概述
React 19 是 React 框架的一个重要里程碑版本,带来了众多突破性的改进和新特性。本文档将详细介绍 React 19 的主要变化,帮助开发者了解并迁移到新版本。
🚀 主要新特性
React Compiler (编译器)
React 19 引入了全新的 React Compiler,这是一个革命性的功能:
核心特点:
- 自动优化组件重新渲染
- 无需手动使用
useMemo、useCallback和memo - 编译时优化,运行时性能显著提升
- 向后兼容,渐进式采用
使用示例:
// React 18 - 需要手动优化
const ExpensiveComponent = memo(({ data }) => {
const processedData = useMemo(() => {
return data.map((item) => expensiveOperation(item));
}, [data]);
return <div>{processedData}</div>;
});
// React 19 - 编译器自动优化
const ExpensiveComponent = ({ data }) => {
const processedData = data.map((item) => expensiveOperation(item));
return <div>{processedData}</div>;
};Actions (动作系统)
Actions 是 React 19 中处理异步操作的新方式:
核心概念:
- 简化异步状态管理
- 内置 pending、error 状态处理
- 自动处理竞态条件
- 更好的用户体验
useActionState Hook:
import { useActionState, useState } from "react";
// 模拟一个异步的用户更新函数
async function updateUserProfile(formData) {
// 模拟网络延迟
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
const name = formData.get("name");
const email = formData.get("email");
// 模拟验证逻辑
if (!name || name.trim().length < 2) {
throw new Error("姓名至少需要2个字符");
}
if (!email || !email.includes("@")) {
throw new Error("请输入有效的邮箱地址");
}
// 模拟随机失败
if (Math.random() < 0.3) {
throw new Error("服务器错误,请稍后重试");
}
return { name, email };
}
function UserProfileForm() {
const [users, setUsers] = useState([]);
const [state, submitAction, isPending] = useActionState(
async (previousState, formData) => {
try {
const userData = await updateUserProfile(formData);
// 更新用户列表
setUsers((prev) => [...prev, { ...userData, id: Date.now() }]);
return {
success: true,
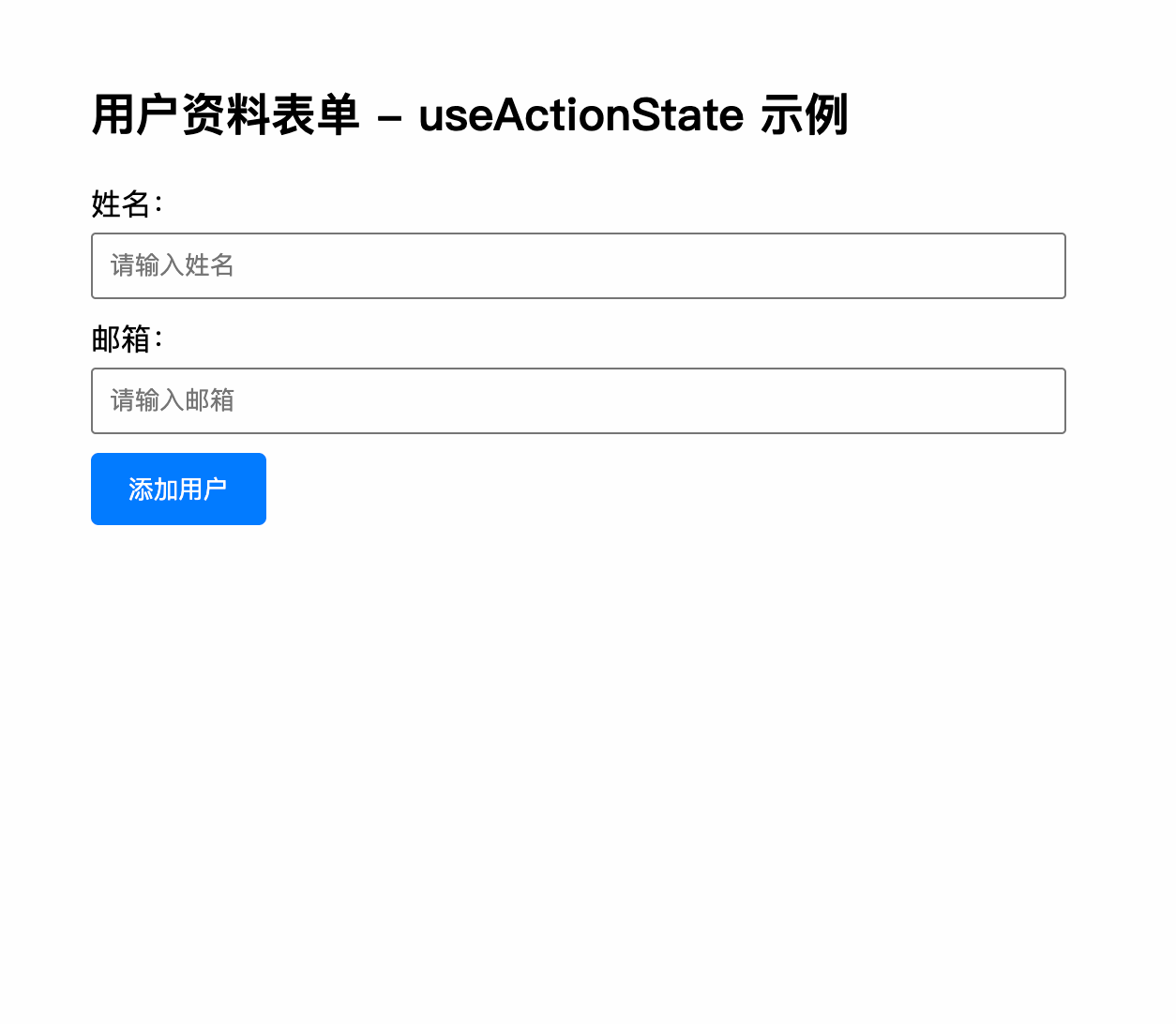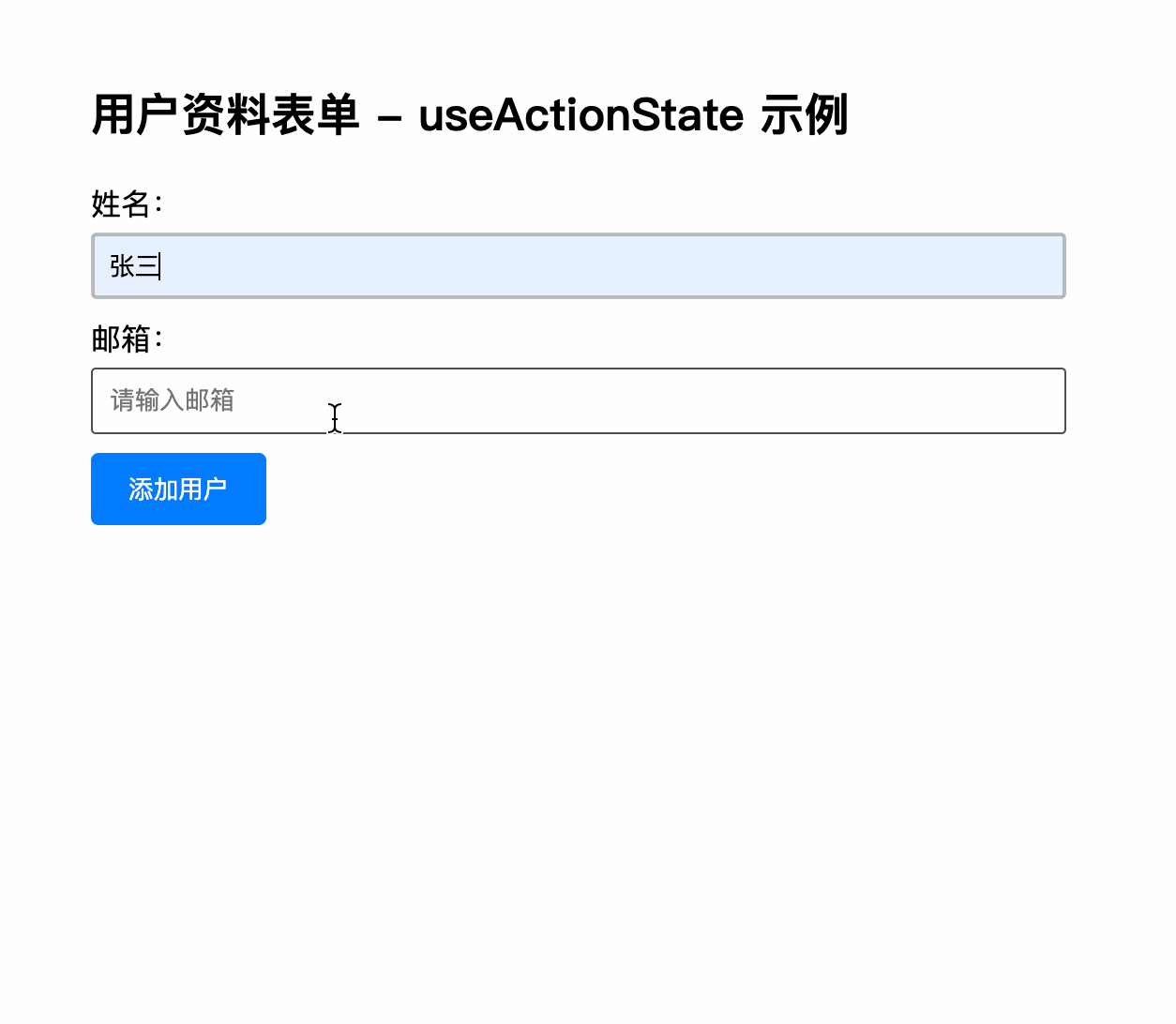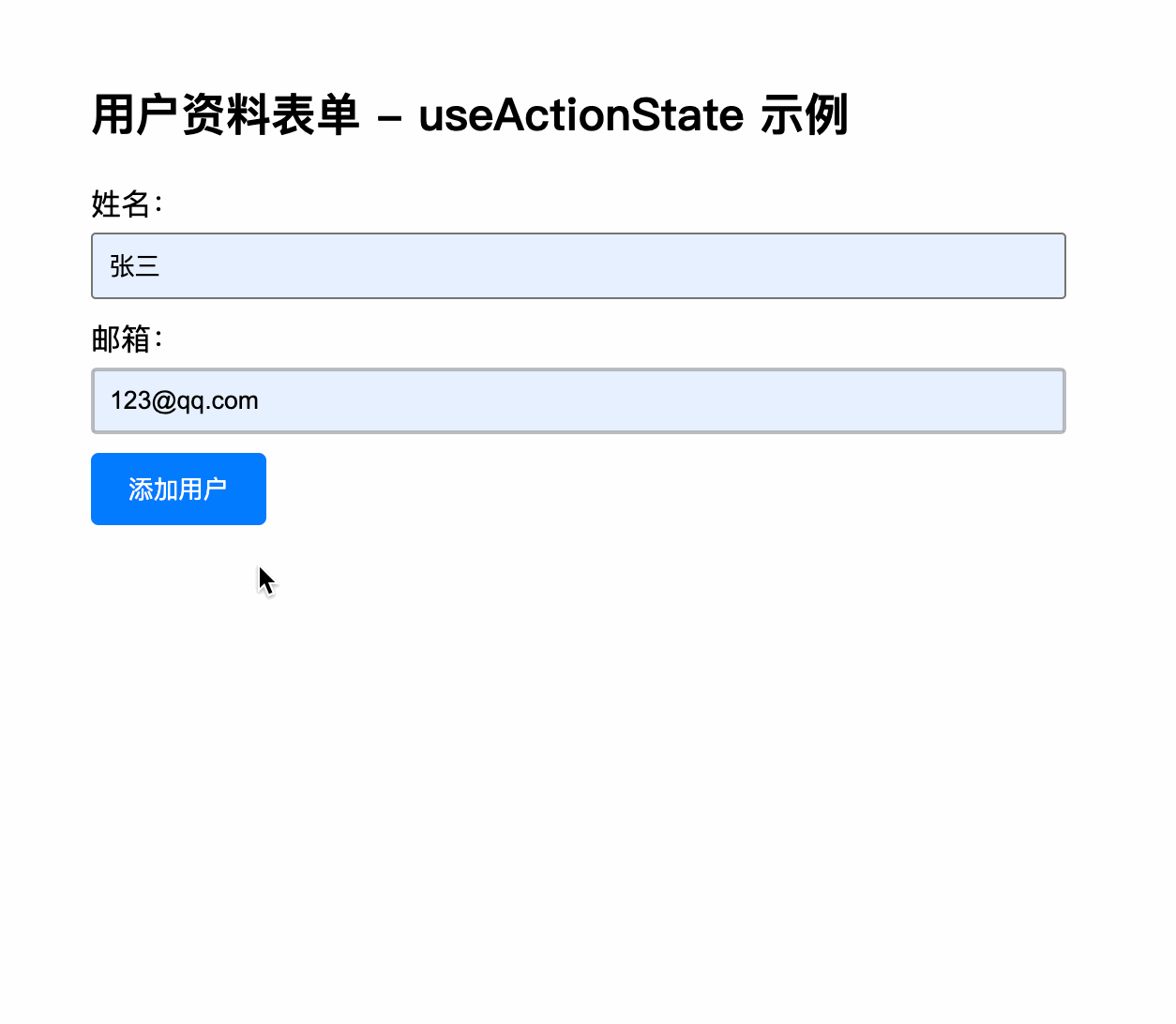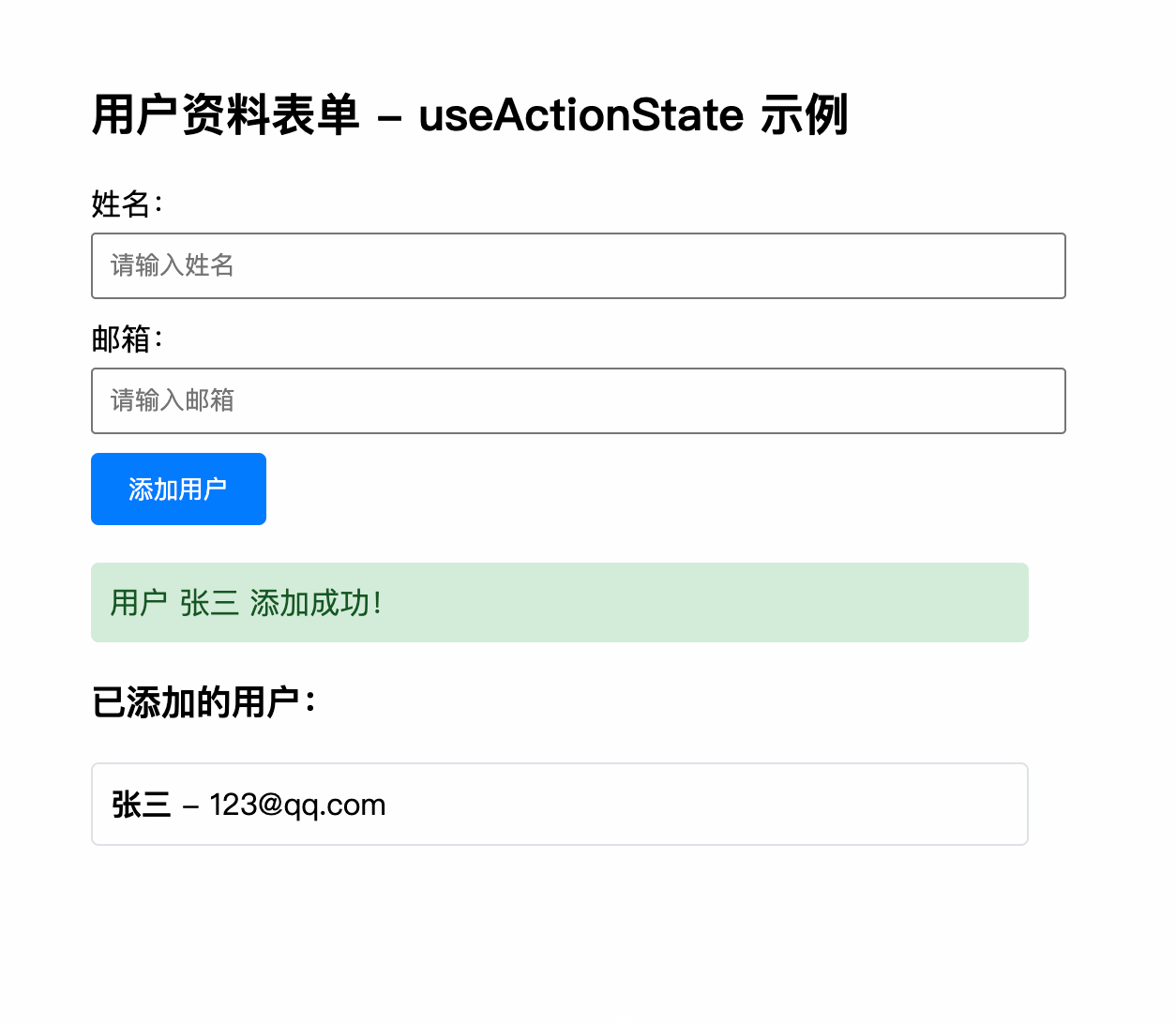
message: `用户 ${userData.name} 添加成功!`,
error: null,
};
} catch (error) {
return {
success: false,
message: null,
error: error.message,
};
}
},
{
success: false,
message: null,
error: null,
}
);
return (
<div style={{ padding: "20px", maxWidth: "500px", margin: "0 auto" }}>
<h2>用户资料表单 - useActionState 示例</h2>
<form action={submitAction} style={{ marginBottom: "20px" }}>
<div style={{ marginBottom: "10px" }}>
<label htmlFor="name">姓名:</label>
<input
type="text"
id="name"
name="name"
required
style={{ width: "100%", padding: "8px", marginTop: "4px" }}
placeholder="请输入姓名"
/>
</div>
<div style={{ marginBottom: "10px" }}>
<label htmlFor="email">邮箱:</label>
<input
type="email"
id="email"
name="email"
required
style={{ width: "100%", padding: "8px", marginTop: "4px" }}
placeholder="请输入邮箱"
/>
</div>
<button
type="submit"
disabled={isPending}
style={{
padding: "10px 20px",
backgroundColor: isPending ? "#ccc" : "#007bff",
color: "white",
border: "none",
borderRadius: "4px",
cursor: isPending ? "not-allowed" : "pointer",
}}
>
{isPending ? "提交中..." : "添加用户"}
</button>
</form>
{/* 显示状态信息 */}
{state.error && (
<div
style={{
padding: "10px",
backgroundColor: "#f8d7da",
color: "#721c24",
borderRadius: "4px",
marginBottom: "10px",
}}
>
错误:{state.error}
</div>
)}
{state.success && state.message && (
<div
style={{
padding: "10px",
backgroundColor: "#d4edda",
color: "#155724",
borderRadius: "4px",
marginBottom: "10px",
}}
>
{state.message}
</div>
)}
{/* 用户列表 */}
{users.length > 0 && (
<div>
<h3>已添加的用户:</h3>
<ul style={{ listStyle: "none", padding: 0 }}>
{users.map((user) => (
<li
key={user.id}
style={{
padding: "10px",
backgroundColor: "#f8f9fa",
marginBottom: "5px",
borderRadius: "4px",
border: "1px solid #dee2e6",
}}
>
<strong>{user.name}</strong> - {user.email}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default UserProfileForm;useOptimistic Hook:
import { useOptimistic, useState, useTransition } from "react";
// 模拟异步 API 调用
const addTodoAPI = async (text) => {
// 模拟网络延迟
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000));
// 模拟可能的失败(10% 概率)
if (Math.random() < 0.1) {
throw new Error("添加失败");
}
return {
id: Date.now(),
text,
completed: false,
};
};
export default function TodoApp() {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([
{ id: 1, text: "学习 React", completed: false },
{ id: 2, text: "写代码", completed: true },
]);
const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition();
// useOptimistic Hook - 用于乐观更新
const [optimisticTodos, addOptimisticTodo] = useOptimistic(
todos,
(state, newTodo) => [...state, { ...newTodo, pending: true }]
);
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState("");
const handleAddTodo = async (text) => {
if (!text.trim()) return;
// 立即显示乐观更新
const optimisticTodo = {
id: Date.now(),
text,
completed: false,
};
addOptimisticTodo(optimisticTodo);
setInputValue("");
startTransition(async () => {
try {
// 调用实际的 API
const newTodo = await addTodoAPI(text);
setTodos((prev) => [...prev, newTodo]);
} catch (error) {
// 如果失败,乐观更新会自动回滚
alert("添加失败: " + error.message);
}
});
};
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
handleAddTodo(inputValue);
};
return (
<div style={{ padding: "20px", maxWidth: "500px", margin: "0 auto" }}>
<h1>useOptimistic 示例 - 待办事项</h1>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} style={{ marginBottom: "20px" }}>
<input
type="text"
value={inputValue}
onChange={(e) => setInputValue(e.target.value)}
placeholder="输入新的待办事项..."
style={{
padding: "8px",
marginRight: "10px",
border: "1px solid #ccc",
borderRadius: "4px",
width: "300px",
}}
/>
<button
type="submit"
disabled={isPending || !inputValue.trim()}
style={{
padding: "8px 16px",
backgroundColor: "#007bff",
color: "white",
border: "none",
borderRadius: "4px",
cursor: "pointer",
}}
>
{isPending ? "添加中..." : "添加"}
</button>
</form>
<div>
<h3>待办事项列表:</h3>
{optimisticTodos.length === 0 ? (
<p>暂无待办事项</p>
) : (
<ul style={{ listStyle: "none", padding: 0 }}>
{optimisticTodos.map((todo) => (
<li
key={todo.id}
style={{
padding: "10px",
margin: "5px 0",
backgroundColor: todo.pending ? "#f0f8ff" : "#f9f9f9",
border: "1px solid #ddd",
borderRadius: "4px",
opacity: todo.pending ? 0.7 : 1,
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<span
style={{
textDecoration: todo.completed ? "line-through" : "none",
flex: 1,
}}
>
{todo.text}
</span>
{todo.pending && (
<span
style={{
fontSize: "12px",
color: "#666",
marginLeft: "10px",
}}
>
添加中...
</span>
)}
</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
</div>
);
}改进的 Suspense
新的 Suspense 特性:
- 更好的错误边界集成
- 改进的加载状态管理
- 更细粒度的控制
function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<Error />}>
<DataComponent />
</ErrorBoundary>
</Suspense>
);
}🔧 API 改进
forwardRef 简化
// React 18
const MyInput = forwardRef(function MyInput(props, ref) {
return <input {...props} ref={ref} />;
});
// React 19 - 不再需要 forwardRef
function MyInput(props) {
return <input {...props} />;
}Context 作为 Provider
// React 18
const ThemeContext = createContext();
function App() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value="dark">
<Page />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}
// React 19
const ThemeContext = createContext();
function App() {
return (
<ThemeContext value="dark">
<Page />
</ThemeContext>
);
}ref 作为 prop
// React 19 - ref 现在是普通 prop
function MyInput({ placeholder, ref }) {
return <input placeholder={placeholder} ref={ref} />;
}
// 使用
<MyInput ref={ref} placeholder="输入文本" />;📱 React Native 集成
React 19 与 React Native 的新架构更好地集成:
- 改进的性能
- 更好的类型安全
- 统一的开发体验
🛠️ 开发者体验改进
更好的错误信息
- 更清晰的错误提示
- 更好的调试信息
- 改进的开发工具支持
TypeScript 支持增强
- 更好的类型推断
- 改进的泛型支持
- 更严格的类型检查
开发工具改进
- React DevTools 增强
- 更好的性能分析
- 改进的组件检查
🔄 迁移指南
从 React 18 迁移
- 更新依赖:
npm install react@19 react-dom@19- 启用 React Compiler:
// babel.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
[
"babel-plugin-react-compiler",
{
// 配置选项
},
],
],
};- 移除不必要的优化:
- 移除手动的
memo、useMemo、useCallback - 让编译器自动优化
- 更新 forwardRef 使用:
- 移除不必要的
forwardRef包装 - 直接使用 ref 作为 prop
🚨 破坏性变更
1. 移除的 API
- 某些过时的生命周期方法
- 废弃的 Context API
- 旧的 Suspense 行为
2. 行为变更
- 更严格的类型检查
- 改变的默认行为
- 新的错误处理机制
🎉 总结
React 19 带来了革命性的改进:
- React Compiler 自动优化性能
- Actions 简化异步操作
- 新的 Hooks 提供更强大的功能
- 改进的 API 简化开发体验
- 更好的性能 和开发者体验
这些改进使 React 应用更快、更易维护,同时保持了向后兼容性。建议开发者逐步迁移到 React 19,享受这些新特性带来的好处。
📚 参考资源
React 19 革命性升级:编译器自动优化,告别手动性能调优时代 - 高质量源码分享平台-免费下载各类网站源码与模板及前沿技术分享