生成式任务
输出Y没有预设的范围,受输入X影响
在人工智能的各个领域都有,包括很多跨领域任务
图像领域:图像/视频生成, 图像补全等
语音领域:语音合成等
文本领域:机器翻译等

seq2seq任务
输入输出均为不定长的序列
如:
机器翻译
机器作诗
自动摘要等
自回归语言模型训练
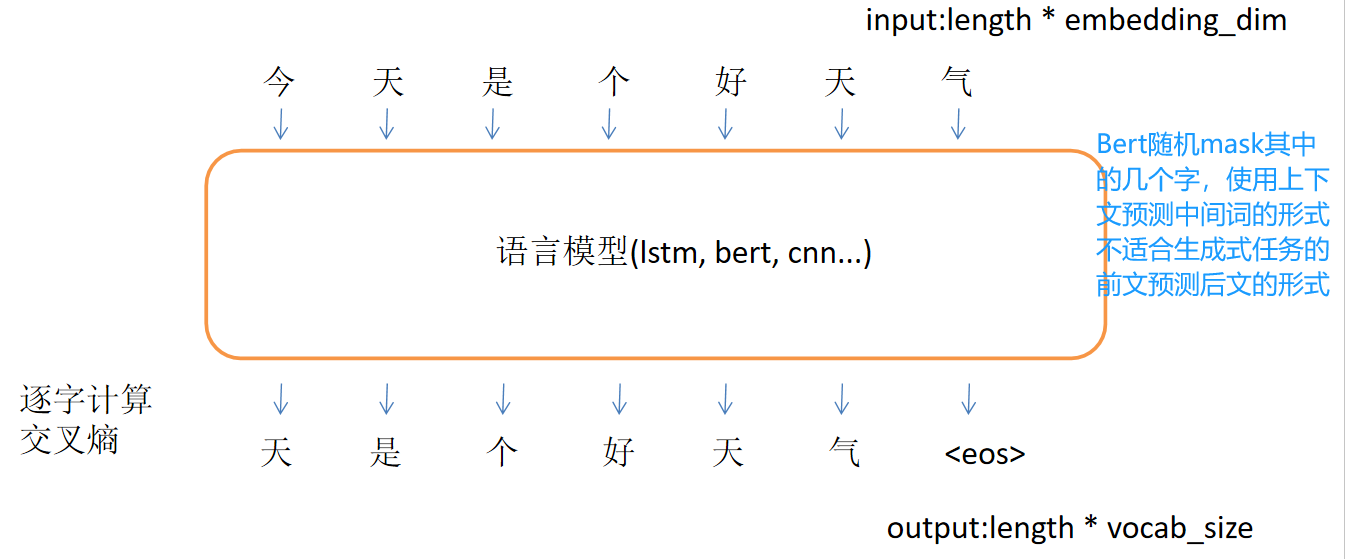
- 文本生成
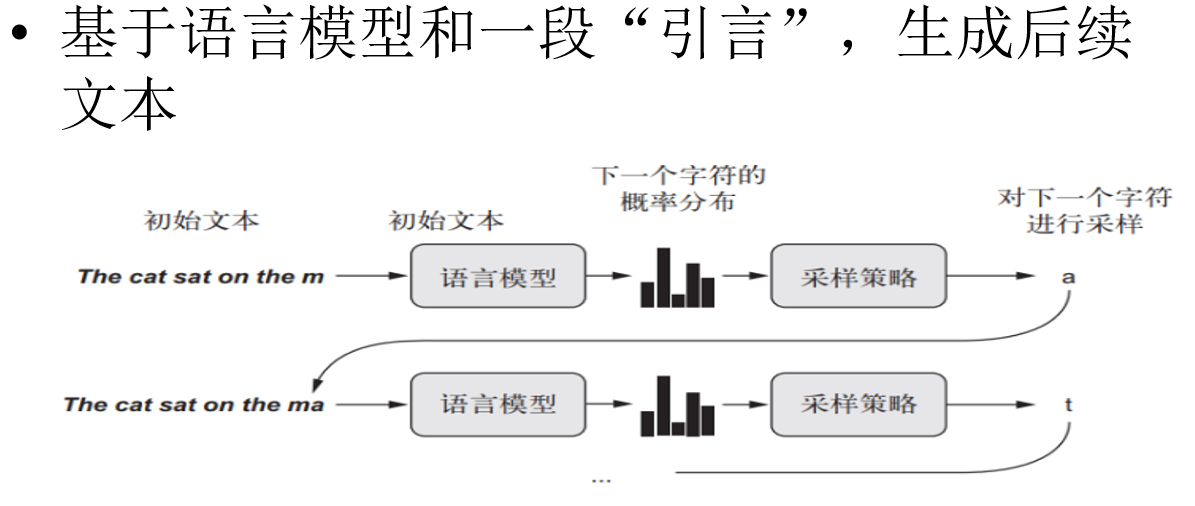
<lstm语言模型生成文本, nnlm.py>
#coding:utf8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import math
import random
import os
"""
基于pytorch的LSTM语言模型
"""
class LanguageModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, vocab):
super(LanguageModel, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(len(vocab), input_dim)
self.layer = nn.LSTM(input_dim, input_dim, num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
self.classify = nn.Linear(input_dim, len(vocab))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.loss = nn.functional.cross_entropy
#当输入真实标签,返回loss值;无真实标签,返回预测值
def forward(self, x, y=None):
x = self.embedding(x) #output shape:(batch_size, sen_len, input_dim)
x, _ = self.layer(x) #output shape:(batch_size, sen_len, input_dim)
y_pred = self.classify(x) #output shape:(batch_size, sen_len, vocab_size)
if y is not None:
return self.loss(y_pred.view(-1, y_pred.shape[-1]), y.view(-1))
else:
return torch.softmax(y_pred, dim=-1)
#加载字表
def build_vocab(vocab_path):
vocab = {"<pad>":0}
with open(vocab_path, encoding="utf8") as f:
for index, line in enumerate(f):
char = line[:-1] #去掉结尾换行符
vocab[char] = index + 1 #留出0位给pad token
return vocab
#加载语料
def load_corpus(path):
corpus = ""
with open(path, encoding="gbk") as f:
for line in f:
corpus += line.strip()
return corpus
#随机生成一个样本
#从文本中截取随机窗口,前n个字作为输入,最后一个字作为输出
def build_sample(vocab, window_size, corpus):
start = random.randint(0, len(corpus) - 1 - window_size)
end = start + window_size
window = corpus[start:end]
target = corpus[start + 1:end + 1] #输入输出错开一位
# print(window, target)
x = [vocab.get(word, vocab["<UNK>"]) for word in window] #将字转换成序号
y = [vocab.get(word, vocab["<UNK>"]) for word in target]
return x, y
#建立数据集
#sample_length 输入需要的样本数量。需要多少生成多少
#vocab 词表
#window_size 样本长度
#corpus 语料字符串
def build_dataset(batch_size, vocab, window_size, corpus):
dataset_x = []
dataset_y = []
for i in range(batch_size):
x, y = build_sample(vocab, window_size, corpus)
dataset_x.append(x)
dataset_y.append(y)
return torch.LongTensor(dataset_x), torch.LongTensor(dataset_y)
#建立模型
def build_model(vocab, char_dim):
model = LanguageModel(char_dim, vocab)
return model
#文本生成测试代码
def generate_sentence(openings, model, vocab, window_size):
reverse_vocab = dict((y, x) for x, y in vocab.items())
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
pred_char = ""
#生成了换行符,或生成文本超过30字则终止迭代
while pred_char != "\n" and len(openings) <= 30:
openings += pred_char
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in openings[-window_size:]]
x = torch.LongTensor([x])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x = x.cuda()
y = model(x)[0][-1]
index = sampling_strategy(y)
pred_char = reverse_vocab[index]
return openings
def sampling_strategy(prob_distribution):
if random.random() > 0.1:
strategy = "greedy"
else:
strategy = "sampling"
if strategy == "greedy":# 取概率最大的字
return int(torch.argmax(prob_distribution))
elif strategy == "sampling":# 按每个字各自的概率,进行采样出1个字
prob_distribution = prob_distribution.cpu().numpy()
return np.random.choice(list(range(len(prob_distribution))), p=prob_distribution)
#计算文本ppl
def calc_perplexity(sentence, model, vocab, window_size):
prob = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for i in range(1, len(sentence)):
start = max(0, i - window_size)
window = sentence[start:i]
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in window]
x = torch.LongTensor([x])
target = sentence[i]
target_index = vocab.get(target, vocab["<UNK>"])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x = x.cuda()
pred_prob_distribute = model(x)[0][-1]
target_prob = pred_prob_distribute[target_index]
prob += math.log(target_prob, 10)
return 2 ** (prob * ( -1 / len(sentence)))
def train(corpus_path, save_weight=True):
epoch_num = 20 #训练轮数
batch_size = 64 #每次训练样本个数
train_sample = 50000 #每轮训练总共训练的样本总数
char_dim = 256 #每个字的维度
window_size = 10 #样本文本长度
vocab = build_vocab("vocab.txt") #建立字表
corpus = load_corpus(corpus_path) #加载语料
model = build_model(vocab, char_dim) #建立模型
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
optim = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01) #建立优化器
print("文本词表模型加载完毕,开始训练")
for epoch in range(epoch_num):
model.train()
watch_loss = []
for batch in range(int(train_sample / batch_size)):
x, y = build_dataset(batch_size, vocab, window_size, corpus) #构建一组训练样本
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.cuda(), y.cuda()
optim.zero_grad() #梯度归零
loss = model(x, y) #计算loss
loss.backward() #计算梯度
optim.step() #更新权重
watch_loss.append(loss.item())
print("=========\n第%d轮平均loss:%f" % (epoch + 1, np.mean(watch_loss)))
print(generate_sentence("让他在半年之前,就不能做出", model, vocab, window_size))
print(generate_sentence("李慕站在山路上,深深的呼吸", model, vocab, window_size))
if not save_weight:
return
else:
base_name = os.path.basename(corpus_path).replace("txt", "pth")
model_path = os.path.join("model", base_name)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
# build_vocab_from_corpus("corpus/all.txt")
train("corpus.txt", False)
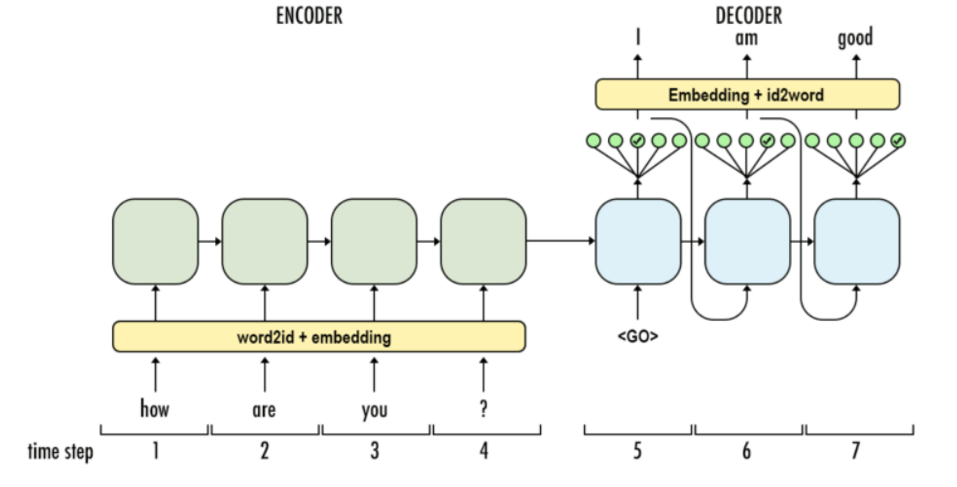
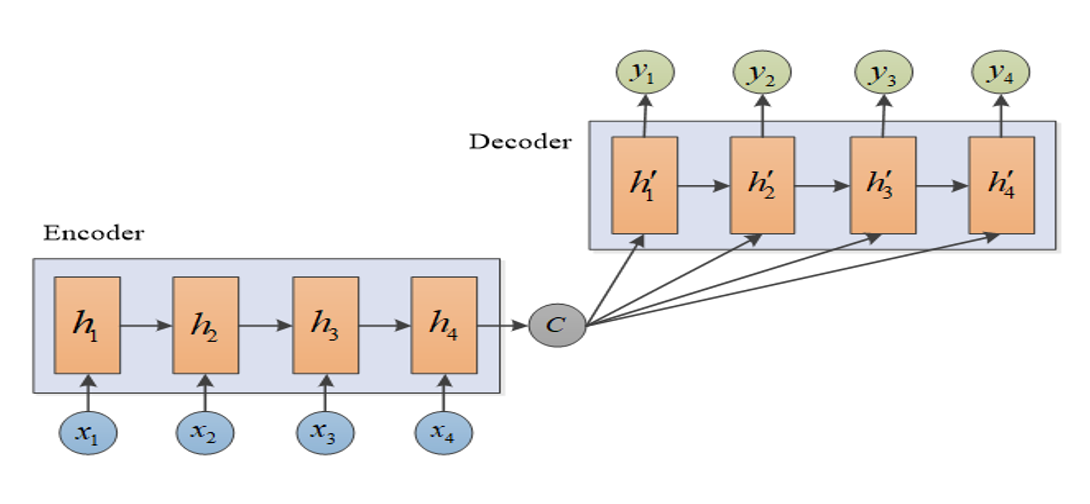
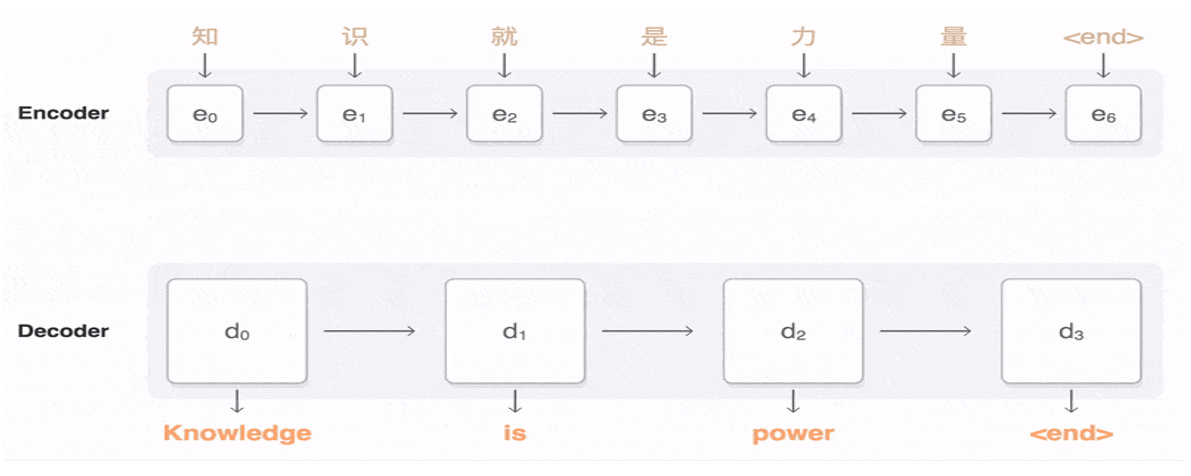
Encoder-Decoder结构
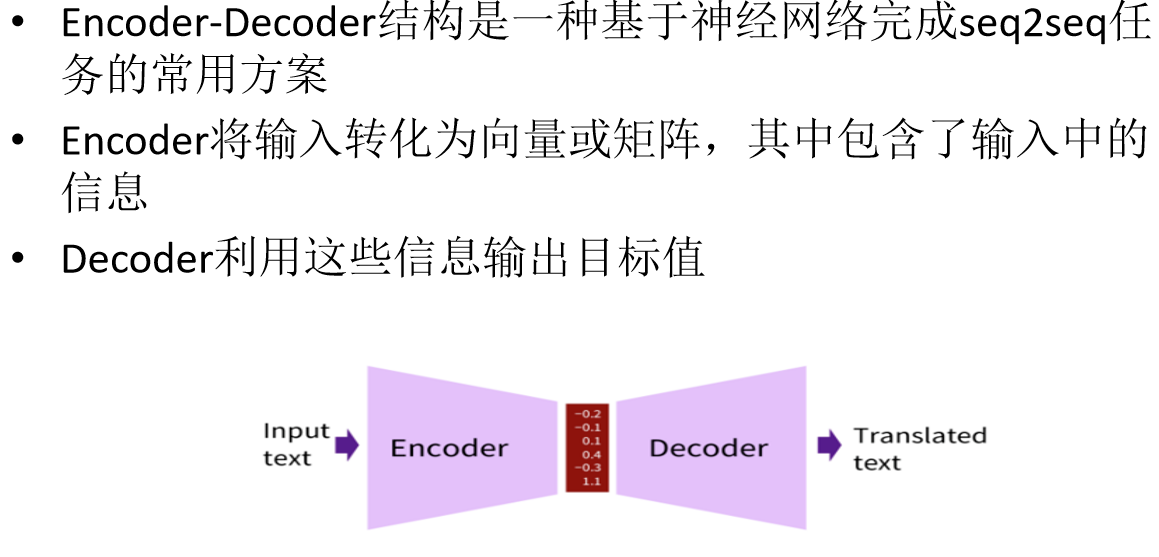
Bert是encoder-only结构,自回归语言模型是decoder-only结构。
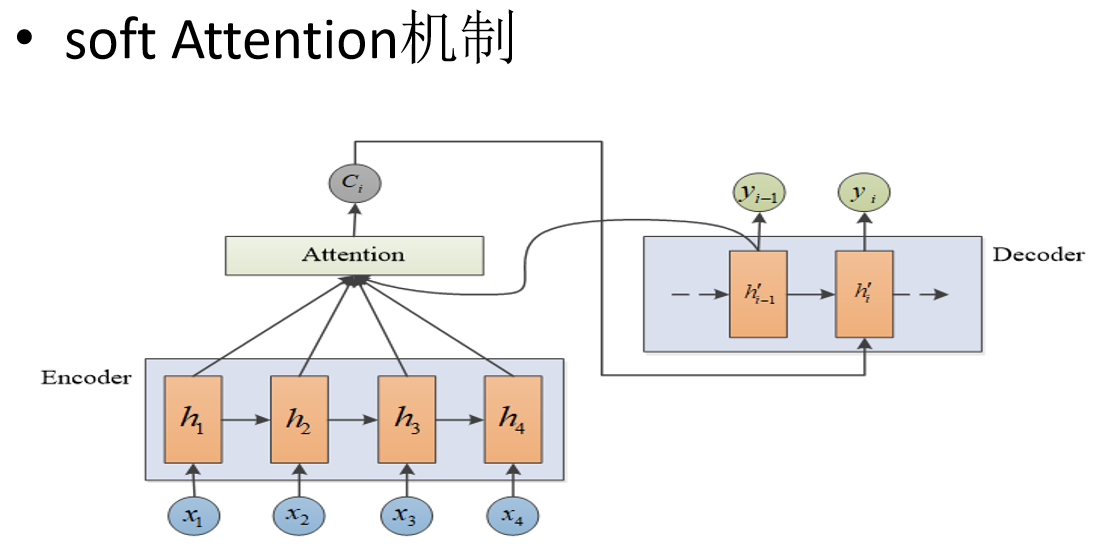
Attention机制
- soft-attention机制(专为机器翻译打造)

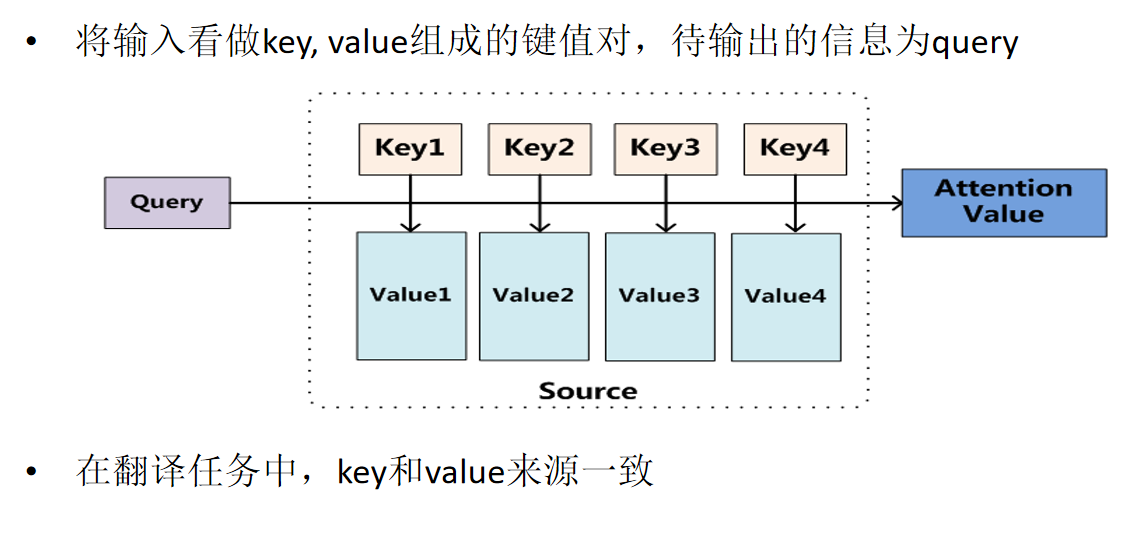
- 判断情感倾向

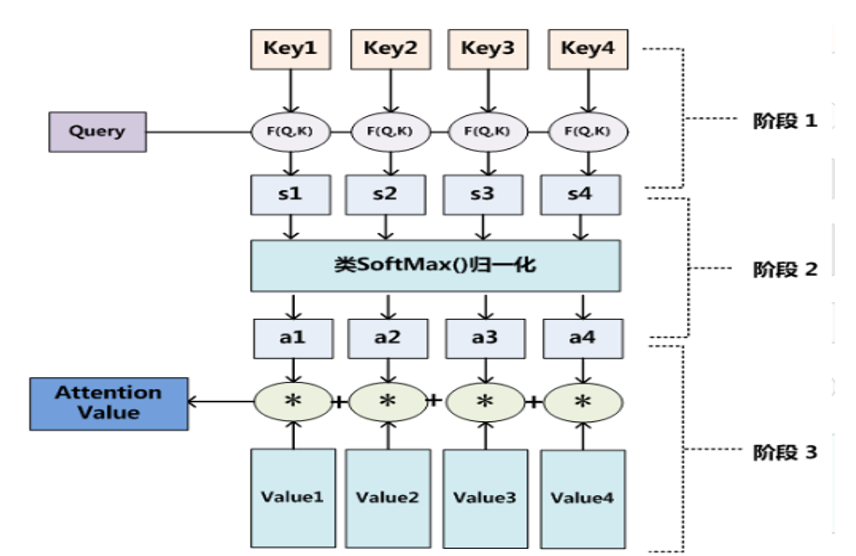
Attention思想
soft-attention
hard-attention
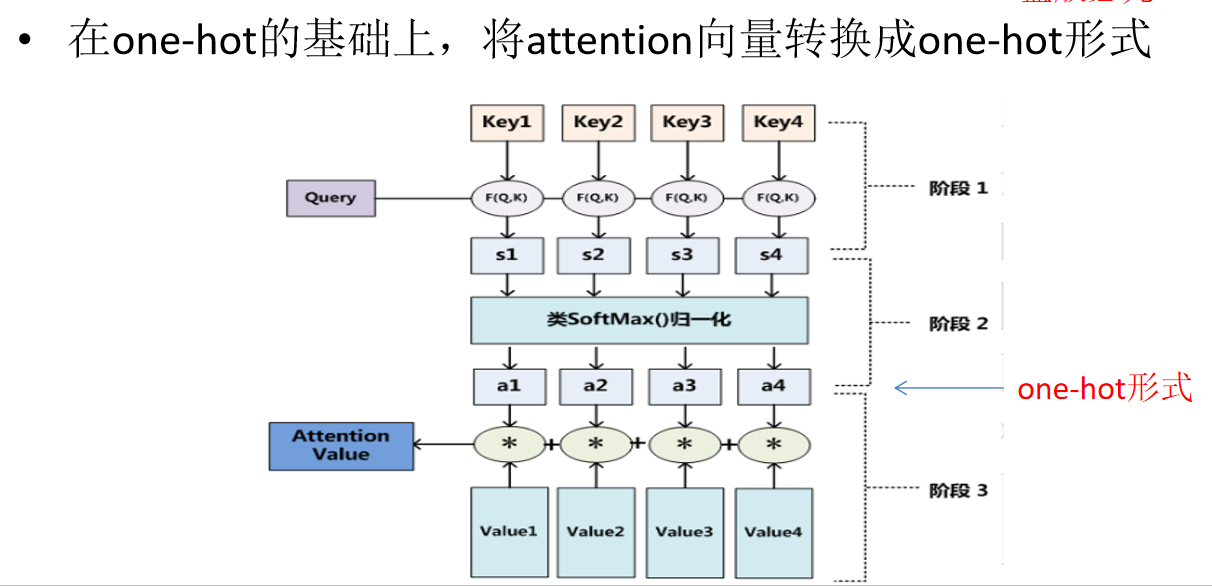
local-attention
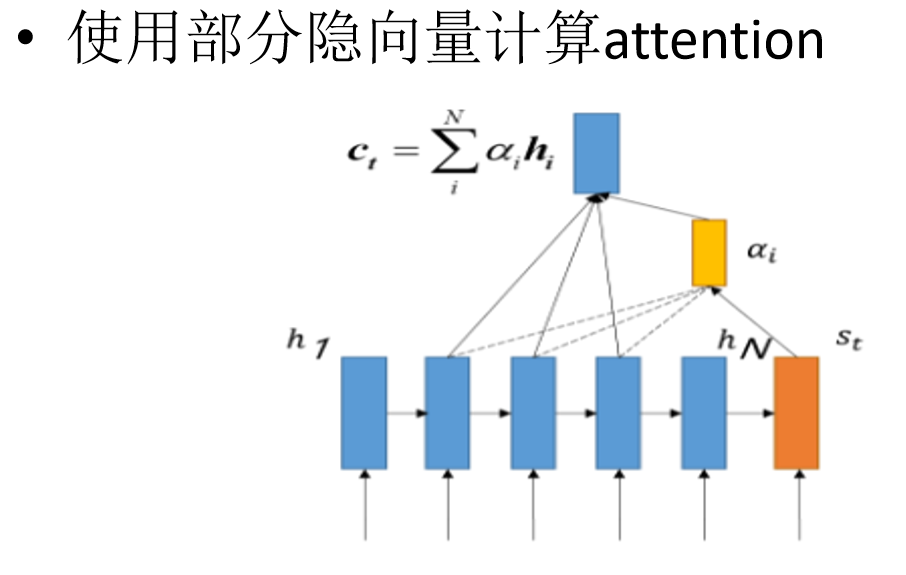
Teacher-Forcing

现在完全使用teacher-forcing的方法,放弃在训练时做解码来换取更高的训练速度。自回归语言模型也是teacher-forcing方式。
self-attention
来源于soft-attention的修改