MyBatis整体架构分析
一图胜千言
1、Mybatis核心框架示意图
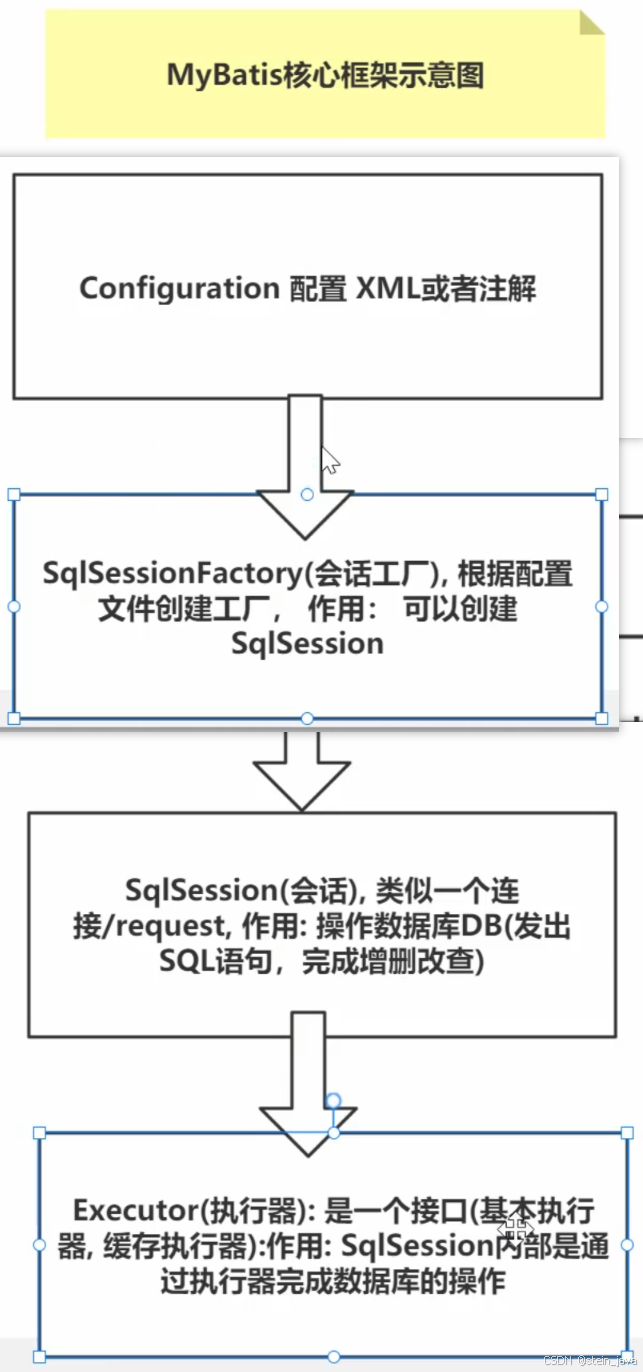
2、对上图的解读
1)mybatis的核配置文件
mybatis-config.xml:进行全局配置,全局只能有一个这样的配置文件
XxxMapper.xml配置多个SQL,可以有多个XxxMappe.xml配置文件
2)通过mybatis-config.xml配置文件得到SqlSessionFactory
3)通过SqlSessionFactory得到SqlSession,用SqlSession就可以操作数据了
4)SqlSession.底层是Executor(执行器),有2个重要的实现类,它们有很多实现方法
4.1基本执行器BaseExecutor
4.2带缓存的执行器CachingExecutor
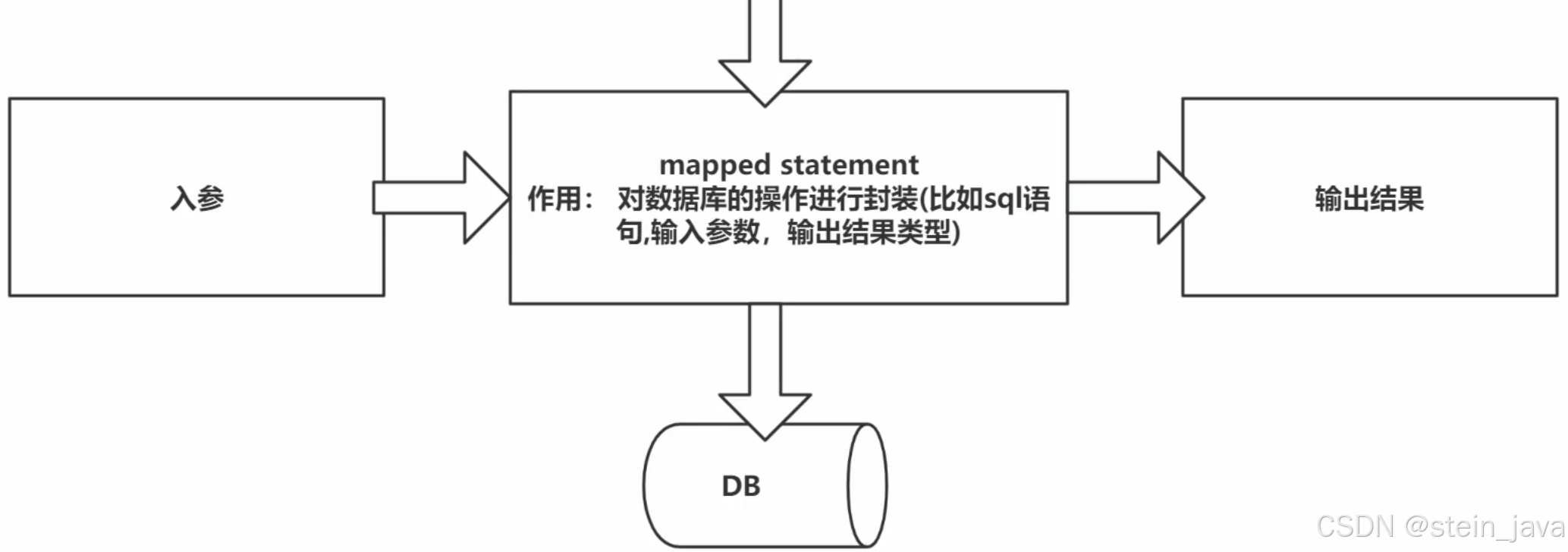
5)MappedStatement是通过XxxMapper.xml中定义,生成的statement对象
6)参数输入执行并输出结果集,无需手动判断参数类型和参数下标位置,且自动将结果集映射为Java对象
搭建MyBatis底层机制开发环境
1.创建Maven项目stein-mybatis
Archetype还是选的quickstart
2.修改文件pom.xml
引入必要的依赖
<dependencies>
<!--解析配置文件,引入dom4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
<!--原来使用的版本,出现异常情况,可以退回该版本-->
<!--<version>5.1.49</version>-->
</dependency>
<!--引入神器lombok,简化entity/pojo/javabean的开发-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<!--原来使用的版本,异常时回退-->
<!--<version>1.18.4</version>-->
</dependency>
<!--测试依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<!--<version>4.12</version>-->
<!--暂时取消了作用域-->
<!--<scope>test</scope>-->
</dependency>
</dependencies>3.创建数据库和表
CREATE DATABASE stein_mybatis;
USE stein_mybatis
CREATE TABLE monster(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`age` INT NOT NULL,
`birthday` DATE DEFAULT NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(255)NOT NULL,
`gender` TINYINT NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(255)NOT NULL,
`salary` DOUBLE NOT NULL
)CHARSET=utf8
-- 测试数据
INSERT INTO `monster` VALUES(NULL,200,'2000-11-11','nmw@sohu.com',1,'牛魔王',8888.88)自己写的Mybatis——设计思路
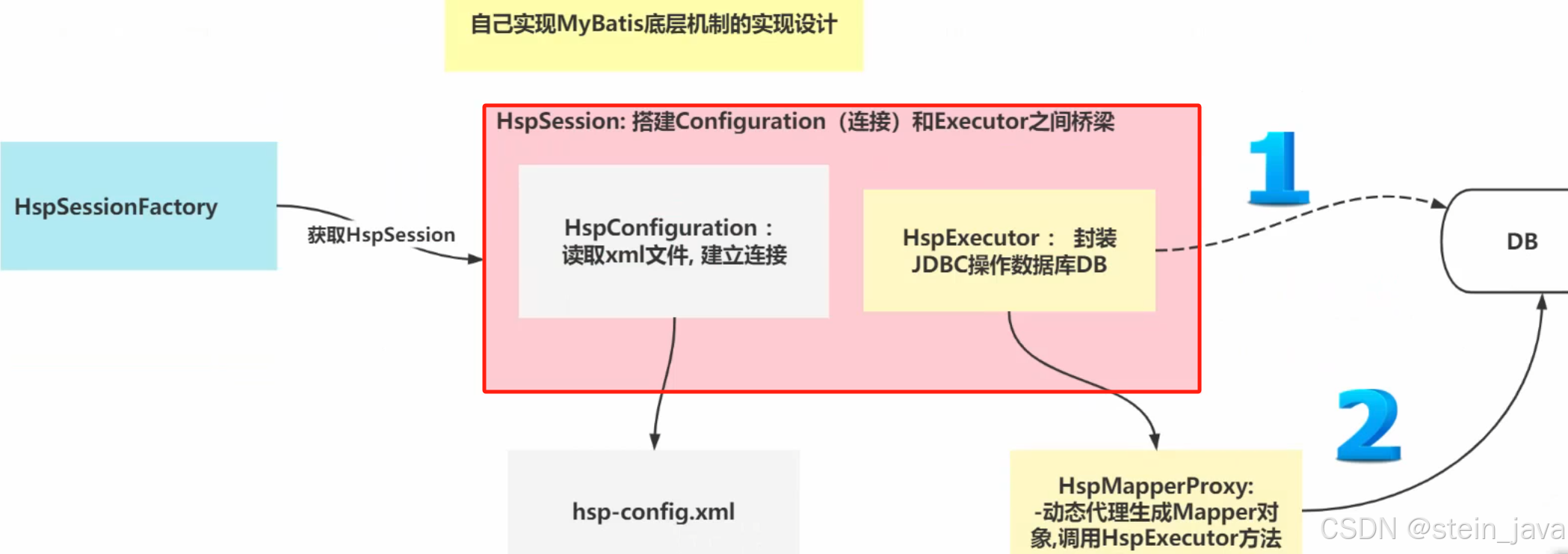
1.自己写Mybatis的底层实现设计
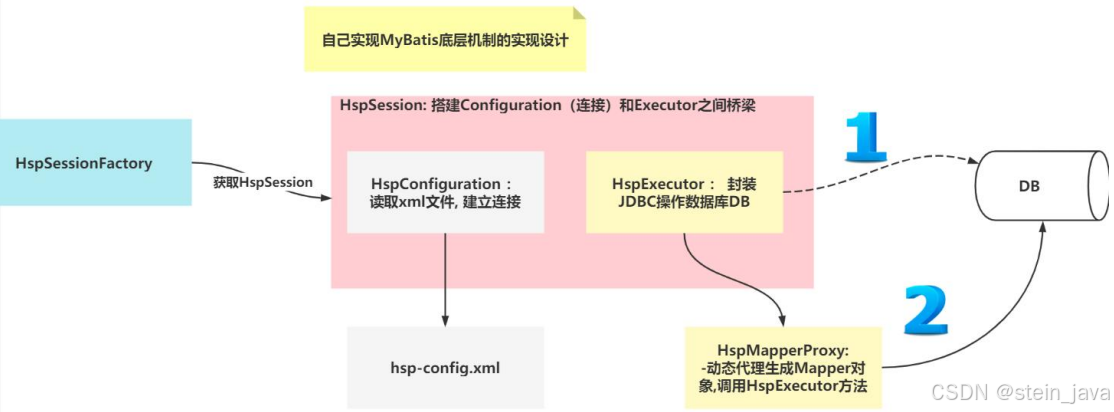
2.对上图的解读
一、传统的方式操作数据库
1)得到HspSession对象
2)调用HspExecutor的方法完成操作
3)HspExecutor的连接是从HspConfiguration获取
二、 MyBatis操作数据库的方式分析
1)得到HspSession
2)不直接调用HspExecutorl的方法完成操作
3)通过HspMapperProxy获取Mapper对象
4)调用Mapper的方法,完成数据库的操作
5)Mapper最终还是动态代理方式,使用HspExecutor的方法完成操作
6)这里比较麻烦的就是HspMapperProxy的动态代理机制的实现
自己实现Mybatis底层机制
实现任务
阶段1-完成读取配置文件,得到数据库连接
完成设计图中的这部分
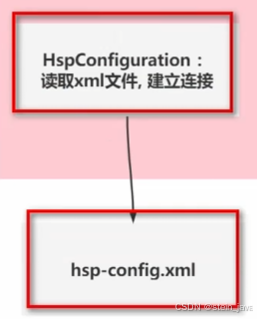
1.创建配置文件
新建resource目录,然后再建src/main/resources/stein-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<database>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stein_mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&charsetEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</database>2.新建读取配置文件的类
src/main/java/com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/SteinConfiguration.java
public class SteinConfiguration {
public ClassLoader classLoader=ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
public Connection build(String xmlConfigFile) {
InputStream resource = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(xmlConfigFile);
Connection connection=null;
try {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(resource);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println("rootElement="+rootElement);
connection = evalDataSource(rootElement);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return connection;
}
public Connection evalDataSource(Element node) {
if(!"database".equals(node.getName())) {
throw new RuntimeException("root节点应当是<database>");
}
String driverClassName = null;
String url = null;
String username = null;
String password = null;
for (Object element : node.elements()) {
Element ele = (Element) element;
String name = ele.attributeValue("name");
String value = ele.attributeValue("value");
//当获取标签之间的文本的时候才用它
//String value = ele.getText();
if(name==null || value==null) {
throw new RuntimeException("节点内容获取失败");
}
//java注意版本
switch(name) {
case "driverClassName":
driverClassName = value;
break;
case "url":
url = value;
break;
case "username":
username = value;
break;
case "password":
password = value;
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("元素异常"+name+";"+value);
}
}
Connection connection =null;
try {
//自动注册,这儿的反射也可以不写了
//Class.forName(driverClassName);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("获取连接失败");
}
return connection;
}
}3.测试
可以在写完读取xml文档,获得root节点时测试一次。再在获得connection后测试一次。这儿两个测试合并一起了。
public class SteinConfigurationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = new SteinConfiguration().build("stein-config.xml");
System.out.println("connection = " + connection);
}
}阶段2-编写执行器,输入SQL语句,完成操作
穿插:lombok的使用
1)引入pom.xml
<!--引入神器lombok,简化entity/pojo/javabean的开发-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<!--演示的版本,异常时回退到该版本-->
<!--<version>1.18.4</version>-->
</dependency>2)常用注解
@NoArgsConstructor 生成无参构造器
@AllArgsConstructor 生成全参构造器
@data 相当于:
@Getter
@Setter
@RequiredArgsConstructor 为每个需要特殊处理的字段生成一个带有1个参数的构造函数。
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
lombok.Value 这个是啥?欢迎评论区指点虽然没有指定无参构造器,但是在没有构造器的时候,它会默认生成一个无参构造器。但是指定有构造器了,就不会默认生成构造器。
3)常用组合
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor或者
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor 因为指定了全参构造器
@NoArgsConstructor 就必须显式的给出无参构造器,否则不会生成1.创建Entity
完成Monster.java的创建
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Monster {
private Integer id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
private String email;
private Date birthday;
private Double salary;
private String gender;
}2.创建执行器
接下来完成图中的这一步:
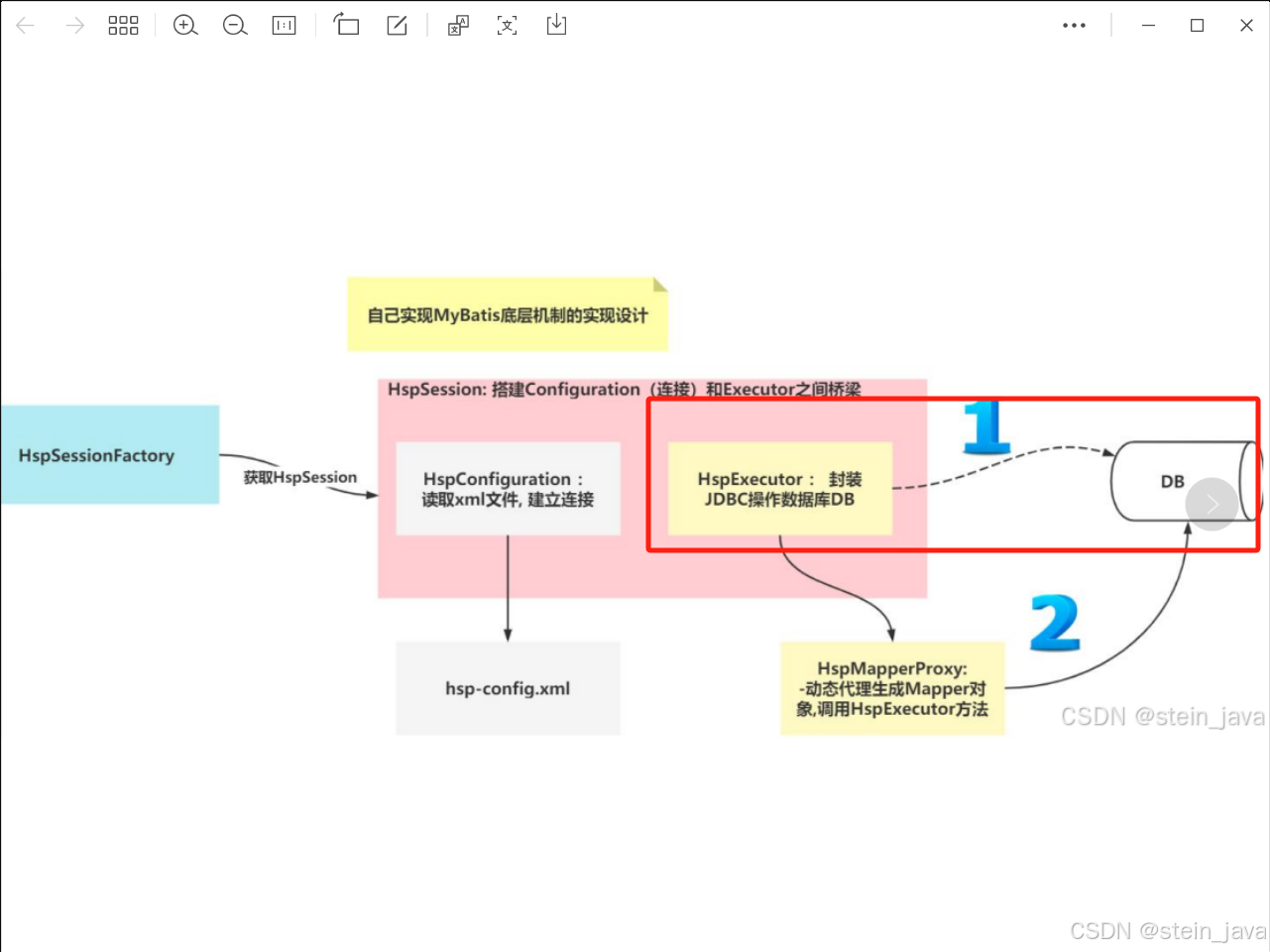
1)创建接口
com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/Executor.java
public interface Executor {
<T> T query(String statement, Object parameter);
}2)实现接口
com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/SteinExecutor.java
public class SteinExecutor implements Executor {
private SteinConfiguration config=new SteinConfiguration();
@Override
public <T> T query(String sql, Object parameter) {
Connection connection = getConnection();
Monster monster = new Monster();
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数,如果参数多,可以使用数组处理
//preparedStatement.setString(1, parameter.toString());
//这两种写法都可以
preparedStatement.setObject(1,parameter);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//这儿的结果集是如何完全循环的?
//实际上只执行了一次循环就将monster赋值完成了
while (resultSet.next()) {
monster.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
monster.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
monster.setAge(resultSet.getInt("age"));
monster.setGender(resultSet.getString("gender"));
monster.setSalary(resultSet.getDouble("salary"));
monster.setEmail(resultSet.getString("email"));
monster.setBirthday(resultSet.getDate("birthday"));
}
//关闭资源
if(resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if(preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if(connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return (T)monster;
}
public Connection getConnection() {
Connection connection = config.build("stein-config.xml");
return connection;
}
}3)测试
@Test
public void query(){
Executor executor = new SteinExecutor();
Monster monster = executor.query("select * from monster where id=?", 1);
System.out.println("monster = " + monster);
}阶段3-将Sqlsession封装到执行器
接下来要做的事情:
搭建Configuration(连接)Executor之间的桥梁
1.创建SteinSession
com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/SteinSession.java
public class SteinSession {
//属性
//执行器
private SteinExecutor executor=new SteinExecutor();
//配置类
private SteinConfiguration config=new SteinConfiguration();
//编写方法,返回一条记录-即一个对象
public <T> T selectOne(String sql, Object parameter) {
return executor.query(sql, parameter);
}
}2.测试
@Test
public void selectOne(){
SteinSession steinSession = new SteinSession();
Monster monster = steinSession.selectOne("select * from monster where id=?", 1);
System.out.println("monster = " + monster);
}阶段4-开发Mapper接口和Mapper.xml(重点)
本次完成的任务:

1.创建Mapper接口
com/stein/mapper/MonsterMapper.java
public interface MonsterMapper {
Monster getMonsterById(Integer id);
}2.配置实现Mapper接口
src\main\resources\MonsterMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<mapper namespace="com.stein.mapper.MonsterMapper" >
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.stein.entity.Monster">
<!--这儿为了简化,没有写成#{id}的形式-->
select * from monster where id=?
</select>
</mapper>阶段5-开发和Mapper接口相映射的MapperBean
接下来完成,MapperBean,它关联了接口与实现类的组件/对象
1.创建Function记录Mapper.xml的方法信息
com/stein/config/Function.java
@Setter
@Getter
public class Function {
//sql类型
private String sqlType;
//方法名
private String functionName;
//结果类型
private Object resultType;
//具体的sql语句
private String sql;
//参数类型,xml里没有设置,是个空的字段
private String parameterType;
}2.创建MapperBean记录XXXMapper接口的信息,和Function
com/stein/config/MapperBean.java
@Getter
@Setter
public class MapperBean {
private String interfaceName;
private Function[] functions;
}
阶段6-读取解析XxxMapper.xml,装填MappperBean对象
1.添加读取方法
com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/SteinConfiguration.java
/**
* @param xmlFile 传入文件名,resource文件夹会在target目录中重建,直接获取即可
* @return
*/
public MapperBean readMapperBean(String xmlFile) {
MapperBean mapperBean = new MapperBean();
InputStream stream = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(xmlFile);
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
Document document = saxReader.read(stream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println("rootElement="+rootElement);
/**
<mapper namespace="com.stein.mapper.MonsterMapper" >
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.stein.entity.Monster">
select * from monster where id=?
</select>
</mapper>
*/
//获取namespace的方法名
if(!"mapper".equals(rootElement.getName())) {
throw new RuntimeException("xml文件找不到<mapper>标签");
}
String interfaceName = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
System.out.println("interfaceName="+interfaceName);
mapperBean.setInterfaceName(interfaceName.trim());
List<Function> functions = new ArrayList<>();
/**
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.stein.entity.Monster">
select * from monster where id=?
</select>
*/
//获取select的内容
List elements = rootElement.elements();
for (Object element : elements) {
//System.out.println("进入元素遍历");
Element ele = (Element) element;
System.out.println("ele="+ele);
Function function = new Function();
//这儿取值为null,可以看出"select"并不是属性"attribute"
//String sqlType = ele.attributeValue("select");
String sqlType = ele.getName().trim();
function.setSqlType(sqlType);
System.out.println("sqlType="+sqlType);
String functionName = ele.attributeValue("id");
function.setFunctionName(functionName);
String resultType = ele.attributeValue("resultType");
//因为resultType是一个Object类型,这儿返回一个实例
Object newInstance = Class.forName(resultType).newInstance();
function.setResultType(newInstance);
//sql语句也明显不是"attribute"
//String sql = ele.attributeValue("sql");
String sql = ele.getTextTrim();
function.setSql(sql);
//这儿的getFunctions并没有new ArrayList,所以是个null,导致出bug的罪魁祸首
//mapperBean.getFunctions().add(function);
functions.add(function);
System.out.println("第一次遍历结束");
}
mapperBean.setFunctions(functions);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("解析填充内容时遇到异常");
}
System.out.println("mapperBean="+mapperBean);
return mapperBean;
}2.进行测试
随时进行一些测试
com/stein/SteinConfigurationTest.java
@Test
public void readMapper(){
SteinConfiguration steinConfiguration = new SteinConfiguration();
MapperBean mapperBean = steinConfiguration.readMapperBean("MonsterMapper.xml");
System.out.println("ok~~");
}输出结果
mapperBean=MapperBean(interfaceName=com.stein.mapper.MonsterMapper, functions=[Function(sqlType=select, functionName=getMonsterById, resultType=Monster(id=null, age=null, name=null, email=null, birthday=null, salary=null, gender=null), sql=select * from monster where id=?, parameterType=null)])
阶段7-实现动态代理Mapper的方法
完成动态代理生成Mapper对象
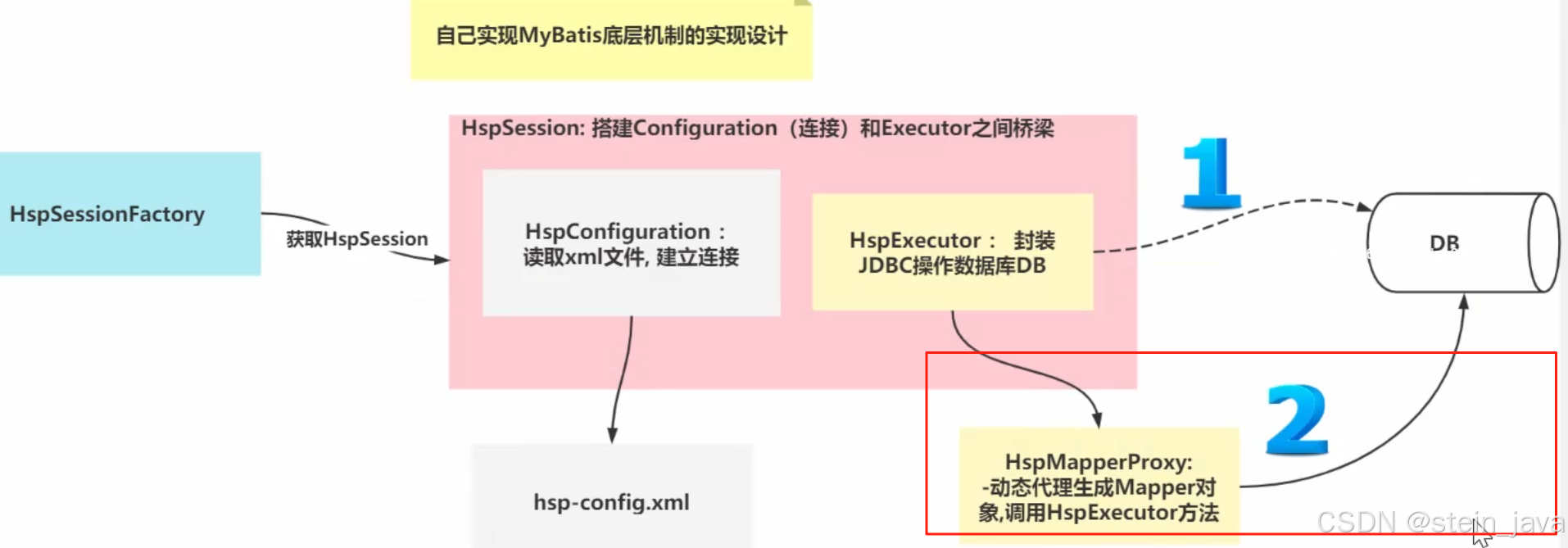
1.创建SteinMapperProxy
com/stein/steinmybatis/sqlSession/SteinMapperProxy.java
public class SteinMapperProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private SteinConfiguration steinConfiguration;
private String mapperFile;
private SteinSession steinSession;
public SteinMapperProxy(SteinConfiguration steinConfiguration,
SteinSession steinSession,
Class clazz) {
this.steinConfiguration = steinConfiguration;
this.mapperFile = clazz.getSimpleName();
this.steinSession = steinSession;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MapperBean mapperBean = steinConfiguration.readMapperBean(mapperFile + ".xml");
String mapperBeanInterfaceName = mapperBean.getInterfaceName();
System.out.println("mapperBeanInterfaceName = " + mapperBeanInterfaceName);
if(!method.getDeclaringClass().getName().equals(mapperBeanInterfaceName)){
return null;
}
List<Function> functions = mapperBean.getFunctions();
//判断内容是否为空
if(functions!=null && 0!=functions.size()){
for (Function function : functions) {
//判断是同一个方法时,就能执行对应的方法
if(method.getName().equals(function.getFunctionName())){
//如果执行的类型是select,就执行selectOne()方法
if("select".equalsIgnoreCase(function.getSqlType())){
return steinSession.selectOne(function.getSql(), String.valueOf(args[0]));
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
}2.完善SteinConfiguration的readMapperBean()方法
/**
* @param xmlFile 传入文件名,resource文件夹会在target目录中重建,直接获取即可
* @return
*/
public MapperBean readMapperBean(String xmlFile) {
MapperBean mapperBean = new MapperBean();
InputStream stream = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(xmlFile);
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
Document document = saxReader.read(stream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println("rootElement="+rootElement);
/**
<mapper namespace="com.stein.mapper.MonsterMapper" >
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.stein.entity.Monster">
select * from monster where id=?
</select>
</mapper>
*/
//获取namespace的方法名
if(!"mapper".equals(rootElement.getName())) {
throw new RuntimeException("xml文件找不到<mapper>标签");
}
String interfaceName = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
System.out.println("interfaceName="+interfaceName);
mapperBean.setInterfaceName(interfaceName.trim());
List<Function> functions = new ArrayList<>();
/**
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.stein.entity.Monster">
select * from monster where id=?
</select>
*/
//获取select的内容
List elements = rootElement.elements();
for (Object element : elements) {
//System.out.println("进入元素遍历");
Element ele = (Element) element;
System.out.println("ele="+ele);
Function function = new Function();
//这儿取值为null,可以看出"select"并不是属性"attribute"
//String sqlType = ele.attributeValue("select");
String sqlType = ele.getName().trim();
function.setSqlType(sqlType);
System.out.println("sqlType="+sqlType);
String functionName = ele.attributeValue("id");
function.setFunctionName(functionName);
String resultType = ele.attributeValue("resultType");
//因为resultType是一个Object类型,这儿返回一个实例
Object newInstance = Class.forName(resultType).newInstance();
function.setResultType(newInstance);
//sql语句也明显不是"attribute"
//String sql = ele.attributeValue("sql");
String sql = ele.getTextTrim();
function.setSql(sql);
//这儿的getFunctions并没有new ArrayList,所以是个null,导致出bug的罪魁祸首
//mapperBean.getFunctions().add(function);
functions.add(function);
System.out.println("第一次遍历结束");
}
mapperBean.setFunctions(functions);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("解析填充内容时遇到异常");
}
System.out.println("mapperBean="+mapperBean);
return mapperBean;
}3.测试
@Test
public void mapperProxy(){
SteinSession steinSession = new SteinSession();
MonsterMapper mapperProxy = steinSession.getMapperProxy(MonsterMapper.class);
Monster monster = mapperProxy.getMonsterById(1);
System.out.println("monster = " + monster);
}以上便是手动实现Mybaits的过程代码。
