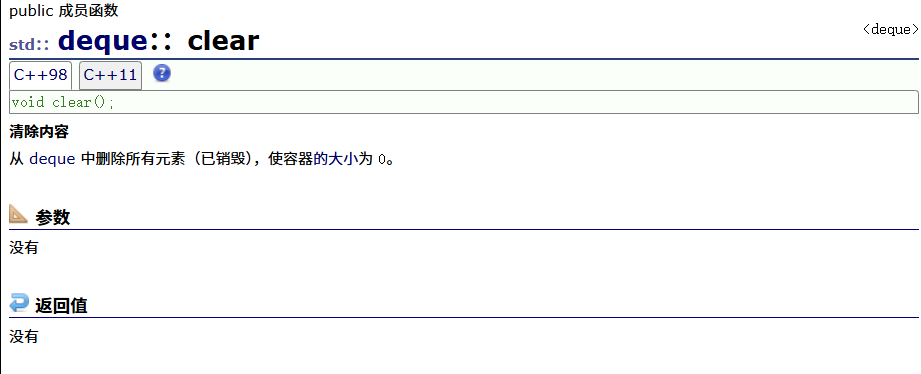 emplace
emplace
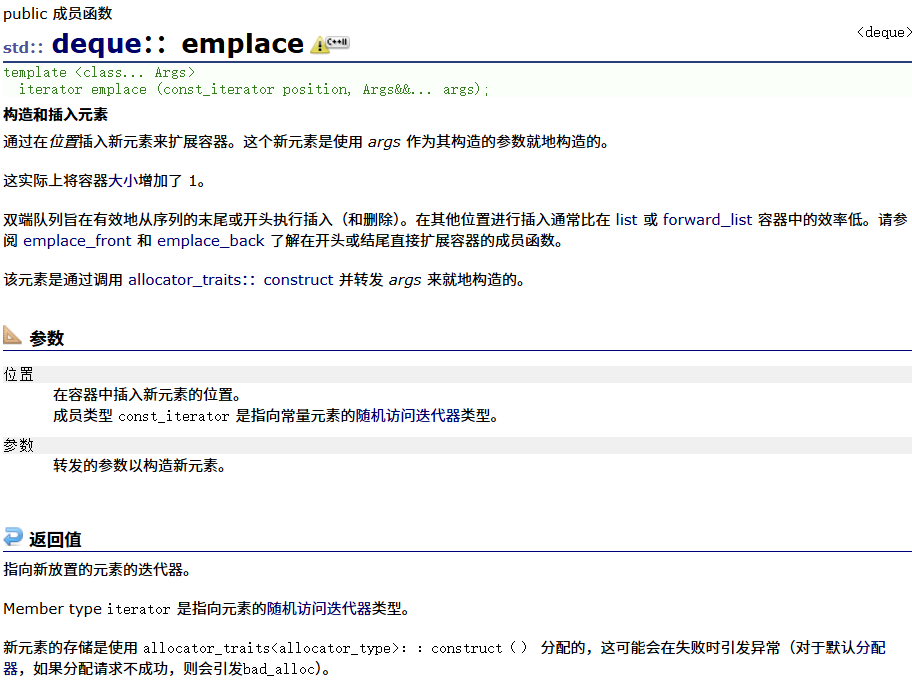
emplace_front
emplace_back

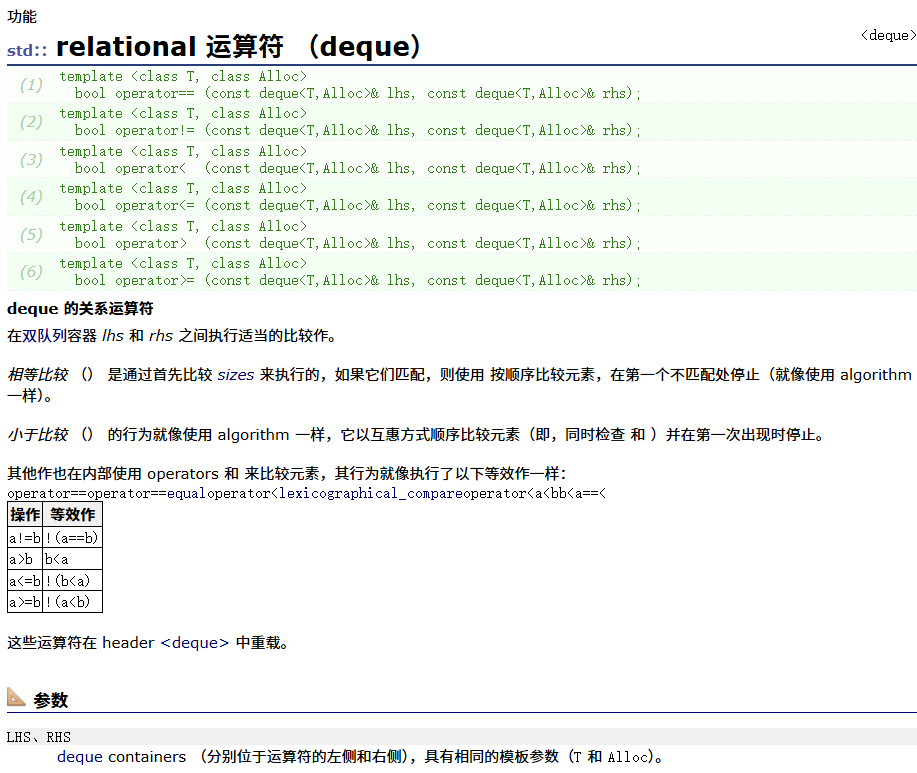
deque非成员函数
关系运算符重载
swap(双队列)
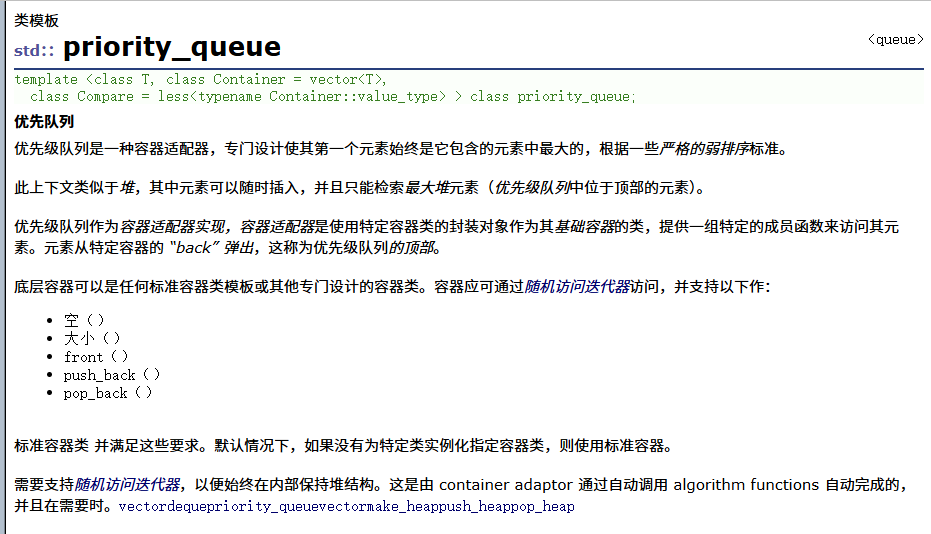
priority_queue的介绍和官方文档
官方文档: priority_queue - C++ 参考
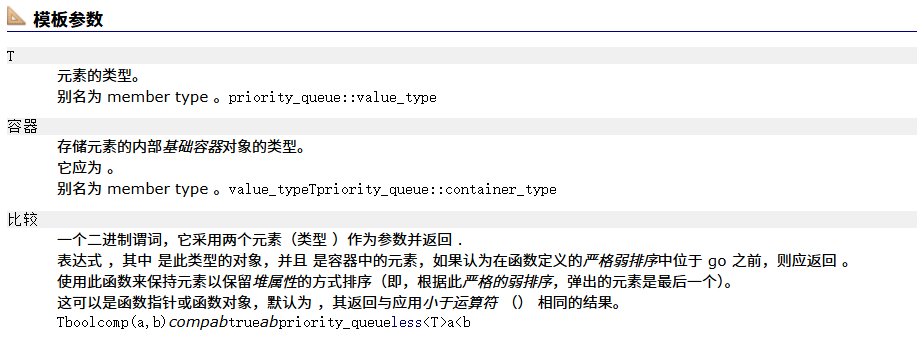
入数据随便入,出数据按优先级高的出队列。
而数据大的优先级高,优先出队列
测试:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int> pq;
//数据大的优先级高;
//优先级高的优先出队列
pq.push(5);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(8);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(6);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
return 0;
}结果为:
![]()
默认情况下priority_queue是大的数据优先级高。如果需要小的数据优先级高则需要通过仿函数控制。
而如下图所示

默认传递的是小于less的仿函数的时候,大的优先级高;因此反过来说,当我们传大于greater的仿函数的时候,小的优先级高
less和greater是标准库内的仿函数
官方文档:
priority_queue
void test_priority_queue()
{
priority_queue<int> pq1;
//数据大的优先级高;
//默认情况下优先级高的优先出队列
//控制小的数据优先级高需要仿函数
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq2;
//less和greater是标准库函数
//greater<int>是仿函数,表示优先级高的元素优先出队列
//小的元素优先级高,所以优先出队列
pq1.push(5);
pq1.push(3);
pq1.push(8);
pq1.push(1);
pq1.push(6);
while (!pq1.empty())
{
cout << pq1.top() << " ";
pq1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
pq2.push(5);
pq2.push(3);
pq2.push(8);
pq2.push(1);
pq2.push(6);
while (!pq2.empty())
{
cout << pq2.top() << " ";
pq2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}结果为:

vector也有类似的用法
void test_vector()
{
vector<int>v = {6,7,4,1,3,5 };
//vector的sort默认小的优先级高
//< 升序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (auto& e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//> 降序
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (auto& e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}结果为:

通过上面两段代码,我们发现这两者第三个参数传的是不一样的。
为什么算法库的sort第三个参数跟仿函数不一样呢?
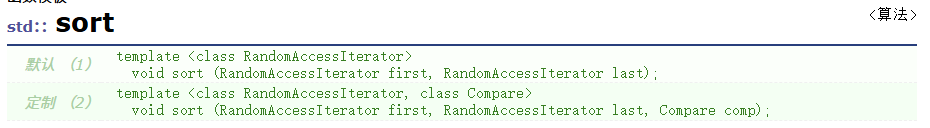

我们会发现,sort第三个参数类型是对象,而priority_queue传递的是类模板参数。
priority_queue的相关函数
构造函数
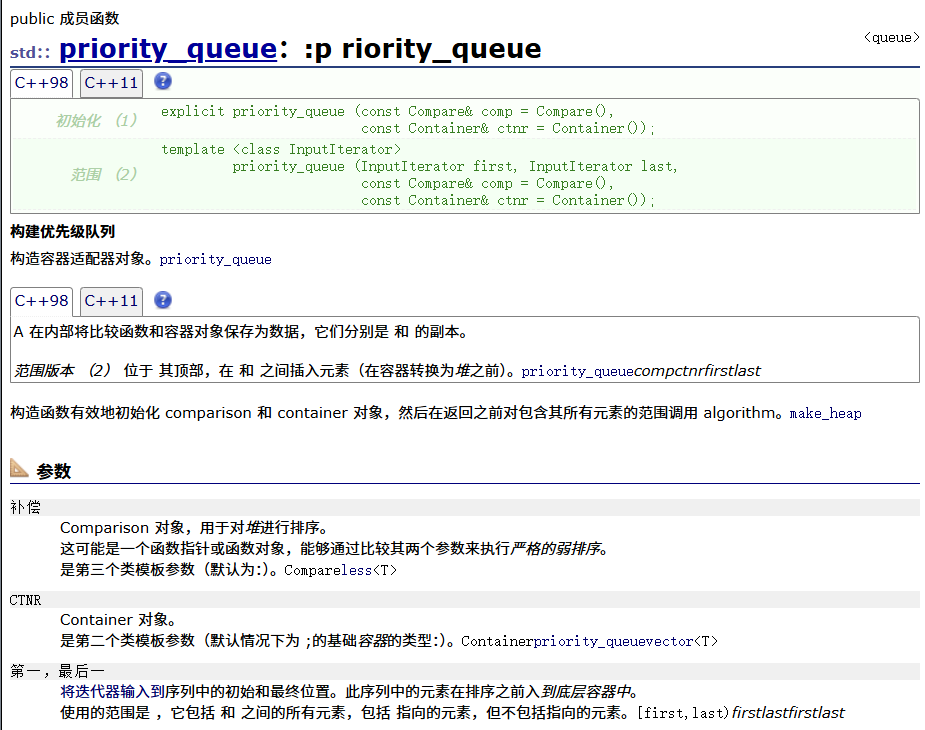
empty

size

top
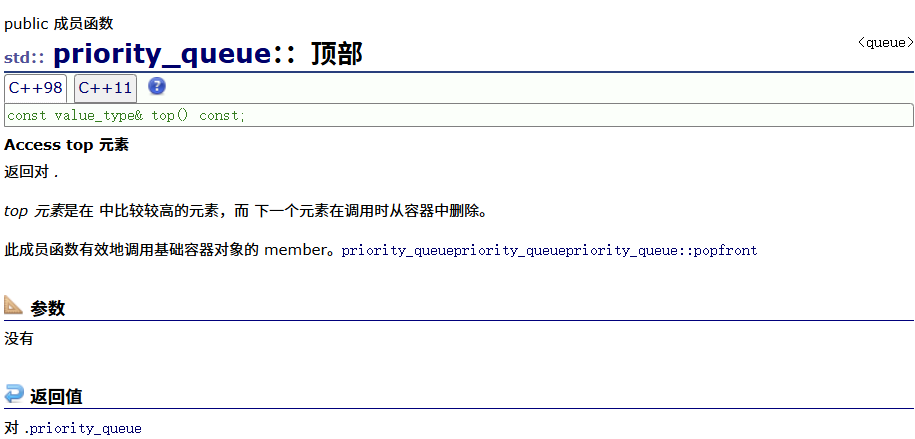
push
pop
emplace
swap

priority_queue相关题目
数组中第K个最大元素
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
priority_queue<int>pq(nums.begin(),nums.end());
while(--k)
{
pq.pop();
}
return pq.top();
}
};priority_queue的模拟实现
逻辑结构图:
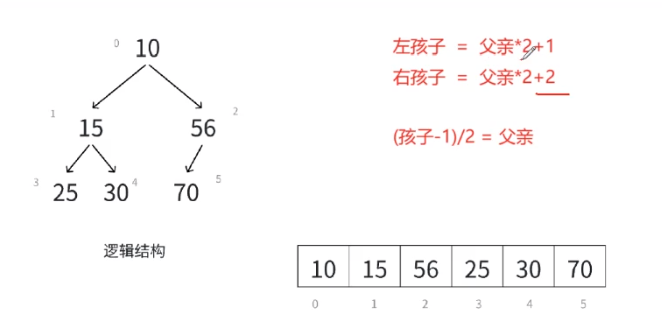
priority_queue的底层结构是堆
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
namespace Boogiepop
{
template<class T, class container =vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
priority_queue() = default;
//迭代器区间初始化
template<class InputItreator>
priority_queue(InputItreator first, InputItreator last)
:_con(first, last)
{
//向下调整堆
for (int i = _con.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0],_con[_con.size()-1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
container _con;
//向上调整
void adjust_up(int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;//不需要考虑左右孩子
while (parent >= 0)
{
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//向下调整
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
//选出大孩子
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])
{
++child;
}
if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
};
}
仿函数(重点!!!)
仿函数是C++为了替代函数指针而存在的(因为函数指针过于复杂)。而且函数指针没法应用于类模板
比如:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//仿函数/函数对象
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a > b;
}
};
int main()
{
Less<int> lessfunc;
cout<<lessfunc(3, 5)<<endl;
//相当于调用了cout<<<lessfunc.operator()(3, 5)<<endl;
}仿函数改造冒泡排序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//仿函数/函数对象
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a > b;
}
};
//仿函数改造冒泡排序
template<class T, class Compare >
void Bubbersort(T* a, int n,Compare cmp)
{
int exhange = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
{
if (cmp(a[j], a[j + 1]))
{
exhange = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = exhange;
}
}
if (exhange == 0)
{
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
/*Less<int> lessfunc;
cout<<lessfunc(3, 5)<<endl;*/
//相当于调用了cout<<<lessfunc.operator()(3, 5)<<endl;
int a[] = { 3,5,2,8,1,9,4,7,6 };
Bubbersort(a,7,Less<int>());
for (auto& i : a)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
for (auto& i : a)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}接下来,我们用仿函数对priority_queue进行改造吧!
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
namespace Boogiepop
{
//仿函数/函数对象
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a > b;
}
};
//仿函数改造
template<class T, class container =vector<T>,class Compare=Less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
priority_queue() = default;
//迭代器区间初始化
template<class InputItreator>
priority_queue(InputItreator first, InputItreator last)
:_con(first, last)
{
//向下调整堆
for (int i = _con.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0],_con[_con.size()-1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
container _con;
//向上调整
void adjust_up(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;//不需要考虑左右孩子
while (child >= 0)
{
//等同于if (_con[child] < _con[parent])
if (com(_con[parent] , _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//向下调整
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
Compare com;
//选出大孩子
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
//等同于if (child + 1 < _con.size() &&_con[child] < _con[child + 1])
if (child + 1 < _con.size() &&com( _con[child ] , _con[child+1]))
{
++child;
}
if (com(_con[parent] , _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
};
}测试:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"priority_queue.h"
void test1()
{
Boogiepop::priority_queue<int> pq;
//Boogiepop::priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> pq;
pq.push(0);
pq.push(6);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(20);
pq.push(1);
while (!pq.empty())
{
std::cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}上下两个优先级队列pq的结果分别为:
![]()
![]()
我们在之前类和对象的时候会接触到一些空类(即没有成员变量的类),它的一个用途就是仿函数。
下面再举一个例子:查找第一个偶数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct OP1
{
bool operator()(int x) const
{
return x % 2 == 0;
}
};
int main()
{
int a[] = { 3,5,2,8,1,9,4,7,6 };
//查找第一个偶数
int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
auto it =find_if(a, a + n, OP1());
cout << *it << endl;
//如果没有找到返回最后一个位置
return 0;
}结果为:
![]()
本期内容就到这里,喜欢的话点个赞谢谢
封面图自取: