数据结构之二叉树(3)
林无静树,川无停流
上次博客我给大家列举了两个重要算法,今天我们探讨一下它们的时间复杂度。
1.向上调整算法建堆的时间复杂度
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HpDataType* arr, int child) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0) {
if (arr[child] > arr[parent]) {
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
//入堆
void HpPush(Hp* php,HpDataType x) {
assert(php);
//空间不够增容
if (php->size == php->capacity) {
int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (php->capacity);
HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newcapacity * sizeof(HpDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail");
exit(1);
}
php->arr = tmp;
php->capacity = newcapacity;
}
php->arr[php->size++] = x;
//向上调整
AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size - 1);
}
堆是完全二叉树,所以我们近似使用满二叉树来证:
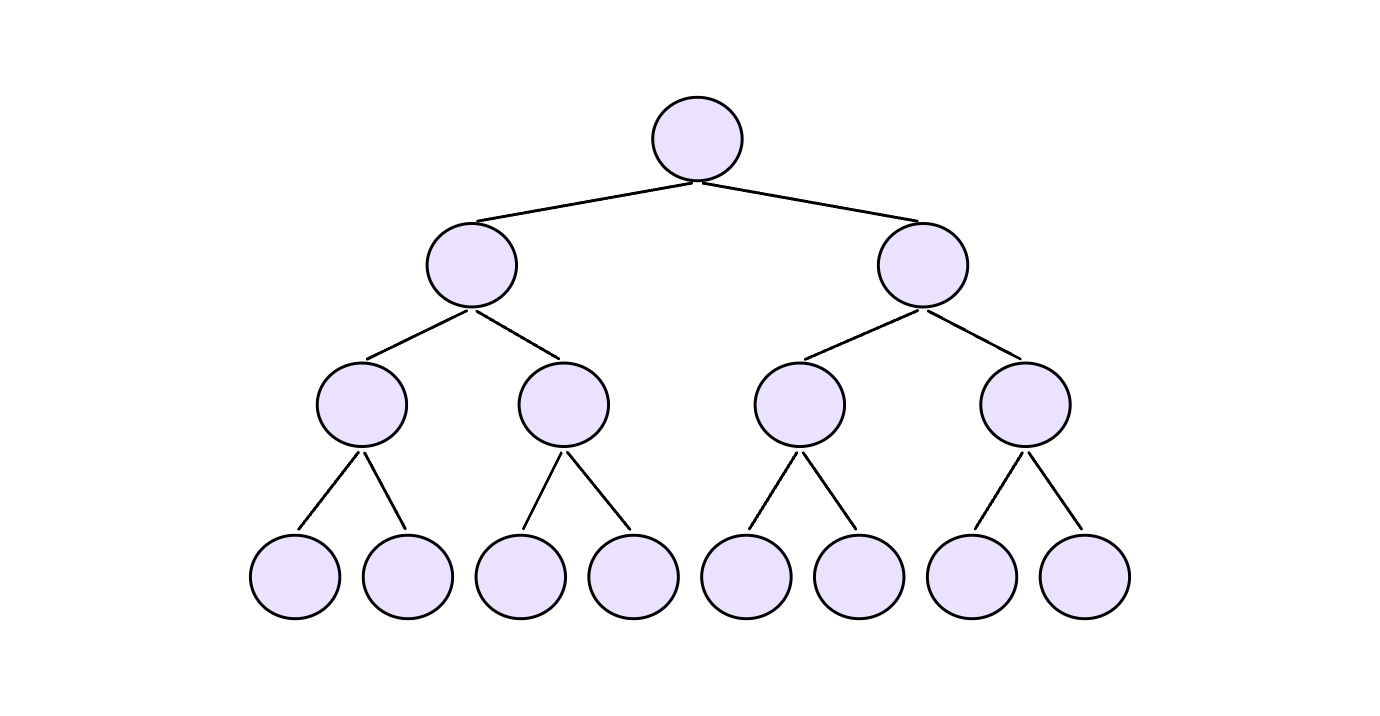
假设每一个结点入堆都需要向上调整至堆顶,那么:
第1层,2^0个结点,需要向上移动0层
第2层,2^1个结点,需要向上移动1层
第3层,2^2个结点,需要向上移动2层
第4层,2^3个结点,需要向上移动3层
…
第h层,2^(h-1)个结点,需要向上移动h-1层
把它们都相加起来:
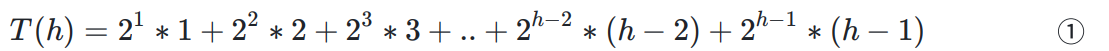
我们使用高中做数列题的功底:×2
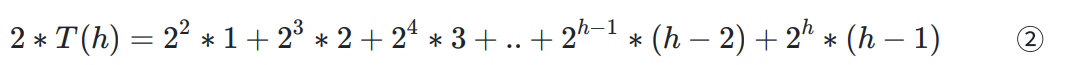
二式减一式,得
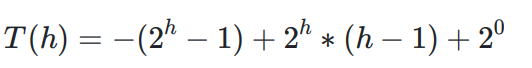
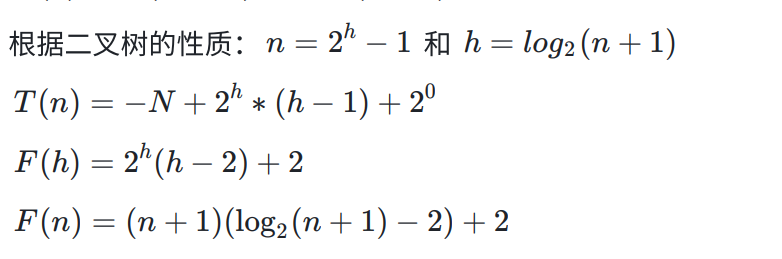
所以,向上调整算法建堆时间复杂度为;O(n*log2n).
2.向下调整算法建堆的时间复杂度
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HpDataType* arr, int parent, int n) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n) {
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] < arr[child + 1]) {
child++;
}
if (arr[child] > arr[parent]) {
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
//入堆
void HpPush(Hp* php,HpDataType x) {
assert(php);
//空间不够增容
if (php->size == php->capacity) {
int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (php->capacity);
HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newcapacity * sizeof(HpDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail");
exit(1);
}
php->arr = tmp;
php->capacity = newcapacity;
}
php->arr[php->size++] = x;
//向下调整
AdjustDown(php->arr, 0,php->size);
}
同理:
第1层,2^0个结点,需要向下移动h-1层
第2层,2^1个结点,需要向上移动h-2层
第3层,2^2个结点,需要向上移动h-3层
第4层,2^3个结点,需要向上移动h-4层
…
第h层,2^(h-1)个结点,需要向上移动0层

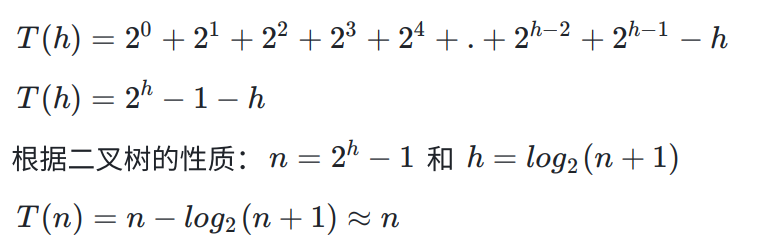
所以,向下调整算法建堆的时间复杂度为O(n).
3.堆排序(Heap Sort)
给出一个无序的数组,先把它建堆。
从最后一个父节点开始,向下调整,之后每次i–使得所有结点都能被遍历到。
//建立堆结构,n为结点个数
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0;i--) {
AdjustDown(arr, i, n);
}
到这里已经把数组的第一个元素变成最大的,每次取出堆顶然后与最后一个元素交换,再向下调整,使其在变成一个堆
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0) {
int top = arr[0];
Swap(&arr[end], &arr[0]);
AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);
end--;
}
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
在向上(下)调整算法中,改变>号或<号就可以改为升序或降序。
//堆排序
void HeapSort(int* arr,int n) {
//建立堆结构
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0;i--) {
AdjustDown(arr, i, n);
}
//到这里已经把数组的第一个元素变成最大的
//每次取出堆顶然后与最后一个元素交换,再向下调整,使其在变成一个堆
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0) {
int top = arr[0];
Swap(&arr[end], &arr[0]);
AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);
end--;
}
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}
完
如果发现错误,欢迎打在评论区。
主页还有更多优质内容OvO