原本每月都有表格汇总的,但领导说要统计一段时间内的内容,如果一个表格一个表格复制粘贴又太累了。所以使用影刀的功能。
文件夹中的数据表格如下
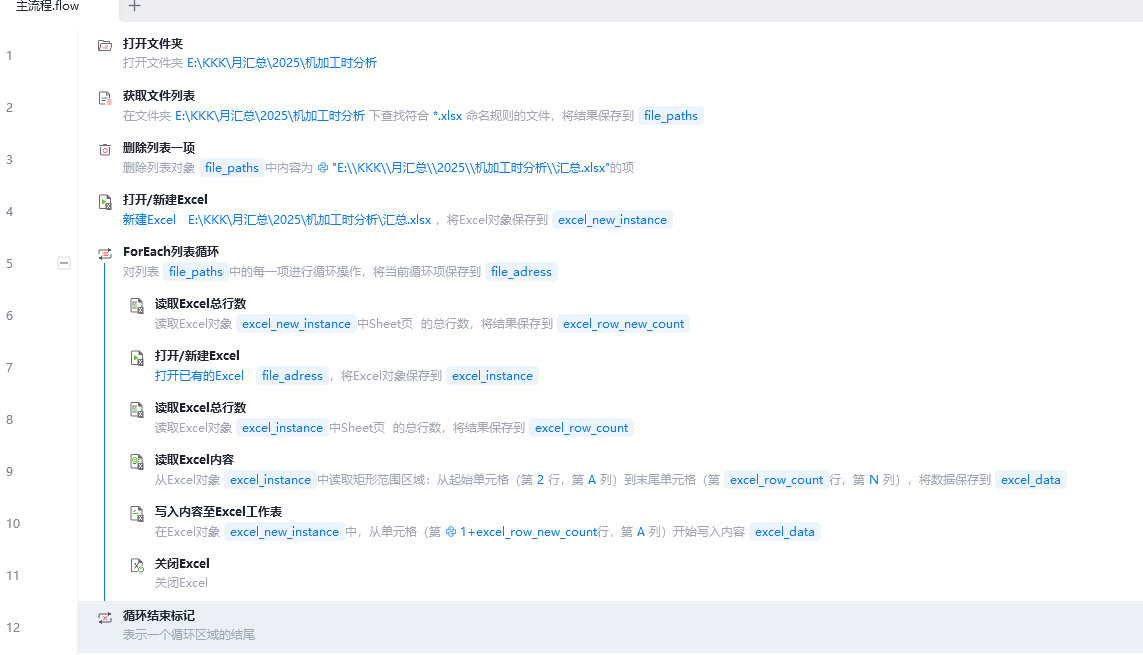
1、打开文件夹
2、获取文件夹中的文件名列表
3、如果文件名列表有“汇总”的内容则先删除
4、在这个文件夹下新建“汇总”的数据表格,用于存放复制来的数据
5、按文件名列表开始循环。
6、获取“汇总”表的总行数
7、依次打开文件夹中的各文件
8、获取打开文件的总行数
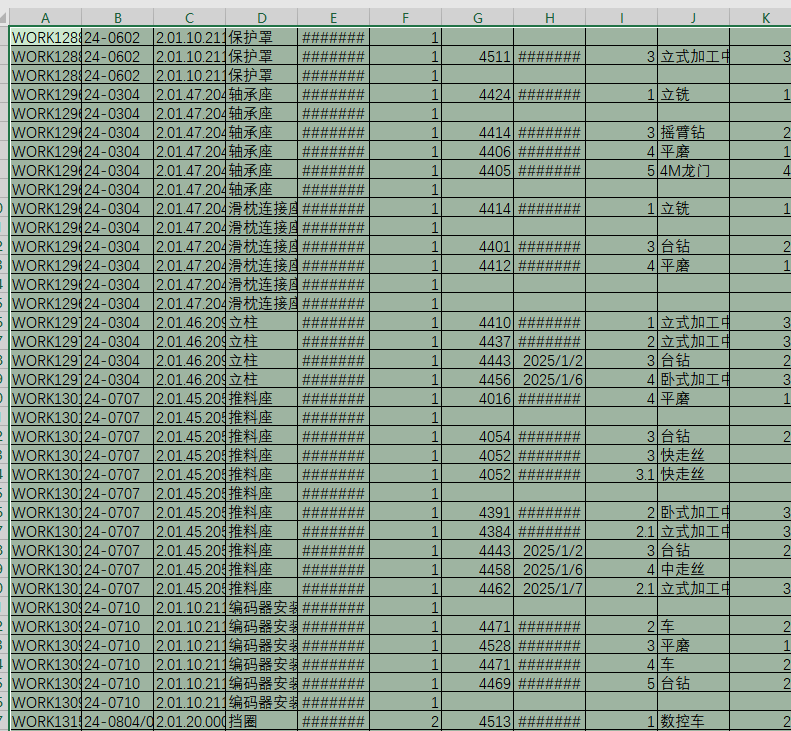
9、读取打开文件的内容,范围从A2到N总行数止。
10、将读取的内容复制到“汇总”数据表,开始行从1+“汇总”表总行数开始
11、关闭打开的文件
12、结束循环
以上基本上已经能获取数据了,但想将“汇总”的数据范围增加边框,经查询,没有很好的办法,后来在论坛上说可以使用魔法指令

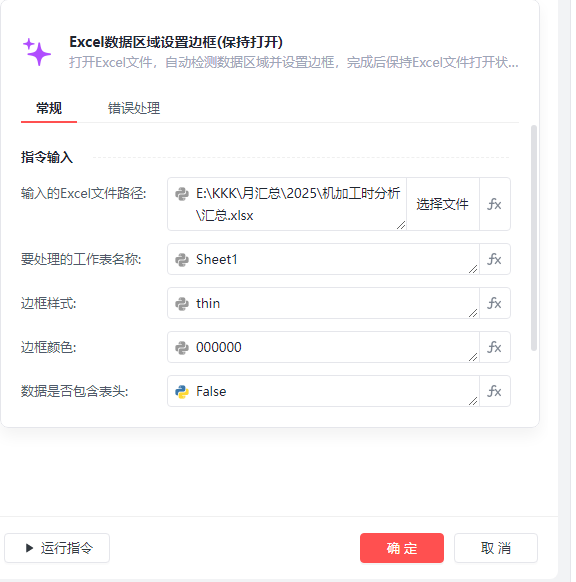
所包含的代码如下
# pip install openpyxl pywin32
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Border, Side
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
import os
import win32com.client
import time
from typing import *
try:
from xbot.app.logging import trace as print
except:
from xbot import print
def set_excel_data_border_keep_open(excel_file, sheet_name=None, border_style="thin", border_color="000000", has_header=True):
"""
title: Excel数据区域设置边框(保持打开)
description: 打开Excel文件,自动检测数据区域并设置边框,完成后保持Excel文件打开状态。
inputs:
- excel_file (file): 输入的Excel文件路径,eg: "data.xlsx"
- sheet_name (str): 要处理的工作表名称,不指定则使用活动工作表,eg: "Sheet1"
- border_style (str): 边框样式,可选值:thin, medium, thick, double, dotted, dashed,eg: "thin"
- border_color (str): 边框颜色,使用十六进制RGB值,eg: "000000"
- has_header (bool): 数据是否包含表头,eg: True
outputs:
- file_path (str): 处理后的Excel文件路径,eg: "E:\\KKK\\月汇总\\2025\\机加工时分析\\汇总.xlsx"
"""
# 检查输入参数有效性
valid_styles = ["thin", "medium", "thick", "double", "dotted", "dashed"]
if border_style not in valid_styles:
raise ValueError(f"边框样式必须是以下值之一: {', '.join(valid_styles)}")
if not isinstance(border_color, str) or len(border_color) != 6:
raise ValueError("边框颜色必须是6位十六进制RGB值,例如:000000")
try:
int(border_color, 16)
except ValueError:
raise ValueError("边框颜色必须是有效的十六进制值")
# 确保文件路径是绝对路径
excel_file = os.path.abspath(excel_file)
# 检查文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(excel_file):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"找不到Excel文件: {excel_file}")
# 使用COM接口打开Excel应用程序
try:
excel = win32com.client.Dispatch("Excel.Application")
excel.Visible = True # 使Excel可见
excel.DisplayAlerts = False # 禁用警告弹窗
# 尝试打开工作簿
try:
workbook = excel.Workbooks.Open(excel_file)
except Exception as e:
excel.Quit()
raise Exception(f"无法打开Excel文件: {str(e)}")
# 选择工作表
if sheet_name:
try:
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(sheet_name)
worksheet.Activate()
except:
excel.Quit()
raise ValueError(f"工作表 '{sheet_name}' 不存在")
else:
worksheet = workbook.ActiveSheet
# 使用openpyxl处理边框设置
# 先关闭Excel以便openpyxl可以访问文件
workbook.Save()
workbook.Close(False)
excel.Quit()
# 使用openpyxl设置边框
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(excel_file)
if sheet_name:
if sheet_name not in wb.sheetnames:
raise ValueError(f"工作表 '{sheet_name}' 不存在")
sheet = wb[sheet_name]
else:
sheet = wb.active
# 检测数据区域
def _detect_data_range():
"""检测工作表中的数据区域"""
# 找到最大行和最大列
max_row = 1
max_col = 1
for row in sheet.iter_rows():
for cell in row:
if cell.value is not None:
max_row = max(max_row, cell.row)
max_col = max(max_col, cell.column)
# 如果没有数据,返回默认范围
if max_row == 1 and max_col == 1 and sheet.cell(1, 1).value is None:
return None
# 找到最小行和最小列
min_row = max_row
min_col = max_col
for row_idx in range(1, max_row + 1):
for col_idx in range(1, max_col + 1):
if sheet.cell(row_idx, col_idx).value is not None:
min_row = min(min_row, row_idx)
min_col = min(min_col, col_idx)
return (min_row, min_col, max_row, max_col)
# 获取数据范围
data_range = _detect_data_range()
if not data_range:
raise ValueError("工作表中没有检测到数据")
min_row, min_col, max_row, max_col = data_range
# 创建边框样式
border_styles = {
"thin": Side(style="thin", color=border_color),
"medium": Side(style="medium", color=border_color),
"thick": Side(style="thick", color=border_color),
"double": Side(style="double", color=border_color),
"dotted": Side(style="dotted", color=border_color),
"dashed": Side(style="dashed", color=border_color)
}
side = border_styles[border_style]
normal_border = Border(left=side, right=side, top=side, bottom=side)
# 如果有表头,为表头设置特殊边框
if has_header and min_row < max_row:
header_bottom = Side(style="double" if border_style == "thin" else border_style, color=border_color)
header_border = Border(
left=side,
right=side,
top=side,
bottom=header_bottom
)
# 为表头应用边框
for col in range(min_col, max_col + 1):
cell = sheet.cell(row=min_row, column=col)
cell.border = header_border
# 为数据行应用边框
for row in range(min_row + 1, max_row + 1):
for col in range(min_col, max_col + 1):
cell = sheet.cell(row=row, column=col)
cell.border = normal_border
else:
# 没有表头,为所有单元格应用相同边框
for row in range(min_row, max_row + 1):
for col in range(min_col, max_col + 1):
cell = sheet.cell(row=row, column=col)
cell.border = normal_border
# 保存工作簿
wb.save(excel_file)
wb.close()
# 打印设置的数据范围信息
range_address = f"{get_column_letter(min_col)}{min_row}:{get_column_letter(max_col)}{max_row}"
print(f"已为数据范围 {range_address} 设置边框")
# 重新打开Excel文件
excel = win32com.client.Dispatch("Excel.Application")
excel.Visible = True
workbook = excel.Workbooks.Open(excel_file)
# 选择之前的工作表
if sheet_name:
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(sheet_name)
worksheet.Activate()
# 选中设置了边框的区域
cell_range = worksheet.Range(
worksheet.Cells(min_row, min_col),
worksheet.Cells(max_row, max_col)
)
cell_range.Select()
# 不关闭Excel,让它保持打开状态
print(f"Excel文件已打开,并已设置数据区域边框")
return excel_file
except Exception as e:
# 确保在出错时关闭Excel
try:
if 'workbook' in locals():
workbook.Close(False)
if 'excel' in locals():
excel.Quit()
except:
pass
raise Exception(f"设置Excel边框时出错: {str(e)}")
效果如下