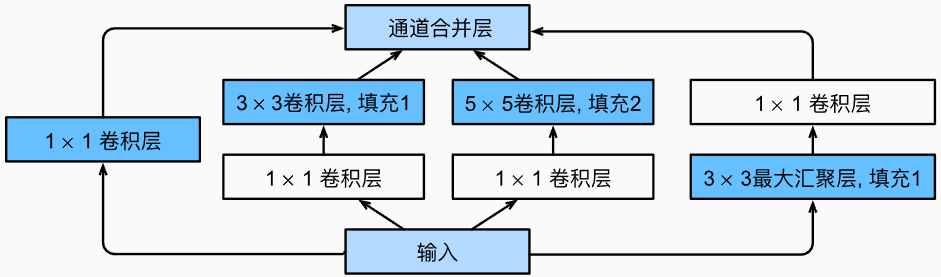
在GoogLeNet中,基本的卷积块被称为Inception块(Inception block)。
- 使用窗口大小为 1 × 1 , 3 × 3 , 5 × 5 1\times1,3\times3,5\times5 1×1,3×3,5×5的卷积层,从不同空间大小中提取信息。
- 使用 1 × 1 1\times1 1×1卷积层来改变通道数,可以降低通道维数。
- 各层中窗口大小始终保持不变与输入的窗口一致。
- 在Inception块中,通常调整的超参数是每层输出通道数。
- 输出结果:各个路径的通道数相加,大小与输入大小一致。
Inception卷积块:
代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, c1, c2, c3, c4, **kwargs):
super(Inception, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.p1_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c1, kernel_size=1)
self.p2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c2[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p2_2 = nn.Conv2d(c2[0], c2[1], kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.p3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c3[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p3_2 = nn.Conv2d(c3[0], c3[1], kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.p4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.p4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
p1 = F.relu(self.p1_1(x))
p2 = F.relu(self.p2_2(F.relu(self.p2_1(x))))
p3 = F.relu(self.p3_2(F.relu(self.p3_1(x))))
p4 = F.relu(self.p4_2(self.p4_1(x)))
return torch.cat((p1, p2, p3, p4), dim=1)
测试:
x = torch.randn(5, 3, 10, 10)
model = Inception(3, c1=8, c2=(2, 4), c3=(3, 6), c4=4)
# 用于打印模型每一层的输出结果
def print_outsize(module, x, y):
print(module.__class__.__name__, y.shape)
for layer in model.children():
layer.register_forward_hook(print_outsize)
out = model(x)
print('output:', out.shape)
结果:
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 8, 10, 10])
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 2, 10, 10])
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 4, 10, 10])
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 3, 10, 10])
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 6, 10, 10])
MaxPool2d torch.Size([5, 3, 10, 10])
Conv2d torch.Size([5, 4, 10, 10])
output: torch.Size([5, 22, 10, 10])
参考文献
[1] 7.4. 含并行连结的网络(GoogLeNet) — 动手学深度学习 2.0.0 documentation (d2l.ai)