多态性时面向对象的一个重要特性,主要由重构和虚函数来实现。重构函数时一种静态的多态性,在编译时完成。虚函数则提供了一种动态多态性,在程序运行时体现。下面给出了静态关联和动态关联的4个例程,大致给出了多态性在面向对象中的应用。
静态多态性之运算符重载
主文件入口代码:
#include "Circle.h"
int main() {
Point p(3.5, 6.4);
cout << "p = " << p <<endl;
Circle c(3.5, 6.4, 2);
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
Point &pR = c;
cout << pR << endl;
return 0;
}
Point.cpp代码:
#include "Point.h"
Point::Point(float a, float b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
void Point::setPoint(float a, float b) {
x = a;
y = b;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &output, const Point &p) {
output << "[" << p.getX() << "," << p.getY() << "]" << endl;
return output;
}
Point::~Point()
{
}
Circle文件代码:
#include "Circle.h"
Circle::Circle(float x, float y, float r): Point(x, y), radius(r)
{
}
void Circle::setRadius(float r) {
radius = r;
}
float Circle::area() {
return 3.14*radius*radius;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &output, Circle c) {
output << "Center = [" << c.x << "," << c.y << "]," << "radius = " << c.radius <<"," << "area = " << c.area()<< endl;
return output;
}
Circle::~Circle()
{
}
输出结果: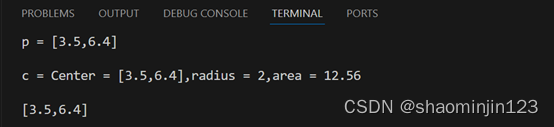
虚函数
虚函数时允许子类中定义与父类相同的函数名和函数参数的函数,在运行的时候通过基类指针或者引用来访问子类和父类中的同名函数。
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
private:
float x,y;
public:
Point(float a, float b);
virtual ~Point();
};
Point::Point(float a, float b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
Point::~Point()
{
cout << "Point::~Point()" <<endl;
}
class Circle : public Point
{
private:
/* data */
public:
Circle();
Circle(float a, float b):Point(a ,b){};
~Circle();
};
Circle::~Circle()
{
cout << "Circle::~Circle()" <<endl;
}
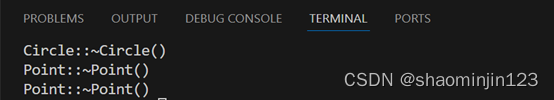
int main() {
Point *p = new Circle(3,4);
delete p;
Point p1(1,2);
//Circle *c = p1;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
纯虚函数
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
private:
/* data */
public:
Shape(/* args */);
virtual void printArea() const=0;//pure virtual function
~Shape();
};
Shape::Shape(/* args */)
{
}
Shape::~Shape()
{
}
class Triangle : public Shape
{
private:
float base;
float height;
public:
Triangle(float b, float h): base(b), height(h){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Triangle();
};
void Triangle::printArea() const {
cout << "Triangle Area = " << base*height/2 <<endl;
}
Triangle::~Triangle()
{
}
class Rectangle : public Shape
{
private:
float length;
float width;
public:
Rectangle(float l, float w): length(l), width(w){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Rectangle();
};
void Rectangle::printArea() const{
cout << "Rectangle area = " << length*width <<endl;
}
Rectangle::~Rectangle()
{
}
class Circle : public Shape
{
private:
float radius;
public:
Circle(float r): radius(r){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Circle();
};
Circle::~Circle()
{
}
void Circle::printArea() const {
cout << "Circle = " << 3.14*radius*radius << endl;
}
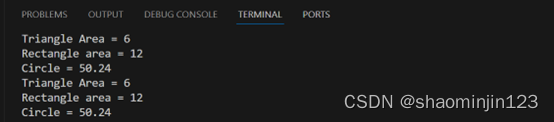
int main() {
Triangle t(3,4);
t.printArea();
Rectangle r(3,4);
r.printArea();
Circle c(4);
c.printArea();
Shape *s;
s = &t;
s->printArea();
s = &r;
s->printArea();
s = &c;
s->printArea();
delete s;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
指针数组指向派生类对象
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
private:
/* data */
public:
Shape(/* args */);
virtual void printArea() const=0;//pure virtual function
~Shape();
};
Shape::Shape(/* args */)
{
}
Shape::~Shape()
{
}
class Triangle : public Shape
{
private:
float base;
float height;
public:
Triangle(float b, float h): base(b), height(h){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Triangle();
};
void Triangle::printArea() const {
cout << "Triangle Area = " << base*height/2 <<endl;
}
Triangle::~Triangle()
{
}
class Rectangle : public Shape
{
private:
float length;
float width;
public:
Rectangle(float l, float w): length(l), width(w){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Rectangle();
};
void Rectangle::printArea() const{
cout << "Rectangle area = " << length*width <<endl;
}
Rectangle::~Rectangle()
{
}
class Circle : public Shape
{
private:
float radius;
public:
Circle(float r): radius(r){};
virtual void printArea() const;
~Circle();
};
Circle::~Circle()
{
}
void Circle::printArea() const {
cout << "Circle = " << 3.14*radius*radius << endl;
}
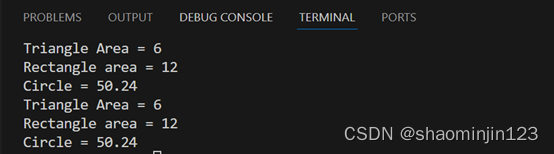
int main() {
Triangle t(3,4);
t.printArea();
Rectangle r(3,4);
r.printArea();
Circle c(4);
c.printArea();
Shape *s[3] = {&t, &r, &c};
s[0]->printArea();
s[1]->printArea();
s[2]->printArea();
return 0;
}
输出结果: