在点云目标检测中,经常会有一系列的误识别,为了减小误识别的概率,可以通过区域过滤来删除不需要的点云,如下图所示
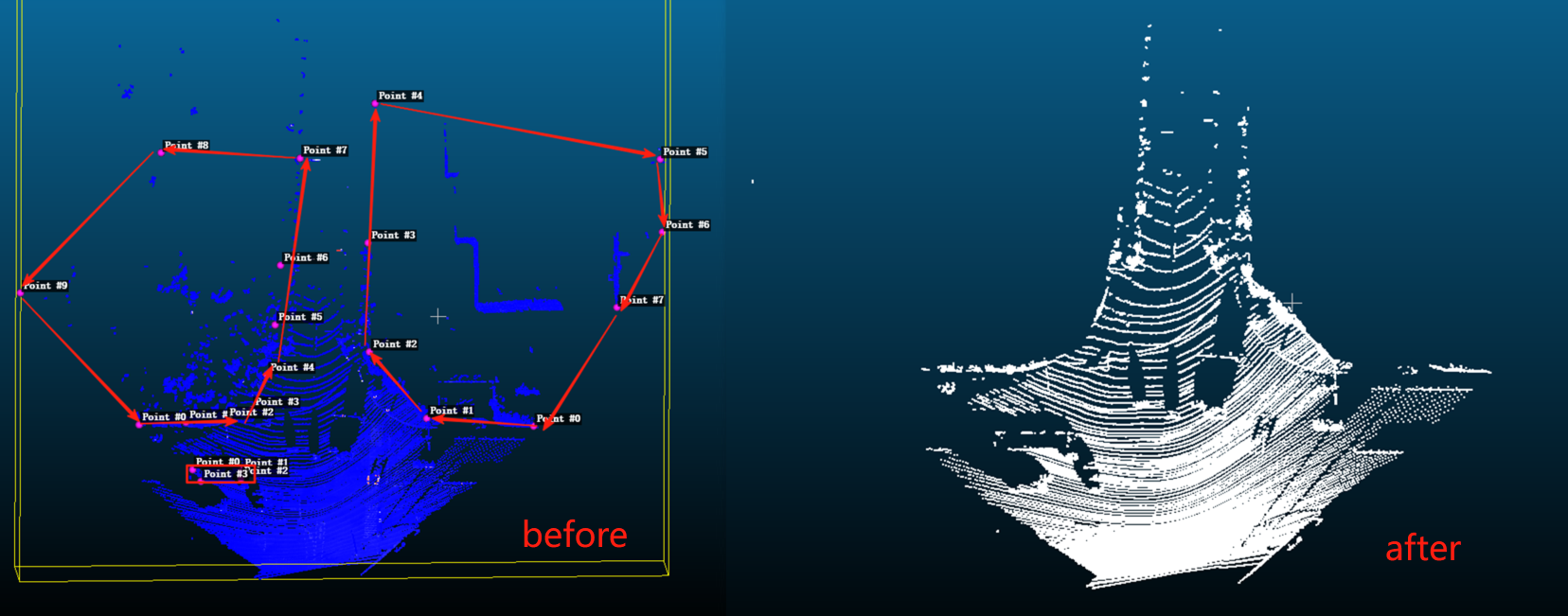
本例中点云的场景为路口交通场景,已经把雷达坐标系的xoy面转换至点云中的地平面,具体原理和操作参考:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_64293675/article/details/145208953?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
这样可以将区域的划分从3维变成2维,只需要给出多边形区域的X和Y坐标,z轴无限延伸即可。
区域过滤的第一种方法是使用PCL库的CropHull滤波器,也就是常说的凸包算法,第二种方法是射线法,即从点出发画一条射线(例如水平向右),统计该射线与多边形边的交点个数。如果交点个数为奇数,点在多边形内;偶数,则在多边形外。
C++实现点云的多边形区域过滤的2种方法
1、使用PCL库的CropHull滤波器
需要安装pcl库,apt安装即可,建议安装版本大于等于1.8,ubuntu20.04用ap安装的pcl默认版本是1.10.0,符合要求。如果想从源码安装,自行baidu。
sudo apt install libpcl-dev
- cut_roi.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/crop_hull.h>
#include <pcl/surface/convex_hull.h>
using namespace std;
// 不需要intensity的可以用typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointXYZI PointT;
// 删除一个多边形区域内的点
// cloud 输入点云
// polygon 多边形区域的顶点坐标
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr removePointsInPolygon(
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud,
const vector<pair<float, float>> &polygon)
{
// 创建多边形点云
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr hullPoints(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
for (const auto &vertex : polygon)
{
// 根据PointT 的内容对应赋值
PointT p;
p.x = vertex.first;
p.y = vertex.second;
p.z = 0.0f;
p.intensity = 0.0f;
hullPoints->push_back(p);
}
// 添加第一个点使多边形闭合
hullPoints->push_back(hullPoints->points[0]);
// 创建凸包对象
pcl::ConvexHull<PointT> hull;
hull.setInputCloud(hullPoints);
hull.setDimension(2); // 2D多边形
// 存储凸包结果的容器
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr hullCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
vector<pcl::Vertices> hullPolygons;
hull.reconstruct(*hullCloud, hullPolygons);
// 创建裁剪对象
pcl::CropHull<PointT> cropFilter;
cropFilter.setHullCloud(hullCloud);
cropFilter.setHullIndices(hullPolygons);
cropFilter.setDim(2); // 2D操作
// 执行裁剪(保留多边形外的点)
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr filteredCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
cropFilter.setInputCloud(cloud);
cropFilter.setCropOutside(false); // 保留多边形外部的点,删除内部的点
cropFilter.filter(*filteredCloud);
return filteredCloud;
}
// 删除多个多边形区域内的点
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr removePointsInPolygons(
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud,
const vector<vector<pair<float, float>>> &polygons)
{
for (const auto &polygon : polygons)
{
cloud = removePointsInPolygon(cloud, polygon);
}
return cloud;
}
int main()
{
using clock = chrono::high_resolution_clock;
using ms = chrono::milliseconds;
using ns = chrono::nanoseconds;
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
//while (1)
{
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("../test.pcd", *cloud);
//示例多区域的顶点(x,y) 顺时针逆时针都可可以
vector<vector<pair<float, float>>> polygons = {
{
{79.5060272217, 79.175064086},
{79.2747802734, 58.571964263},
{81.6638717651, 41.394405365},
{86.0577163696, 30.583795547},
{101.274185181, 24.103635788},
{122.022064209, 20.140935897},
{149.628707886, 18.349731445},
{195.621643066, 9.6359605789},
{198.321121216, 69.765792846},
{138.335754395, 130.86445617}
},
{
{77.3776473999, -91.604118347},
{80.9268569946, -45.400650024},
{109.261535645, -20.841529846},
{158.885635376, -19.598711013},
{219.02204895, -22.8725452423},
{188.727401733, -147.86555481},
{159.747970581, -147.89741516},
{126.374259949, -128.46434021}
},
{
{59.590133667, 55.9770889282},
{59.0997047424, 34.932685852},
{54.9787826538, 34.951171875},
{54.4650382996, 52.371749877}
}
};
auto start1 = clock::now();
// 删除多边形区域内的点
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr filteredCloud = removePointsInPolygons(cloud, polygons);
auto end1 = clock::now();
ns duration1 = chrono::duration_cast<ns>(end1 - start1);
cout << "CPU上 使用pcl库的CropHull滤波器删除多个多边形区域内的点 耗时: " << duration1.count() / 1000000.0 << " 毫秒" << endl;
// 保存结果
// pcl::io::savePCDFile("../filtered.pcd", *filteredCloud);
cout << "num_input: " << cloud->size() << endl;
cout << "num_output: " << filteredCloud->size() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(lidar_process)
add_definitions(-std=c++11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
# set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
cmake_policy(SET CMP0074 NEW)
find_package(PCL)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
include_directories("include/")
add_executable(lidar_process src/cut_roi.cpp)
target_link_libraries(lidar_process ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
- 编译运行
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
./lidar_process
2、射线法的CUDA实现
需要安装合适版本的CUDA,可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_64293675/article/details/141166292?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
- cut_roi_kernel.cuh
#ifndef CUT_LIDAR_ROI_CUH
#define CUT_LIDAR_ROI_CUH
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
// 点云数据结构
struct Point_cuda
{
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
// 多边形信息结构体
struct PolygonInfo {
int start_idx; // 在顶点数组中的起始索引
int num_vertices; // 多边形的顶点数
int is_negative; // 0=将该区域删除, 1=将该区域保留
};
// CUDA核函数:判断点是否在单个多边形内,若返回true 表示点在多边形内
__device__ bool isPointInSinglePolygon(
float px, float py,
const float2* polygon,
int num_vertices);
// CUDA核函数:标记点是否在任何一个多边形内
__global__ void markPointsInPolygonsKernel(
const float3* points,
const float2* all_vertices,
const PolygonInfo* polygons_info,
int num_points,
int num_polygons,
int* flags);
// CUDA核函数:压缩点云(保留flags[idx]标记为0的点,不保留flags[idx]标记为1的点)
__global__ void compactPointsKernel(
const float3* points,
const int* flags,
int num_points,
float3* output,
int* output_index);
// CUDA实现点云多区域裁剪
std::vector<Point_cuda> removePointsInPolygonsCUDA(
std::vector<Point_cuda> cloud,
const std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<float,float>>>& polygons,
const std::vector<int>& polygon_types);
#endif
- cut_roi_kernel.cu
#include "cut_roi_kernel.cuh"
// CUDA错误检查宏
#define CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(call) \
do { \
cudaError_t err = call; \
if (err != cudaSuccess) { \
std::cerr << "CUDA error at " << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ \
<< " - " << cudaGetErrorString(err) << std::endl; \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} \
} while(0)
// CUDA核函数:判断点是否在单个多边形内,若返回true 表示点在多边形内
__device__ bool isPointInSinglePolygon(
float px, float py,
const float2* polygon,
int num_vertices)
{
int crossings = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertices; i++) {
int next = (i + 1) % num_vertices;
float2 v1 = polygon[i];
float2 v2 = polygon[next];
// 检查射线是否穿过边
if (((v1.y <= py) && (v2.y > py)) ||
((v1.y > py) && (v2.y <= py))) {
float x = v1.x + (py - v1.y) * (v2.x - v1.x) / (v2.y - v1.y);
if (x > px) {
crossings++;
}
}
}
// 奇数交点表示在多边形内
return (crossings % 2 == 1);
}
// CUDA核函数:标记点是否在任何一个多边形内
__global__ void markPointsInPolygonsKernel(
const float3* points,
const float2* all_vertices,
const PolygonInfo* polygons_info,
int num_points,
int num_polygons,
int* flags)
{
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (idx >= num_points) return;
float px = points[idx].x;
float py = points[idx].y;
// 初始化标记为0(点不在任何多边形内)
int inside_any = 0;
// 遍历所有多边形
for (int p = 0; p < num_polygons; p++) {
PolygonInfo poly_info = polygons_info[p];
const float2* poly_vertices = &all_vertices[poly_info.start_idx];
// 检查点是否在当前多边形内
bool inside_current = isPointInSinglePolygon(px, py, poly_vertices, poly_info.num_vertices);
// 根据多边形类型更新标记
if (inside_current) {
// 点在多边形内,如果is_negative == 0,表示要将该区域内的点删除,需要将inside_any标志记为1
//如果is_negative == 1,表示要将该区域内的点保留,inside_any标志不变(仍为0)
if (poly_info.is_negative == 0) {
inside_any = 1;
break; // 点在一个区域,无需检查其他多边形
}
}
}
flags[idx] = inside_any;
}
// CUDA核函数:压缩点云(保留flags[idx]标记为0的点,不保留flags[idx]标记为1的点)
__global__ void compactPointsKernel(
const float3* points,
const int* flags,
int num_points,
float3* output,
int* output_index)
{
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (idx >= num_points) return;
// 获取输出索引
if (flags[idx] == 0) {
int pos = atomicAdd(output_index, 1);
output[pos] = points[idx];
}
}
// CUDA实现点云多区域裁剪
std::vector<Point_cuda> removePointsInPolygonsCUDA(
std::vector<Point_cuda> cloud,
const std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<float,float>>>& polygons,
const std::vector<int>& polygon_types)
{
// 1. 准备数据
int num_points = cloud.size();
int num_polygons = polygons.size();
// 2. 准备主机端数据结构
thrust::host_vector<float3> h_points(num_points);
thrust::host_vector<float2> h_all_vertices;
thrust::host_vector<PolygonInfo> h_polygons_info(num_polygons);
// 转换点云数据
for (int i = 0; i < num_points; i++) {
h_points[i] = make_float3(
cloud[i].x,
cloud[i].y,
cloud[i].z
);
}
std::cout<<"num_input:"<<num_points<<std::endl;
// 构建多边形顶点数组和索引信息
int vertex_offset = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < num_polygons; p++) {
const auto& poly = polygons[p];
int num_vertices = poly.size();
h_polygons_info[p].start_idx = vertex_offset;
h_polygons_info[p].num_vertices = num_vertices;
h_polygons_info[p].is_negative = polygon_types[p];
for (const auto& vertex : poly) {
h_all_vertices.push_back(make_float2(vertex.first, vertex.second));
}
vertex_offset += num_vertices;
}
// 3. 分配设备内存
thrust::device_vector<float3> d_points = h_points;
thrust::device_vector<float2> d_all_vertices = h_all_vertices;
thrust::device_vector<PolygonInfo> d_polygons_info = h_polygons_info;
thrust::device_vector<int> d_flags(num_points, 0);
// 4. 创建输出索引
thrust::device_vector<int> d_output_index(1, 0);
// 5. 配置核函数参数
dim3 blockSize(256);
dim3 gridSize((num_points + blockSize.x - 1) / blockSize.x);
// 6. 执行标记核函数
markPointsInPolygonsKernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_points.data()),
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_all_vertices.data()),
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_polygons_info.data()),
num_points,
num_polygons,
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_flags.data())
);
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(cudaDeviceSynchronize());
// 7. 统计需要保留的点数
thrust::host_vector<int> h_flags = d_flags;
int num_inside = thrust::count(h_flags.begin(), h_flags.end(), 1);
int num_outside = num_points - num_inside;
// 8. 分配输出内存
thrust::device_vector<float3> d_output(num_outside);
// 重置输出索引
thrust::fill(d_output_index.begin(), d_output_index.end(), 0);
// 9. 执行压缩核函数
compactPointsKernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_points.data()),
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_flags.data()),
num_points,
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_output.data()),
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_output_index.data())
);
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(cudaDeviceSynchronize());
// 10. 复制结果回主机
thrust::host_vector<float3> h_output = d_output;
std::cout<<"num_output:"<<num_outside<<std::endl;
// 11. 赋值
std::vector<Point_cuda> filteredCloud;
for (int i = 0; i < num_outside; i++) {
Point_cuda tmp;
tmp.x = h_output[i].x;
tmp.y = h_output[i].y;
tmp.z = h_output[i].z;
filteredCloud.emplace_back(tmp);
}
return filteredCloud;
}
- main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include "cut_roi_kernel.cuh"
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
using namespace std;
// 读取离线点云.bin文件, 这里避免用pcl库,以免还需安装pcl,当然也可以使用pcl的io读取.pcd格式的点云文件。
vector<Point_cuda> read_bin_files(string filename)
{
vector<Point_cuda> pc_data_;
std::ifstream file(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (!file)
{
std::cerr << "无法打开文件: " << filename << std::endl;
return pc_data_;
}
// 读取文件直到文件末尾
while (file.peek() != EOF)
{
Point_cuda point;
// 依次读取 x, y, z 坐标
file.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&point.x), sizeof(float));
file.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&point.y), sizeof(float));
file.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&point.z), sizeof(float));
pc_data_.push_back(point);
}
file.close();
return pc_data_;
}
// 保存删掉区域后的点云文件为txt,cloud compare软件也可以可视化.txt格式的点云文件
void write_all_pc_to_file(string filename, vector<Point_cuda> all_Point)
{
// 打开文件以写入数据
std::ofstream outFile(filename);
// 检查文件是否成功打开
if (outFile.is_open())
{
// 遍历 vector 并将每个元素写入文件
for (auto num : all_Point)
{
outFile << num.x << "," << num.y << "," << num.z << std::endl;
}
// 关闭文件
outFile.close();
std::cout << "数据已成功保存到" << filename << "文件。" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cerr << "无法打开文件。" << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
using clock = chrono::high_resolution_clock;
using ms = chrono::milliseconds;
using ns = chrono::nanoseconds;
// while (1)
{
vector<Point_cuda> test_data = read_bin_files("../test.bin");
//示例多区域的顶点(x,y) 顺时针逆时针都可可以
vector<vector<pair<float, float>>> polygons = {
{
{79.5060272217, 79.175064086},
{79.2747802734, 58.571964263},
{81.6638717651, 41.394405365},
{86.0577163696, 30.583795547},
{101.274185181, 24.103635788},
{122.022064209, 20.140935897},
{149.628707886, 18.349731445},
{195.621643066, 9.6359605789},
{198.321121216, 69.765792846},
{138.335754395, 130.86445617}
},
{
{77.3776473999, -91.604118347},
{80.9268569946, -45.400650024},
{109.261535645, -20.841529846},
{158.885635376, -19.598711013},
{219.02204895, -22.8725452423},
{188.727401733, -147.86555481},
{159.747970581, -147.89741516},
{126.374259949, -128.46434021}
},
{
{59.590133667, 55.9770889282},
{59.0997047424, 34.932685852},
{54.9787826538, 34.951171875},
{54.4650382996, 52.371749877}
}
};
std::vector<int> polygon_types; // 0=将该区域删除, 1=将该区域保留
for(int i = 0; i < polygons.size(); i++)
{
polygon_types.push_back(0);
}
auto start1 = clock::now();
vector<Point_cuda> filteredCloud = removePointsInPolygonsCUDA(test_data, polygons, polygon_types);
auto end1 = clock::now();
ns duration1 = chrono::duration_cast<ns>(end1 - start1);
cout << "CUDA 射线法删除多个多边形区域内的点 耗时: " << duration1.count() / 1000000.0 << " 毫秒" << endl;
write_all_pc_to_file("../filtered.txt", filteredCloud);
}
return 0;
}
- CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(lidar_process)
add_definitions(-std=c++11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
# set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
cmake_policy(SET CMP0074 NEW)
# find_package(PCL)
# include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
# add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
find_package(CUDA)
include_directories(${CUDA_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# 根据自己的cuda路径和版本修改
include_directories("/usr/local/cuda-11.8/targets/x86_64-linux/include"
"/usr/local/cuda/include"
"/usr/local/include")
link_directories("/usr/local/cuda/lib64"
"/usr/local/cuda/targets/x86_64-linux/lib"
"/usr/local/lib")
include_directories("include/")
cuda_add_executable(lidar_process
src/cut_roi_kernel.cu
src/main.cpp
)
- 编译运行
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
./lidar_process