1. 红黑树的概念
红⿊树是⼀棵⼆叉搜索树,他的每个结点增加⼀个数据来表⽰结点的颜⾊,可以是红⾊或者⿊⾊。 通过对任何⼀条从根到叶⼦的路径上各个结点的颜⾊进⾏约束,红⿊树确保没有⼀条路径会⽐其他路径⻓出2倍,因⽽是接近平衡的
红黑树有以下几条规则
- 每个结点不是红⾊就是⿊⾊
- 根结点是⿊⾊的
- 如果⼀个结点是红⾊的,则它的两个孩⼦结点必须是⿊⾊的,也就是说任意⼀条路径不会有连续的
红⾊结点- 对于任意⼀个结点,从该结点到其所有NULL结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数量的⿊⾊结点
2. 红黑树的实现
2.1 基本结构
// 枚举 => 用来表示一个节点是红还是黑 enum Color{ RED, BLACK }; // Node的结构 ( 以key/value 做演示 ) template<class K,class V> struct RBTNode{ RBTNode(const K& key,const V& value):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_key(key),_value(value),_color(RED){} RBTNode<K,V>* _left; RBTNode<K,V>* _right; RBTNode<K,V>* _parent; K _key; V _value; Color _color; }; // 树的结构 template <class K, class V> class RBT { typedef RBTNode<K, V> Node; private: Node *_root = nullptr; };
2.2 插入
红黑树的插入也需要针对不同情况作处理 => 插入一个新节点后不能破坏红黑树的性质
如果是空树插⼊,新增结点是⿊⾊结点;如果是⾮空树插⼊,新增结点必须红⾊结点,因为⾮空树插⼊,新增⿊⾊结点就破坏了规则4,规则4是很难维护的。
⾮空树插⼊后,新增结点必须红⾊结点,如果⽗亲结点是⿊⾊的,则没有违反任何规则,插⼊结束
⾮空树插⼊后,新增结点必须红⾊结点,如果⽗亲结点是红⾊的,则违反规则3 => 此时需要根据不同情况作处理
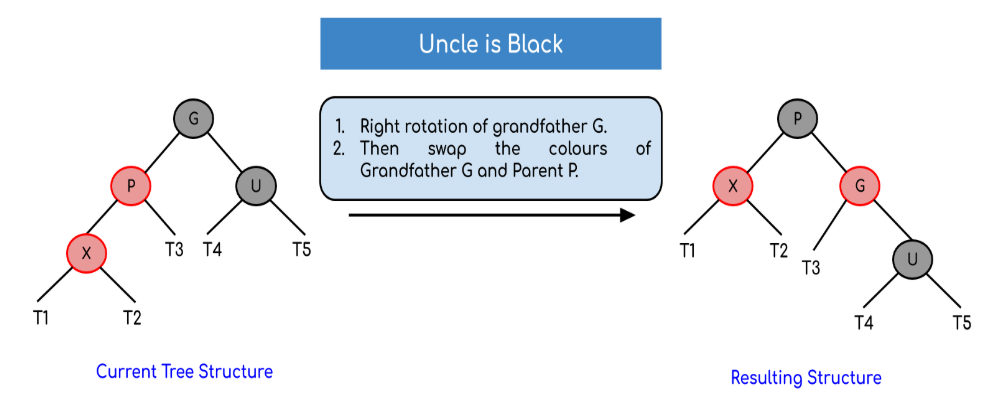
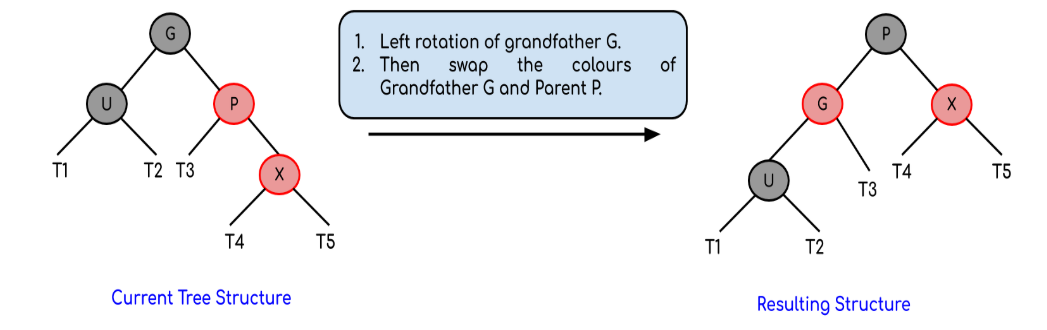
(1) 变色、不旋转 => 连续红节点且叔叔节点为红节点
旋转的特点为叔叔节点是黑节点
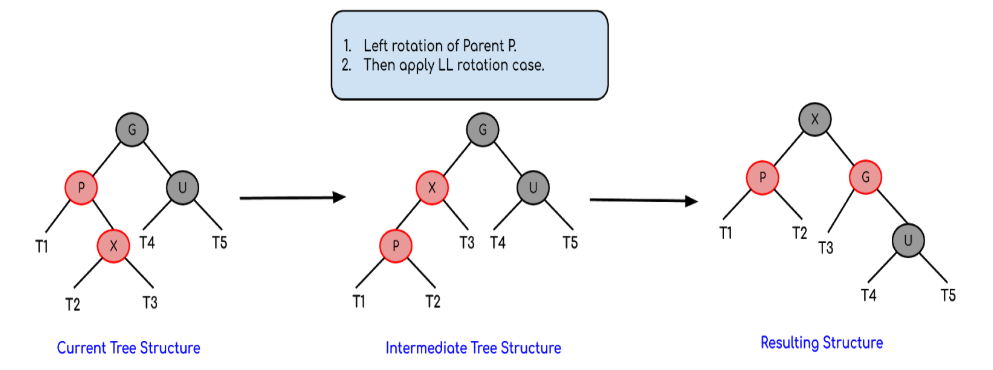
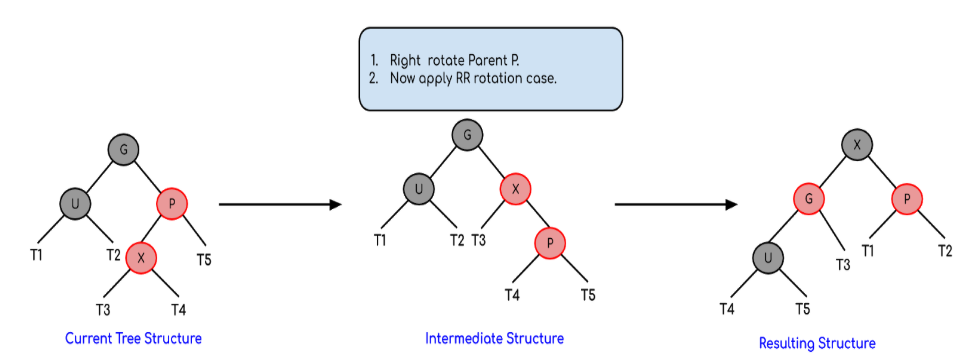
(2) 变色、单旋
//右旋逻辑 => 和AVL树是一样的,只是不用调整平衡因子 void RotateR(Node *parent) { /* 右旋的目标: 1. 将parent的左子节点subL提升为新的根节点 2. 将subL的右子节点subLR接到parent的左子节点位置 3. 将parent接到subL的右子节点位置 4. 更新所有相关的父节点指针,维护树的完整性 */ Node *subL = parent->_left; // 获取左子节点(将成为新的根节点) Node *subLR = subL->_right; // 获取左子节点的右子节点(需要重新接) // 步骤1:将subLR接到parent的左子节点位置 parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) { subLR->_parent = parent; // 更新subLR的父节点指针 } // 步骤2:将parent接到subL的右子节点位置 subL->_right = parent; // 步骤3:更新祖父节点的指向关系 Node *parentParent = parent->_parent; // 获取祖父节点 parent->_parent = subL; // 更新parent的父节点指针 if (parentParent == nullptr) { // 情况A:parent是根节点,subL成为新的根节点 _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; // 根节点没有父节点 } else { // 情况B:parent不是根节点,需要更新祖父节点的指向 if (parent == parentParent->_left) { parentParent->_left = subL; // parent原本是左子节点,subL也成为左子节点 } else { parentParent->_right = subL; // parent原本是右子节点,subL也成为右子节点 } subL->_parent = parentParent; // 更新subL的父节点指针 } }// 左旋逻辑 void RotateL(Node *parent) { /* 左旋的目标: 1. 将parent的右子节点subR提升为新的根节点 2. 将subR的左子节点subRL接到parent的右子节点位置 3. 将parent接到subR的左子节点位置 4. 更新所有相关的父节点指针,维护树的完整性 */ Node *subR = parent->_right; // 获取右子节点(将成为新的根节点) Node *subRL = subR->_left; // 获取右子节点的左子节点(需要重新接) // 步骤1:将subRL接到parent的右子节点位置 parent->_right = subRL; if (subRL) { subRL->_parent = parent; // 更新subRL的父节点指针 } // 步骤2:将parent接到subR的左子节点位置 subR->_left = parent; // 步骤3:更新祖父节点的指向关系 Node *parentParent = parent->_parent; // 获取祖父节点 parent->_parent = subR; // 更新parent的父节点指针 if (parentParent == nullptr) { // 情况A:parent是根节点,subR成为新的根节点 _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; // 根节点没有父节点 } else { // 情况B:parent不是根节点,需要更新祖父节点的指向 if (parent == parentParent->_right) { parentParent->_right = subR; // parent原本是右子节点,旋转后subR成为新的右子节点 } else { parentParent->_left = subR; // parent原本是左子节点,旋转后subR成为新的左子节点 } subR->_parent = parentParent; // 更新subR的父节点指针 } }(3) 双旋、变色
bool insert(const pair<K, V> &kv) { // 1. 如果根节点为空,直接插入为根节点,并设为黑色 if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(kv); _root->_color = BLACK; return true; } // 2. 根节点不为空,寻找插入位置 Node *parent = nullptr; Node *cur = _root; while (cur) { // 如果当前节点的key小于插入key,往右子树找 if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first) { // 如果当前节点的key大于插入key,往左子树找 parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { // 如果已经存在相同key,不插入 return false; } } // 2.2 插入新节点到找到的位置 cur = new Node(kv); if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } cur->_parent = parent; // 2.3 插入后进行红黑树性质调整 while (parent && parent->_color == RED) { Node *grandfather = parent->_parent; // 祖父节点 // 情况1:父节点是祖父的左孩子 if (grandfather->_left == parent) { Node *uncle = grandfather->_right; // 叔叔节点 // 1.1 叔叔存在且为红色,进行颜色翻转 if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) { parent->_color = BLACK; uncle->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; // 继续向上调整 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } // 1.2 叔叔不存在或为黑色,需要旋转 else { // 当前节点是父节点的左孩子,右旋祖父 if (cur == parent->_left) { RotateR(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } else { // 当前节点是父节点的右孩子,先左旋父节点再右旋祖父 RotateL(parent); RotateR(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } break; // 调整完毕,跳出循环 } // 情况2:叔叔不存在或为黑 } else { Node *uncle = grandfather->_left; // 叔叔节点 // 2.1 叔叔存在且为红 if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) { parent->_color = BLACK; uncle->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; // 继续向上调整 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } // 2.2 叔叔不存在或为黑 else { // 当前节点是父节点的右孩子,左旋祖父 if (cur == parent->_right) { RotateL(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } else { // 当前节点是父节点的左孩子,先右旋父节点再左旋祖父 RotateR(parent); RotateL(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } break; // 调整完毕,跳出循环 } } } // 最后确保根节点为黑色 _root->_color = BLACK; return true; }
2.3 查找
Node *find(const K &key) { Node *cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return cur; } } return nullptr; }
2.4 判断红黑树是否平衡
// 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质 // root: 当前检查的节点 // blackNum: 当前路径经过的黑色节点数 // refNum: 标准黑色节点数(根到最左叶子的黑色节点数) // 返回true表示满足红黑树性质 bool Check(Node *root, int blackNum, const int refNum) { if (root == nullptr) { // 遍历到空节点,检查黑色节点数是否一致 if (refNum != blackNum) { cout << "存在黑色结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl; return false; } return true; } // 检查是否有连续红色节点 if (root->_color == RED && root->_parent->_color == RED) { cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色结点" << endl; return false; } if (root->_color == BLACK) { blackNum++; } return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum); } // 判断红黑树是否平衡(即是否满足红黑树所有性质) bool IsBalance() { if (_root == nullptr) { return true; } if (_root->_color == RED) { cout << "根节点是红色" << endl; return false; } int refNum = 0; Node *left = _root; // 统计根到最左叶子的黑色节点数 while (left) { if (left->_color == BLACK) { refNum++; } left = left->_left; } return Check(_root, 0, refNum); }
3. AVL树 vs. 红黑树
与红黑树相比,AVL 树更加平衡,但在插入和删除操作中可能需要更多旋转。因此,如果应用程序涉及频繁的插入和删除操作,则应优先选择红黑树。如果插入和删除操作较少,而搜索操作较为频繁,则应优先选择AVL 树而非红黑树。
此外,AVL树性质被破坏时一定会旋转,而红黑树不一定 ( 可能只是变色 )
4. set 和 map 的实现
set 和 map 的实现底层是用红黑树实现的,因此在这里也模拟实现
再模拟实现 set 和 map 前要先修改一下我们前面写的红黑树
enum Color { RED, BLACK }; // 红黑树节点结构体模板 // T:节点存储的数据类型(如 pair<K, V> 或自定义 struct) // 设计原因:模板化节点类型,支持多种数据结构 template <class T> struct RBTNode { // 构造函数,初始化数据并默认颜色为红色 RBTNode(const T &data) : _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _color(RED) {} RBTNode<T> *_left; RBTNode<T> *_right; RBTNode<T> *_parent; T _data; // 节点存储的数据类型 Color _color; }; // 红黑树迭代器模板 // T:节点数据类型,Ref/Ptr:引用和指针类型 template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct RBTreeIterator { typedef RBTNode<T> Node; typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; Node *_node; // 当前迭代器指向的节点 Node *_root; // 整棵树的根节点(用于--到end时定位最大节点) RBTreeIterator(Node *node, Node *root) : _node(node), _root(root) {} Ref operator*() { return _node->_data; } // 解引用,返回节点数据 Ptr operator->() { return &_node->_data; } // 指针访问 // 前置++,移动到下一个节点(中序遍历) Self &operator++() { if (_node->_right) { Node *leftmost = _node->_right; while (leftmost->_left) leftmost = leftmost->_left; _node = leftmost; } else { Node *cur = _node, *parent = cur->_parent; while (parent && cur == parent->_right) { cur = parent; parent = parent->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this; } // 前置--,移动到上一个节点(中序遍历) Self &operator--() { if (_node == nullptr) { // 如果为空 => 找最右边的节点 Node *rightmost = _root; while (rightmost->_right) rightmost = rightmost->_right; _node = rightmost; // 如果左子树存在 => 找左子树的最右的节点 } else if (_node->_left) { Node *rightmost = _node->_left; while (rightmost->_right) rightmost = rightmost->_right; _node = rightmost; } else { Node *cur = _node, *parent = cur->_parent; while (parent && cur == parent->_left) { cur = parent; parent = parent->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this; } bool operator!=(const Self &s) const { return _node != s._node; } bool operator==(const Self &s) const { return _node == s._node; } }; // 红黑树主类模板 // K:键类型,T:节点数据类型,KeyOfT:仿函数,从T中提取K // 设计原因:支持泛型键值类型,KeyOfT适配不同数据结构 template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBT { typedef RBTNode<T> Node; public: typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T &, T *> Iterator; typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T &, const T *> ConstIterator; RBT() = default; // 返回最左节点的迭代器(begin) Iterator begin() { Node *leftmost = _root; while (leftmost && leftmost->_left) leftmost = leftmost->_left; return Iterator(leftmost, _root); } // 返回end迭代器(空节点) Iterator end() { return Iterator(nullptr, _root); } ConstIterator begin() const { Node *leftmost = _root; while (leftmost && leftmost->_left) leftmost = leftmost->_left; return ConstIterator(leftmost, _root); } ConstIterator end() const { return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root); } // 析构函数,递归释放所有节点 ~RBT() { Destroy(_root); _root = nullptr; } // 插入数据,返回插入位置和是否插入成功 // 设计思路:先查找插入位置,若已存在则返回已存在节点,否则插入并调整红黑树 pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const T &data) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(data); _root->_color = BLACK; return make_pair(Iterator(_root, _root), true); } KeyOfT kot; Node *parent = nullptr, *cur = _root; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { // 已存在 return make_pair(Iterator(cur, _root), false); } } cur = new Node(data); if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)) parent->_right = cur; else parent->_left = cur; cur->_parent = parent; // 插入后调整红黑树性质 while (parent && parent->_color == RED) { Node *grandfather = parent->_parent; if (grandfather->_left == parent) { Node *uncle = grandfather->_right; if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) { parent->_color = BLACK; uncle->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { RotateR(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } else { RotateL(parent); RotateR(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } break; } } else { Node *uncle = grandfather->_left; if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) { parent->_color = BLACK; uncle->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else { if (cur == parent->_right) { RotateL(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } else { RotateR(parent); RotateL(grandfather); parent->_color = BLACK; grandfather->_color = RED; } break; } } } _root->_color = BLACK; return make_pair(Iterator(cur, _root), true); } // 查找数据,返回迭代器 Iterator find(const T &data) { KeyOfT kot; Node *cur = _root; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) cur = cur->_right; else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)) cur = cur->_left; else return Iterator(cur, _root); } return end(); } // 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质 bool Check(Node *root, int blackNum, const int refNum) { if (root == nullptr) { if (refNum != blackNum) { cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl; return false; } return true; } if (root->_color == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_color == RED) { cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl; return false; } if (root->_color == BLACK) blackNum++; return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum); } // 判断红黑树是否平衡 bool IsBalance() { if (_root == nullptr) return true; if (_root->_color == RED) { cout << "根节点是红色" << endl; return false; } int refNum = 0; Node *left = _root; while (left) { if (left->_color == BLACK) refNum++; left = left->_left; } return Check(_root, 0, refNum); } private: // 递归销毁所有节点 void Destroy(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return; Destroy(root->_left); Destroy(root->_right); delete root; } Node *_root = nullptr; // 红黑树根节点 // 右旋操作,维护红黑树平衡 void RotateR(Node *parent) { Node *subL = parent->_left; Node *subLR = subL->_right; parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; subL->_right = parent; Node *parentParent = parent->_parent; parent->_parent = subL; if (parentParent == nullptr) { _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parent == parentParent->_left) parentParent->_left = subL; else parentParent->_right = subL; subL->_parent = parentParent; } } // 左旋操作,维护红黑树平衡 void RotateL(Node *parent) { Node *subR = parent->_right; Node *subRL = subR->_left; parent->_right = subRL; if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent; subR->_left = parent; Node *parentParent = parent->_parent; parent->_parent = subR; if (parentParent == nullptr) { _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parent == parentParent->_right) parentParent->_right = subR; else parentParent->_left = subR; subR->_parent = parentParent; } } };
// myset.h // 要include 红黑树的代码,再复用 template <class K> class set { // 仿函数,直接返回key本身 // 设计原因:set的元素就是key,不需要从pair中提取d struct SetKeyOfT { const K &operator()(const K &key) { return key; } }; public: // 迭代器类型定义,直接复用RBT的迭代器 typedef typename RBT<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator; typedef typename RBT<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator; // begin/end接口,支持范围for遍历 iterator begin() { return _t.begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.end(); } const_iterator begin() const { return _t.begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return _t.end(); } // 插入元素,返回插入结果 pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K &key) { return _t.insert(key); } // 查找元素,返回迭代器 iterator find(const K &key) { return _t.find(key); } private: RBT<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t; // 底层用红黑树实现 };// mymap.h // map模板类,K为key类型,V为value类型 template <class K, class V> class map { // 仿函数,从pair<K, V>中提取key struct MapKeyOfT { const K &operator()(const pair<K, V> &kv) { return kv.first; } }; public: // 迭代器类型定义,复用RBT的迭代器 typedef typename RBT<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator; typedef typename RBT<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator; iterator begin() { return _t.begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.end(); } const_iterator begin() const { return _t.begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return _t.end(); } // 下标操作符,若key不存在则插入默认值 V &operator[](const K &key) { pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V())); return ret.first->second; } // 插入键值对 pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V> &kv) { return _t.insert(kv); } // 查找key,返回迭代器 iterator find(const K &key) { return _t.find(key); } private: RBT<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t; // 底层用红黑树实现 };