文章目录
1、路由代码块
1.1 apollo-master/modules/routing/routing.cc:
实现的功能:
整体作用:
这段代码实现了 Routing 模块的核心逻辑,主要负责:
1、初始化与启动 Routing 服务,加载高精地图和拓扑图。
2、处理 Routing 请求:接收用户输入的起点、终点等路由请求。
3、补全缺失的车道信息:当请求中的 waypoint 没有车道 ID 时,根据位置坐标去高精地图里查找最近的车道并填充。
4、生成候选请求:如果某个点落在多个车道上,会生成多个候选请求。
5、调用 Navigator 搜索路径:在所有候选请求里,选择 最短路径 作为最终路由结果。
6、返回 RoutingResponse 并输出日志(成功/失败)。
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2017 The Apollo Authors. All Rights Reserved.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*****************************************************************************/
/*实现的功能:接收 Routing 请求 → 自动补齐缺失车道信息 → 在地图上搜索路径 → 选择最优路线 → 返回 RoutingResponse*/
#include "modules/routing/routing.h"
#include <limits>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "modules/common/util/point_factory.h"
#include "modules/map/hdmap/hdmap_common.h"
#include "modules/routing/common/routing_gflags.h"
namespace apollo {
namespace routing {
using apollo::common::ErrorCode;
using apollo::common::PointENU;
// const:表示该成员函数是 常量成员函数,承诺在函数体内不会修改类的成员变量,
// const 修饰符表明该函数不会修改类的成员变量。编译器会强制检查函数内部是否违反了这一规则
std::string Routing::Name() const { return FLAGS_routing_node_name; } // const 方法,无副作用,直接返回字符串
// 初始化列表:monitor_logger_buffer_ 被初始化为与 ROUTING 相关的监控/日志条目类型
Routing::Routing()
: monitor_logger_buffer_(common::monitor::MonitorMessageItem::ROUTING) {}
// 创建导航器并获取地图指针。若地图未加载成功,程序会通过断言中止(强烈依赖于正确的地图加载)
apollo::common::Status Routing::Init() {
const auto routing_map_file = apollo::hdmap::RoutingMapFile();
AINFO << "Use routing topology graph path: " << routing_map_file;
navigator_ptr_.reset(new Navigator(routing_map_file));
hdmap_ = apollo::hdmap::HDMapUtil::BaseMapPtr();
ACHECK(hdmap_) << "Failed to load map file:" << apollo::hdmap::BaseMapFile();
return apollo::common::Status::OK();
}
apollo::common::Status Routing::Start() {
if (!navigator_ptr_->IsReady()) {
AERROR << "Navigator is not ready!";
return apollo::common::Status(ErrorCode::ROUTING_ERROR,
"Navigator not ready");
}
AINFO << "Routing service is ready.";
monitor_logger_buffer_.INFO("Routing started");
return apollo::common::Status::OK();
}
std::vector<routing::RoutingRequest> Routing::FillLaneInfoIfMissing(
const routing::RoutingRequest& routing_request) {
std::vector<routing::RoutingRequest> fixed_requests; // fixed_requests:最终返回的请求集合
std::unordered_map<int, std::vector<LaneWaypoint>> // additional_lane_waypoint_map: 键是 waypoint 的索引 int,值是该索引可能的额外 LaneWaypoint 候选(除第一个最优 lane 以外)
additional_lane_waypoint_map;
routing::RoutingRequest fixed_request(routing_request); // fixed_request:先把原始请求拷贝一份,后续在这个基础上填充第一个找到的 lane id
for (int i = 0; i < routing_request.waypoint_size(); ++i) {
LaneWaypoint lane_waypoint(routing_request.waypoint(i));
if (lane_waypoint.has_id()) { // 遍历每个 waypoint。如果该 waypoint 已经有 id(即已指定 lane),则跳过(不需要填充)
continue;
}
// fill lane info when missing, // 将 waypoint 的 pose 转换为 PointENU(x, y, z),用于查找地图上的 lane
const auto point =
common::util::PointFactory::ToPointENU(lane_waypoint.pose());
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const hdmap::LaneInfo>> lanes; // 定义 lanes 容器用于存放找到的车道指针
/*使用半径 kRadius(0.3 米)尝试查找。如果找不到,逐步增大 radius(0.3, 0.6, 0.9, ..., 6.0 米,最多 20 次)。
hdmap_->GetLanes(point, radius, &lanes):把找到的 lane 塞入 lanes。
一旦找到至少一个 lane 就跳出循环。
注意:此处 i 变量在外部循环也被使用(函数最外层也用 i),
但这里又用 for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) ——实际源码中这是隐藏的重定义(编译器允许,因为内层 i 是新的局部变量),但出于可读性建议改名(避免混淆)*/
// look for lanes with bigger radius if not found
constexpr double kRadius = 0.3;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
hdmap_->GetLanes(point, kRadius + i * kRadius, &lanes);
if (lanes.size() > 0) {
break;
}
}
// 如果最终 lanes.empty(),会打印错误并直接返回 fixed_requests(此时为空)。上层 Process() 会看到返回的集合为空并处理(通常表示路由失败)
if (lanes.empty()) {
AERROR << "Failed to find nearest lane from map at position: "
<< point.DebugString();
return fixed_requests; // return empty vector
}
// GetProjection 把点投影到 lane 坐标系上,得到 s(沿车道的纵向位置)和 l(横向偏移),常用于路由定位
/*
将第一个 lane 填回原始请求;其他 lane 作为候选保存:
对于找到的第一个 lane(j == 0),直接写回 fixed_request 的对应 waypoint:设置 id 和 s。
对于其余 lane,把它们封装成 LaneWaypoint 并放入 additional_lane_waypoint_map[i](按 waypoint 索引 i 分组)。
这些候选将用于生成多个 routing 请求(组合不同候选 lane 的可能性)
*/
for (size_t j = 0; j < lanes.size(); ++j) {
double s = 0.0;
double l = 0.0;
lanes[j]->GetProjection({point.x(), point.y()}, &s, &l);
if (j == 0) {
auto waypoint_info = fixed_request.mutable_waypoint(i);
waypoint_info->set_id(lanes[j]->id().id());
waypoint_info->set_s(s);
} else {
// additional candidate lanes
LaneWaypoint new_lane_waypoint(lane_waypoint);
new_lane_waypoint.set_id(lanes[j]->id().id());
new_lane_waypoint.set_s(s);
additional_lane_waypoint_map[i].push_back(new_lane_waypoint);
}
}
}
// first routing_request
// 把用第一个候选车道(对每个未指定车道的 waypoint)填充得到的 fixed_request 放入 fixed_requests 作为第一个候选请求
fixed_requests.push_back(fixed_request);
// additional routing_requests because of lane overlaps
/*
对 additional_lane_waypoint_map 中的每个项(每个有额外候选的 waypoint 索引 m.first):
记录当前 fixed_requests 的 cur_size(注意:我们只迭代到 cur_size,因为接下来会扩展 fixed_requests,这样保证新加的请求不会在当前轮次重复被扩展)。
对于已有的每一个 fixed_requests[i](原先的候选),为当前 waypoint 的每个额外 lane 候选生成一个新的请求 new_request,替换第 m.first 个 waypoint
的 id/s ,然后 push_back。
效果:如果多个 waypoint 各自有 N1, N2, ... 额外候选,则最终生成的 fixed_requests 数量为原始 1 × (1+N1) × (1+N2) × ...(即形成笛卡尔乘积的扩展)。
这会导致组合爆炸,需注意性能与数量限制
*/
for (const auto& m : additional_lane_waypoint_map) {
size_t cur_size = fixed_requests.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cur_size; ++i) {
// use index to iterate while keeping push_back
for (const auto& lane_waypoint : m.second) {
routing::RoutingRequest new_request(fixed_requests[i]);
auto waypoint_info = new_request.mutable_waypoint(m.first);
waypoint_info->set_id(lane_waypoint.id());
waypoint_info->set_s(lane_waypoint.s());
fixed_requests.push_back(new_request);
}
}
}
/*
用 DEBUG 级别打印每个修正后的请求的 protobuf 字符串(便于调试)。
返回 fixed_requests(可能包含 0 个、1 个或多个请求)
*/
for (const auto& fixed_request : fixed_requests) {
ADEBUG << "Fixed routing request:" << fixed_request.DebugString();
}
return fixed_requests;
}
// 这是 routing 的核心处理函数:接收请求、尝试搜索并返回最佳路由(最短的那个)
bool Routing::Process(
const std::shared_ptr<routing::RoutingRequest>& routing_request,
routing::RoutingResponse* const routing_response) {
if (nullptr == routing_request) {
AWARN << "Routing request is empty!";
return true;
}
CHECK_NOTNULL(routing_response);
AINFO << "Get new routing request:" << routing_request->DebugString();
/*
从 FillLaneInfoIfMissing 得到一组 fixed_requests(可能为空)。
min_routing_length 初始化为极大值(用于选最短路径)。
对每个 fixed_request:
1. 用 navigator_ptr_->SearchRoute(fixed_request, &routing_response_temp) 发起路由搜索;SearchRoute 返回 bool 表示是否找到路径,
并把结果写入 routing_response_temp。
2. 若找到路径,取 routing_response_temp.measurement().distance() 作为该路径的长度(或代价)。
3. 若该长度比当前最小值小,则用 routing_response_temp 覆盖输入 routing_response(最终输出最短路径)并更新 min_routing_length。
*/
const auto& fixed_requests = FillLaneInfoIfMissing(*routing_request);
double min_routing_length = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (const auto& fixed_request : fixed_requests) {
routing::RoutingResponse routing_response_temp;
if (navigator_ptr_->SearchRoute(fixed_request, &routing_response_temp)) {
const double routing_length =
routing_response_temp.measurement().distance();
if (routing_length < min_routing_length) {
routing_response->CopyFrom(routing_response_temp);
min_routing_length = routing_length;
}
}
}
/*
如果 min_routing_length 被更新过(不再是极大值),表示至少找到一条路径:记录监控信息并返回 true(处理成功)。
否则(没有任何候选成功),记录错误日志 + 监控警告(routing_response->status().msg() 被用作附加信息,
但此时 routing_response 可能为空或内容未被设置;若未设置,以空字符串或默认值参与拼接),然后返回 false 表示失败
*/
if (min_routing_length < std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) {
monitor_logger_buffer_.INFO("Routing success!");
return true;
}
AERROR << "Failed to search route with navigator.";
monitor_logger_buffer_.WARN("Routing failed! " +
routing_response->status().msg());
return false;
}
} // namespace routing
} // namespace apollo
/*
注意点(Process):
当 FillLaneInfoIfMissing 返回空集合时,for 循环不会执行,最终进入失败分支 -> 返回 false。
这与 routing_request == nullptr 时直接 return true 的处理逻辑不一致(可能设计上认为“无请求”并非错误,而“有请求但无法匹配地图”是错误),需明确调用约定。
使用 routing_response->status().msg() 在失败日志中:若此前没有对 routing_response 设置 status,可能取到默认/空字符串。
在遍历多个候选请求时,选择最短路径作为最终输出(贪心地以距离做度量)。这是合理的常见选择,但在复杂场景下需要确保 measurement().distance()
是恰当的代价函数(有时应考虑时间、车道合法性等)。
*/
输入和输出数据分别如下:
输入数据:
{
"header": {
"timestamp_sec": 1690000000.123,
"module_name": "dreamview",
"sequence_num": 1
},
"waypoint": [
{
"pose": {
"x": 586123.45,
"y": 4145678.90,
"z": 0.0
}
// 没有提供 lane_id,这种情况 Routing 模块会去 HDMap 里自动补齐
},
{
"id": "lane_1234", // 指定目标车道 ID
"s": 25.0 // 在该车道上的纵向距离
}
]
}
这个请求表示:
- 起点:只给了坐标点 (x, y),没有车道 ID。
- 终点:指定了车道 ID 和 s 值。
- Routing 模块会先补齐起点车道信息,然后计算从起点到终点的路径。
输出数据:
{
"header": {
"timestamp_sec": 1690000001.456,
"module_name": "routing",
"sequence_num": 1
},
"status": {
"error_code": "OK",
"msg": "Routing successfully computed"
},
"measurement": {
"distance": 325.7, // 总路径长度(米)
"time": 45.3 // 估计行驶时间(秒)
},
"road": [
{
"id": "road_1001",
"passage": [
{
"lane_segment": [
{
"id": "lane_5678",
"start_s": 10.5,
"end_s": 80.0
},
{
"id": "lane_5679",
"start_s": 0.0,
"end_s": 50.0
}
]
}
]
},
{
"id": "road_1002",
"passage": [
{
"lane_segment": [
{
"id": "lane_1234",
"start_s": 0.0,
"end_s": 25.0
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
这个返回表示:
- 状态:成功。
- 路径总长 325.7m,预计 45.3s。
- 经过的道路:road_1001 → road_1002。
- 在每条 road 下,路径由多个 LaneSegment 拼接而成,精确到车道 ID 和 s 范围。
总结:
RoutingRequest:起点/终点 waypoints(可只给坐标点)。
RoutingResponse:完整路径(道路序列 + 车道序列 + 路径长度/时间 + 状态)。
1.2 输入和输出数据格式
apollo-master/modules/common_msgs/routing_msgs/routing.proto:
syntax = "proto2";
package apollo.routing;
import "modules/common_msgs/routing_msgs/geometry.proto";
import "modules/common_msgs/basic_msgs/header.proto";
import "modules/common_msgs/basic_msgs/error_code.proto";
import "modules/common_msgs/routing_msgs/poi.proto";
message RoutingRequest {
optional apollo.common.Header header = 1;
// at least two points. The first is start point, the end is final point.
// The routing must go through each point in waypoint. 路径途经点(至少包含起点和终点)
repeated apollo.routing.LaneWaypoint waypoint = 2;
// 禁止经过的车道段(LaneSegment,包含 id+起止 s)
repeated apollo.routing.LaneSegment blacklisted_lane = 3;
// 禁止经过的整条 road(road id)
repeated string blacklisted_road = 4;
// broadcast:是否广播 RoutingResponse。默认 true,Routing 模块会将结果发布到 topic
optional bool broadcast = 5 [default = true];
// parking_info:停车相关信息(已废弃,不再使用)
optional apollo.routing.ParkingInfo parking_info = 6 [deprecated = true];
// If the start pose is set as the first point of "way_point".
// is_start_pose_set:是否将起点的 pose 设置为精确位置标记(一般为 true,表示第一个 waypoint 就是车辆当前 pose)
optional bool is_start_pose_set = 7 [default = false];
}
message RoutingResponse {
optional apollo.common.Header header = 1;
// road:路径经过的 road 列表,每个 road 里会包含 passage(通行车道集合),passage 再包含 LaneSegment(具体的车道片段)
repeated apollo.routing.RoadSegment road = 2;
// measurement:统计信息,例如路径总距离、预计时间
optional apollo.routing.Measurement measurement = 3;
// routing_request:原始请求的拷贝,方便调试/验证。
optional RoutingRequest routing_request = 4;
//构建路网时使用的地图版本号(保证 Routing 与 HDMap 一致性)
// the map version which is used to build road graph
optional bytes map_version = 5;
// status:结果状态(OK / FAILED + 错误消息)
optional apollo.common.StatusPb status = 6;
}
apollo-master/modules/common_msgs/routing_msgs/geometry.proto:
syntax = "proto2";
package apollo.routing;
import "modules/common_msgs/basic_msgs/geometry.proto";
message LaneWaypoint {
// 车道 ID
optional string id = 1;
// 车道纵向距离
optional double s = 2;
// 世界坐标点 (x, y, z)
optional apollo.common.PointENU pose = 3;
// When the developer selects a point on the dreamview route editing
// the direction can be specified by dragging the mouse
// dreamview calculates the heading based on this to support construct lane way point with heading
optional double heading = 4;
}
message LaneSegment {
optional string id = 1;
optional double start_s = 2;
optional double end_s = 3;
}
enum DeadEndRoutingType {
ROUTING_OTHER = 0;
ROUTING_IN = 1;
ROUTING_OUT = 2;
}
message Measurement {
optional double distance = 1;
}
enum ChangeLaneType {
FORWARD = 0;
LEFT = 1;
RIGHT = 2;
};
message Passage {
repeated LaneSegment segment = 1;
optional bool can_exit = 2;
optional ChangeLaneType change_lane_type = 3 [default = FORWARD];
}
message RoadSegment {
optional string id = 1;
repeated Passage passage = 2;
}
2、路径数据结构代码块
apollo-master/modules/map/pnc_map/path.cc
实现流程图如下:
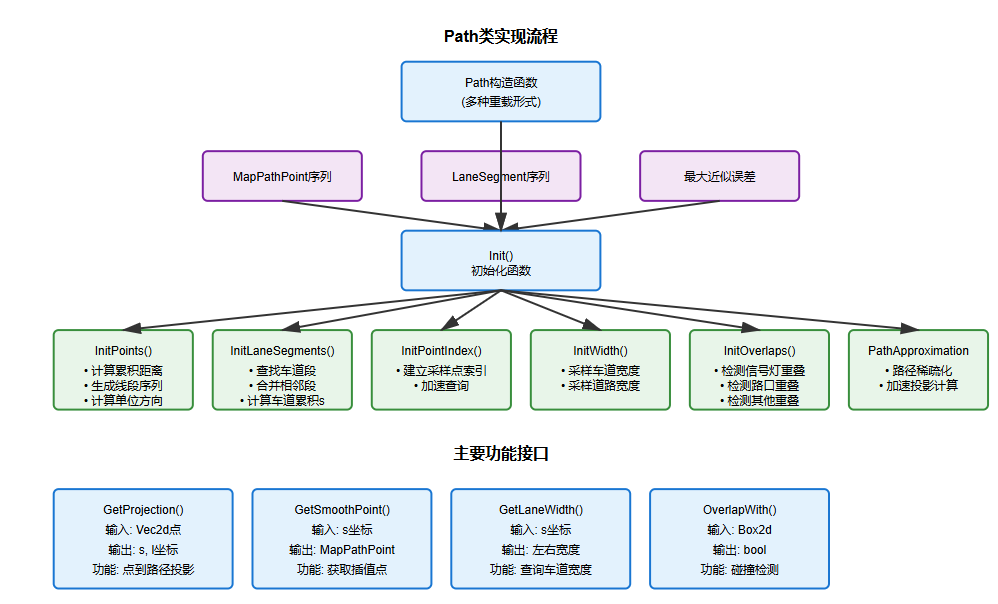
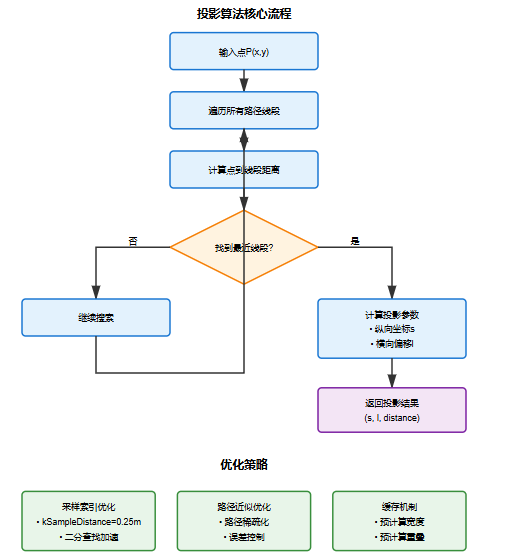
这段代码是Apollo自动驾驶系统中的Path模块实现,主要用于处理高精地图中的路径规划和管理。我将详细说明其功能并提供流程图。
2.1 主要功能实现
1. 核心数据结构
- LaneWaypoint: 车道路点,包含车道指针和纵向坐标s
- LaneSegment: 车道段,包含起始和结束s坐标
- MapPathPoint: 地图路径点,包含x/y坐标、航向角和关联的车道路点
- Path: 主路径类,由一系列路径点和车道段组成
- PathApproximation: 路径近似优化类,用于加速投影计算
2. 主要功能模块
路径构建功能
- 从路径点序列构建路径
- 从车道段序列构建路径
- 支持路径近似优化
投影与查询功能
- 将任意点投影到路径上,获取纵向s和横向l坐标
- 查询指定s位置的平滑插值点
- 获取路径上指定位置的车道宽度和道路宽度
重叠检测功能
- 检测与信号灯、停止标志、人行横道等地图元素的重叠
- 支持与Box2d几何体的碰撞检测
邻居车道功能
- 查找左右相邻车道的对应路点
- 获取车道边界类型
2.2 代码功能总结
这段Apollo Path模块代码实现了一个完整的高精地图路径管理系统,主要包括以下核心功能:
核心功能列表
路径表示与构建
- 支持从路径点序列或车道段序列构建路径
- 自动去重和插值处理
- 支持路径近似优化以提升性能
坐标投影系统
- 将任意世界坐标点投影到路径上,获取Frenet坐标(s, l)
- 支持带航向角约束的投影
- 支持热启动投影(从已知s位置开始搜索)
路径查询功能
- 根据s坐标获取平滑插值点
- 查询指定位置的车道宽度和道路宽度
- 判断点是否在路径上
重叠检测系统
- 检测与交通信号灯、停止标志、人行横道的重叠
- 检测与路口、停车位、减速带等地图元素的重叠
- 支持与Box2d几何体的碰撞检测
邻居车道处理
- 查找左右相邻车道的对应路点
- 获取车道边界类型(实线、虚线等)
性能优化机制
- 采样索引加速(默认0.25米采样间隔)
- 路径近似算法(PathApproximation类)
- 预计算缓存机制
关键算法特点
- 投影算法:通过遍历所有线段找到最近点,考虑了端点特殊情况
- 宽度插值:使用线性插值在采样点之间获取连续宽度值
- 路径近似:使用Douglas-Peucker类算法稀疏化路径点,在保证误差范围内减少计算量
- 重叠合并:自动合并距离小于1.5米的连续重叠区域
这个模块是Apollo自动驾驶系统路径规划的基础组件,为上层的轨迹规划、决策控制等模块提供了高效可靠的路径管理服务。
3、发布参考线代码块
apollo-master/modules/planning/planning_base/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
3.1 代码功能总结
这个代码实现了Apollo自动驾驶系统中的参考线提供器(ReferenceLineProvider),主要负责为规划模块生成和管理参考线(Reference Line)。参考线是车辆行驶的理想路径,用于后续的轨迹规划。
1. 核心功能
参考线生成与管理
- 基于高精地图和路由信息生成参考线
- 支持多条参考线(用于车道变换等场景)
- 实时更新和维护参考线
参考线平滑处理
- 使用不同的平滑算法(QP样条、螺旋线、离散点)对原始参考线进行平滑
- 确保参考线的连续性和可行性
两种工作模式
- 导航模式:基于相对地图(relative map)生成参考线
- 正常模式:基于高精地图和路由信息生成参考线
参考线拼接与扩展
- 支持参考线的历史拼接(stitching)以保证连续性
- 根据车辆状态动态扩展参考线
线程化处理
- 支持后台线程持续生成参考线,减少主线程阻塞
2. 输入数据格式
PlanningCommand(规划命令)
- 包含路由信息、目标点等规划指令
- protobuf格式
VehicleState(车辆状态)
- x, y: 车辆位置坐标 - heading: 车辆朝向角 - linear_velocity: 线速度 - 其他运动学参数RelativeMap(相对地图)- 导航模式下使用
- navigation_path: 导航路径信息 - 包含车道ID和路径优先级 - protobuf格式HDMap(高精地图)
- 车道信息(LaneInfo)
- 道路拓扑结构
- 车道边界、宽度等几何信息
3. 输出数据格式
ReferenceLine(参考线)
- reference_points: 参考点序列 - 每个点包含:位置(x,y)、朝向(theta)、曲率(kappa)、曲率导数(dkappa) - 支持坐标转换(笛卡尔坐标与Frenet坐标)RouteSegments(路由段)
- 车道段列表(LaneSegment) - 每段包含: - lane_ptr: 车道指针 - start_s, end_s: 段的起止位置 - 车道变换信息(NextAction, PreviousAction) - 是否为当前车道(IsOnSegment) - 是否为邻近车道(IsNeighborSegment)
4. 主要接口
UpdatePlanningCommand(): 更新规划命令GetReferenceLines(): 获取参考线列表UpdateVehicleState(): 更新车辆状态Start()/Stop(): 启动/停止参考线生成线程
5. 数据流程
- 接收规划命令和车辆状态
- 根据模式选择数据源(导航地图或高精地图)
- 生成原始路径段
- 应用平滑算法优化路径
- 输出平滑后的参考线供规划模块使用
这个模块是自动驾驶规划系统的关键组件,为后续的轨迹规划提供基础路径参考。
3.2 代码详细总结
这是Apollo自动驾驶系统中的参考线提供者(ReferenceLineProvider)实现文件。参考线是自动驾驶规划模块的核心组件,为车辆提供平滑可跟踪的行驶路径。我将按功能模块详细解释这个代码:
1. 文件头部和依赖
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2017 The Apollo Authors. All Rights Reserved.
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0
*****************************************************************************/
#include "modules/planning/planning_base/reference_line/reference_line_provider.h"
// ... 其他包含文件
- 版权声明和Apache 2.0许可证
- 包含必要的头文件(Cyber框架、地图、规划模块等)
2. 命名空间和别名定义
namespace apollo {
namespace planning {
using apollo::common::VehicleConfigHelper;
using apollo::common::VehicleState;
// ... 其他using声明
定义命名空间和类型别名,简化代码书写。
3. 构造函数和析构函数
ReferenceLineProvider::~ReferenceLineProvider() {}
ReferenceLineProvider::ReferenceLineProvider(
const common::VehicleStateProvider *vehicle_state_provider,
const ReferenceLineConfig *reference_line_config,
const std::shared_ptr<relative_map::MapMsg> &relative_map)
: vehicle_state_provider_(vehicle_state_provider) {
输入参数:
vehicle_state_provider: 车辆状态提供者,获取车辆位置、速度等信息reference_line_config: 参考线配置relative_map: 相对地图消息(导航模式使用)
功能:
- 初始化成员变量
- 加载平滑器配置(QpSpline、Spiral或DiscretePoints)
- 加载PncMap插件(默认使用LaneFollowMap)
4. 更新规划命令
bool ReferenceLineProvider::UpdatePlanningCommand(
const planning::PlanningCommand &command) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> routing_lock(routing_mutex_);
bool find_matched_pnc_map = false;
for (const auto &pnc_map : pnc_map_list_) {
if (pnc_map->CanProcess(command)) {
current_pnc_map_ = pnc_map;
find_matched_pnc_map = true;
break;
}
}
功能:
- 接收新的规划命令(包含路由信息)
- 查找合适的PncMap处理命令
- 更新路由信息
输入: PlanningCommand - 包含目标点、路由等信息
输出: bool - 是否成功更新
5. 启动和停止线程
bool ReferenceLineProvider::Start() {
if (FLAGS_enable_reference_line_provider_thread) {
task_future_ = cyber::Async(&ReferenceLineProvider::GenerateThread, this);
}
return true;
}
void ReferenceLineProvider::GenerateThread() {
while (!is_stop_) {
static constexpr int32_t kSleepTime = 50; // milliseconds
cyber::SleepFor(std::chrono::milliseconds(kSleepTime));
// ... 生成参考线
}
}
功能:
- 启动后台线程持续生成参考线
- 每50ms更新一次参考线
6. 创建参考线核心逻辑
bool ReferenceLineProvider::CreateReferenceLine(
std::list<ReferenceLine> *reference_lines,
std::list<hdmap::RouteSegments> *segments) {
// 获取车辆状态
common::VehicleState vehicle_state;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(vehicle_state_mutex_);
vehicle_state = vehicle_state_;
}
// 创建路由段
if (!CreateRouteSegments(vehicle_state, segments)) {
AERROR << "Failed to create reference line from routing";
return false;
}
// 对每个路由段进行平滑处理
for (auto iter = segments->begin(); iter != segments->end();) {
reference_lines->emplace_back();
if (!SmoothRouteSegment(*iter, &reference_lines->back())) {
// 失败则移除
reference_lines->pop_back();
iter = segments->erase(iter);
} else {
// 根据车辆位置进行裁剪
Shrink(sl, &reference_lines->back(), &(*iter));
++iter;
}
}
主要步骤:
- 获取当前车辆状态
- 根据路由创建路段(RouteSegments)
- 对每个路段进行平滑处理
- 根据车辆位置裁剪参考线
7. 参考线平滑处理
bool ReferenceLineProvider::SmoothReferenceLine(
const ReferenceLine &raw_reference_line,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
if (!FLAGS_enable_smooth_reference_line) {
*reference_line = raw_reference_line;
return true;
}
// 生成锚点
std::vector<AnchorPoint> anchor_points;
GetAnchorPoints(raw_reference_line, &anchor_points);
// 使用平滑器进行平滑
smoother_->SetAnchorPoints(anchor_points);
if (!smoother_->Smooth(raw_reference_line, reference_line)) {
AERROR << "Failed to smooth reference line";
return false;
}
// 验证平滑结果
if (!IsReferenceLineSmoothValid(raw_reference_line, *reference_line)) {
AERROR << "The smoothed reference line error is too large";
return false;
}
功能:
- 使用配置的平滑算法(QpSpline/Spiral/DiscretePoints)
- 生成锚点用于约束平滑过程
- 验证平滑后的参考线与原始线的偏差
8. 锚点生成
AnchorPoint ReferenceLineProvider::GetAnchorPoint(
const ReferenceLine &reference_line, double s) const {
AnchorPoint anchor;
// 设置纵向边界
anchor.longitudinal_bound = smoother_config_.longitudinal_boundary_bound();
// 获取参考点
auto ref_point = reference_line.GetReferencePoint(s);
// 计算横向边界(考虑车道宽度、路缘等)
double left_width = 0.0;
double right_width = 0.0;
waypoint.lane->GetWidth(waypoint.s, &left_width, &right_width);
// 减去车辆宽度
double safe_lane_width = left_width + right_width;
safe_lane_width -= adc_width;
// 考虑路缘偏移
if (hdmap::RightBoundaryType(waypoint) == hdmap::LaneBoundaryType::CURB) {
safe_lane_width -= smoother_config_.curb_shift();
}
功能:
- 在参考线上生成约束点
- 考虑车道宽度、车辆宽度、路缘等因素
- 计算横向和纵向约束边界
9. 参考线拼接和扩展
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(
const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// 查找前一条参考线
auto prev_segment = route_segments_.begin();
while (prev_segment != route_segments_.end()) {
if (prev_segment->IsConnectedSegment(*segments)) {
break;
}
++prev_segment;
}
// 计算剩余距离
const double remain_s = prev_segment_length - sl_point.s();
const double look_forward_required_distance =
planning::PncMapBase::LookForwardDistance(state.linear_velocity());
// 如果剩余距离足够,直接使用前一条参考线
if (remain_s > look_forward_required_distance) {
*segments = *prev_segment;
*reference_line = *prev_ref;
return true;
}
// 否则扩展参考线
if (!current_pnc_map_->ExtendSegments(*prev_segment, future_start_s,
future_end_s, &shifted_segments)) {
AERROR << "Failed to shift route segments forward";
return false;
}
功能:
- 实现参考线的连续性
- 根据车速计算前视距离
- 必要时扩展参考线
10. 参考线裁剪
bool ReferenceLineProvider::Shrink(const common::SLPoint &sl,
ReferenceLine *reference_line,
RouteSegments *segments) {
double new_backward_distance = sl.s();
double new_forward_distance = reference_line->Length() - sl.s();
// 检查后向距离
if (sl.s() > planning::FLAGS_look_backward_distance * 1.5) {
new_backward_distance = planning::FLAGS_look_backward_distance;
need_shrink = true;
}
// 检查航向角变化
while (last_index < ref_points.size() &&
std::fabs(AngleDiff(cur_heading, ref_points[last_index].heading()))
FLAGS_reference_line_max_forward_heading_diff) {
++last_index;
}
功能:
- 根据车辆位置裁剪过长的参考线
- 限制前后视距离
- 确保航向角变化在合理范围内
11. 导航模式支持
bool ReferenceLineProvider::GetReferenceLinesFromRelativeMap(
std::list<ReferenceLine> *reference_lines,
std::list<hdmap::RouteSegments> *segments) {
// 获取导航路径
for (const auto &path_pair : relative_map_->navigation_path()) {
const auto &lane_id = path_pair.first;
const auto &path_points = path_pair.second.path().path_point();
// 创建参考点
std::vector<ReferencePoint> ref_points;
for (const auto &path_point : path_points) {
ref_points.emplace_back(
MapPathPoint{Vec2d{path_point.x(), path_point.y()},
path_point.theta(),
LaneWaypoint(lane_ptr, path_point.s())},
path_point.kappa(), path_point.dkappa());
}
// 创建参考线
reference_lines->emplace_back(ref_points.begin(), ref_points.end());
}
功能:
- 支持导航模式(无高精地图)
- 从相对地图消息创建参考线
输入输出数据总结
主要输入:
- PlanningCommand: 包含路由请求、目标点等规划命令
- VehicleState: 车辆当前位置、速度、航向等状态
- HDMap数据: 高精地图车道信息
- RelativeMap: 导航模式下的相对地图
- 配置参数: 平滑器配置、前视距离、裁剪参数等
主要输出:
- ReferenceLine列表: 平滑后的参考线,包含:
- 参考点序列(位置、航向、曲率)
- 车道信息
- 速度限制
- RouteSegments列表: 对应的路由段信息:
- 车道ID
- 起止位置
- 变道类型
- 参考线属性:
- 优先级
- 是否可退出
- 停车点信息
这个模块是规划系统的基础组件,为后续的轨迹规划提供平滑、可行的参考路径。