(学习笔记)
一、入门
1、官网
Spring Security :: Spring Security
官方代码示例:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-security-samples/tree/main
2、功能
- 身份认证(authentication)
验证
谁正在访问系统资源,判断用户是否为合法用户。认证用户的常见方式是要求用户输入用户名和密码。
- 授权(authorization)
用户进行身份认证后,系统会控制
谁能访问哪些资源,这个过程叫做授权。用户无法访问没有权限的资源。
- 防御常见攻击(protection against common attacks)
- CSRF
- HTTP Headers
- HTTP Requests
3、示例
3.1、创建SpringBoot项目
JDK:17
SpringBoot:3.5.4(依赖了Spring Security 6.5.2)
Dependencies:Spring Web、Spring Security、Thymeleaf
添加示例代码(示例代码来源github,下图所示):
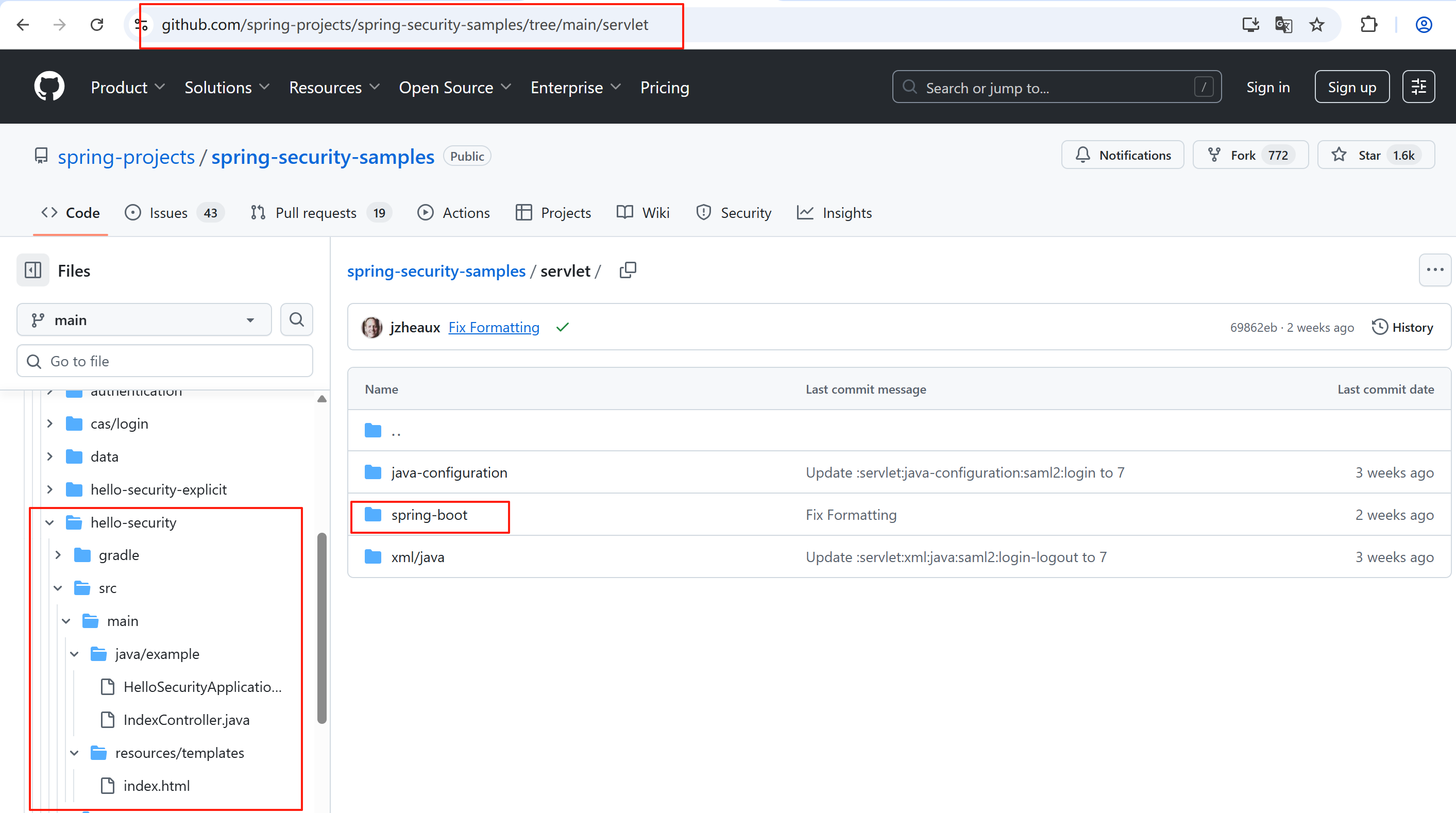
3.2、添加Controller
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}3.3、添加HTML
<html xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Hello Security!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello Security</h1>
<a th:href="@{/logout}">Log Out</a>
</body>
</html>3.4、测试
浏览器中访问:http://localhost:8080,自动跳转到:http://localhost:8080/login
输入用户名:user
输入密码:在控制台的启动日志中查找初始的默认密码
点击"Sign in"进行登录,浏览器就跳转到了index页面
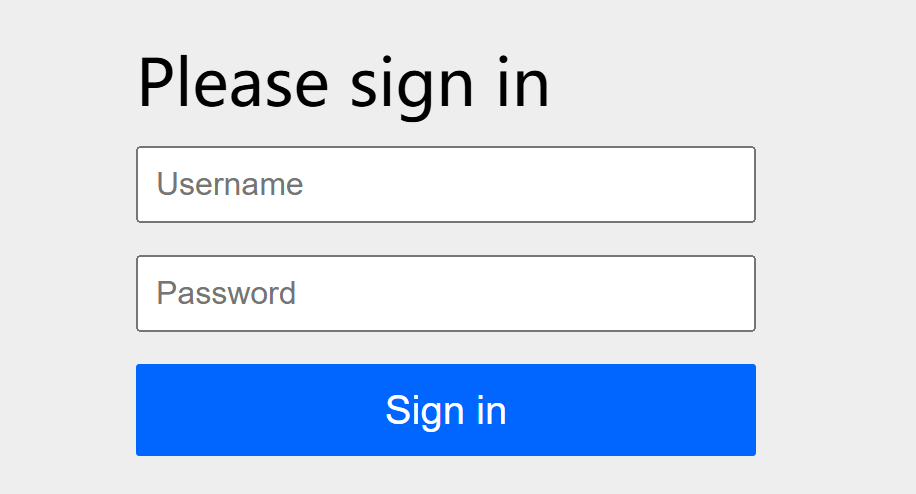
3.5、Spring Security默认做了什么
- 保护应用程序URL,要求对应用程序的任何交互进行身份验证。
- 程序启动时生成一个默认用户“user”。
- 生成一个默认的随机密码,并将此密码记录在控制台上。
- 生成默认的登录表单和注销页面。
- 提供基于表单的登录和注销流程。
- 对于Web请求,重定向到登录页面;
- 对于服务请求,返回401未经授权。
- 处理跨站请求伪造(CSRF)攻击。
- 处理会话劫持攻击。
- 写入Strict-Transport-Security以确保HTTPS。
- 写入X-Content-Type-Options以处理嗅探攻击。
- 写入Cache Control头来保护经过身份验证的资源。
- 写入X-Frame-Options以处理点击劫持攻击。
4、Spring Security底层原理
官方文档:Architecture :: Spring Security
Spring Security之所以默认帮助我们做了那么多事情,它的底层原理是传统的Servlet过滤器。
4.1、Filter
Spring Security 的 Servlet 支持基于 Servlet 过滤器,因此首先查看过滤器的作用会很有帮助。 下图显示了单个 HTTP 请求的处理程序的典型分层。
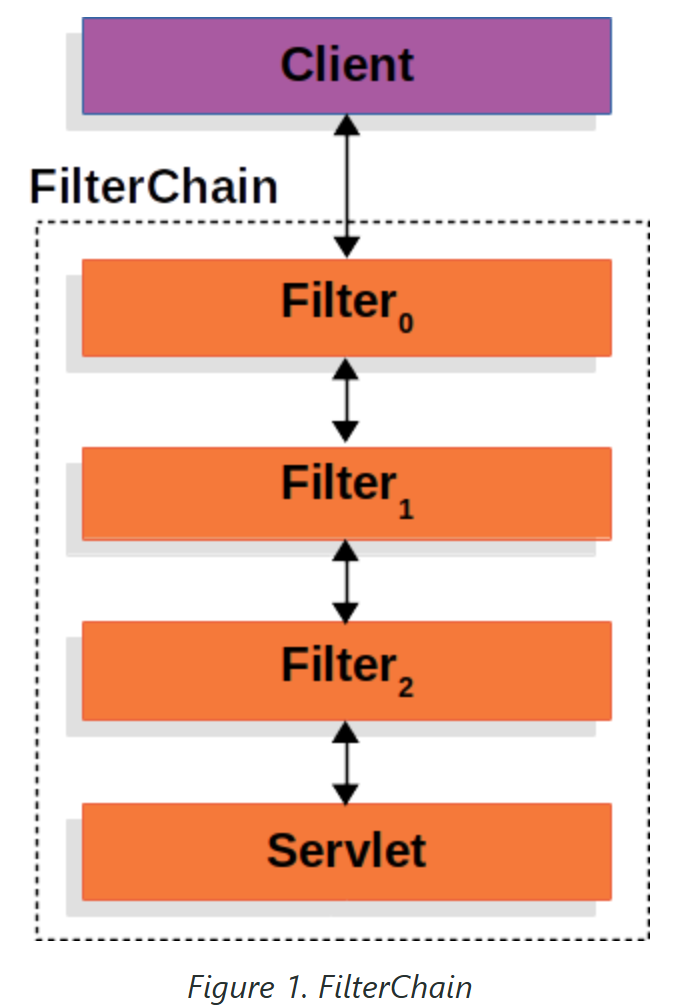
客户端向应用程序发送请求,容器根据请求URI的路径创建一个FilterChain,其中包含应处理HttpServletRequest的Filter实例和Servlet。在Spring MVC应用程序中,Servlet是DispatcherServlet的实例。最多一个Servlet可以处理单个HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse。但是,可以使用多个Filter:
(1)阻止下游的Filter实例或Servlet被调用。在这种情况下,Filter通常会写入HttpServletResponse。
(2)修改下游过滤器实例和Servlet使用的HttpServletRequest或HttpServletResponse。
Filter的核心能力源自其入参FilterChain,通过调用chain.doFilter(request, response)委派执行链中后续组件,或终止调用链。这种机制体现了责任链模式,支持灵活扩展请求处理流程。
示例:
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// do something before the rest of the application
chain.doFilter(request, response); // invoke the rest of the application
// do something after the rest of the application
}4.2、DelegatingFilterProxy
Spring 提供了一个名为 DelegatingFilterProxy 的 Filter 实现,它允许在 Servlet 容器的生命周期和 Spring 的 ApplicationContext 之间建立桥梁。Servlet 容器允许使用其自己的标准注册 Filter 实例,但它并不识别 Spring 定义的 Bean。您可以通过标准的 Servlet 容器机制注册 DelegatingFilterProxy,但将所有工作委托给一个实现 Filter 的 Spring Bean。
DelegatingFilterProxy 是 Spring Security 提供的一个 Filter 实现,可以在 Servlet 容器和 Spring 容器之间建立桥梁。通过使用 DelegatingFilterProxy,这样就可以将Servlet容器中的 Filter 实例放在 Spring 容器中管理。
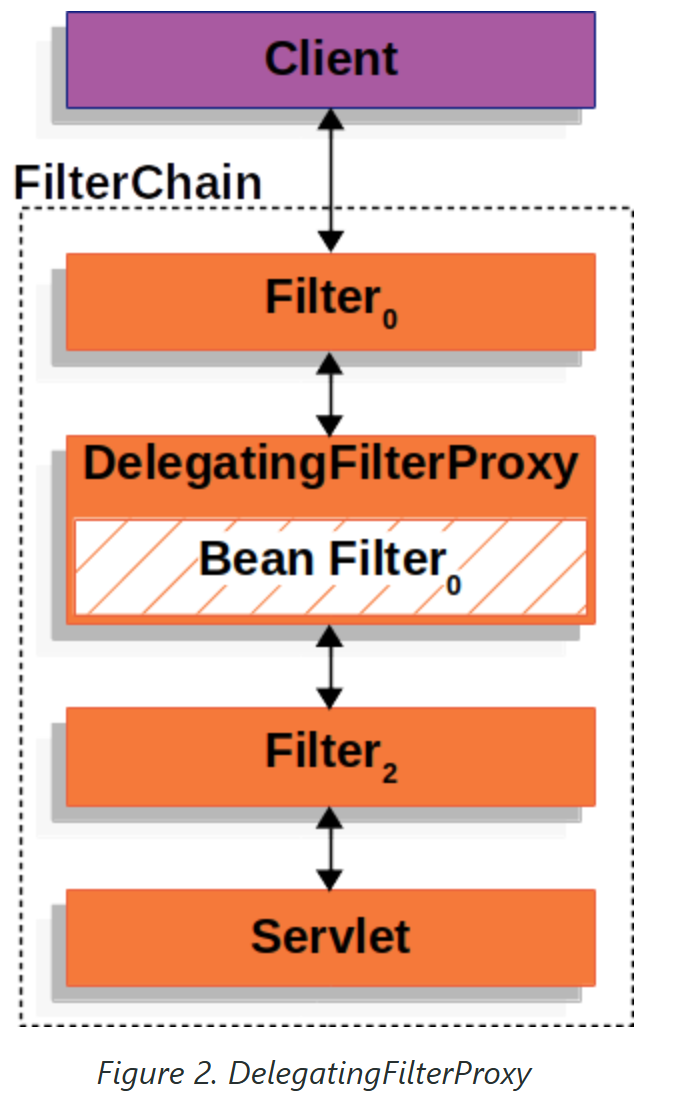
DelegatingFilterProxy从ApplicationContext中查找Bean Filter0,然后调用Bean Filter0。以下显示了DelegatingFilterProxy的伪代码:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName);
delegate.doFilter(request, response);
}DelegatingFilterProxy 的工作流程:
初始化阶段
DelegatingFilterProxy 通过 FilterConfig 获取 ServletContext,并从中获取 ApplicationContext。
它不会立即查找目标 Filter Bean,而是等待第一次调用 doFilter 方法。
过滤阶段
在 doFilter 方法被调用时,DelegatingFilterProxy 通过 ApplicationContext 查找目标 Filter Bean。
如果目标 Filter Bean 还未被初始化,Spring 会在此时进行初始化。
然后,DelegatingFilterProxy 将请求委托给目标 Filter Bean 的 doFilter 方法进行处理。
销毁阶段
- DelegatingFilterProxy 会调用目标 Filter Bean 的 destroy 方法,完成资源清理。
DelegatingFilterProxy的另一个好处是,它允许延迟查找Filter bean实例。这一点很重要,因为容器需要在启动之前注册Filter实例。然而,Spring通常使用ContextLoaderListener来加载Spring Bean,而这一过程直到需要注册Filter实例之后才会进行。
4.3、FilterChainProxy
Spring Security 的 Servlet 支持主要通过 FilterChainProxy 实现。FilterChainProxy 是 Spring Security 提供的一个特殊 Filter,它允许通过 SecurityFilterChain 委托给多个 Filter 实例。由于 FilterChainProxy 是一个 Spring 管理的 Bean,因此通常将其封装在 DelegatingFilterProxy 中。
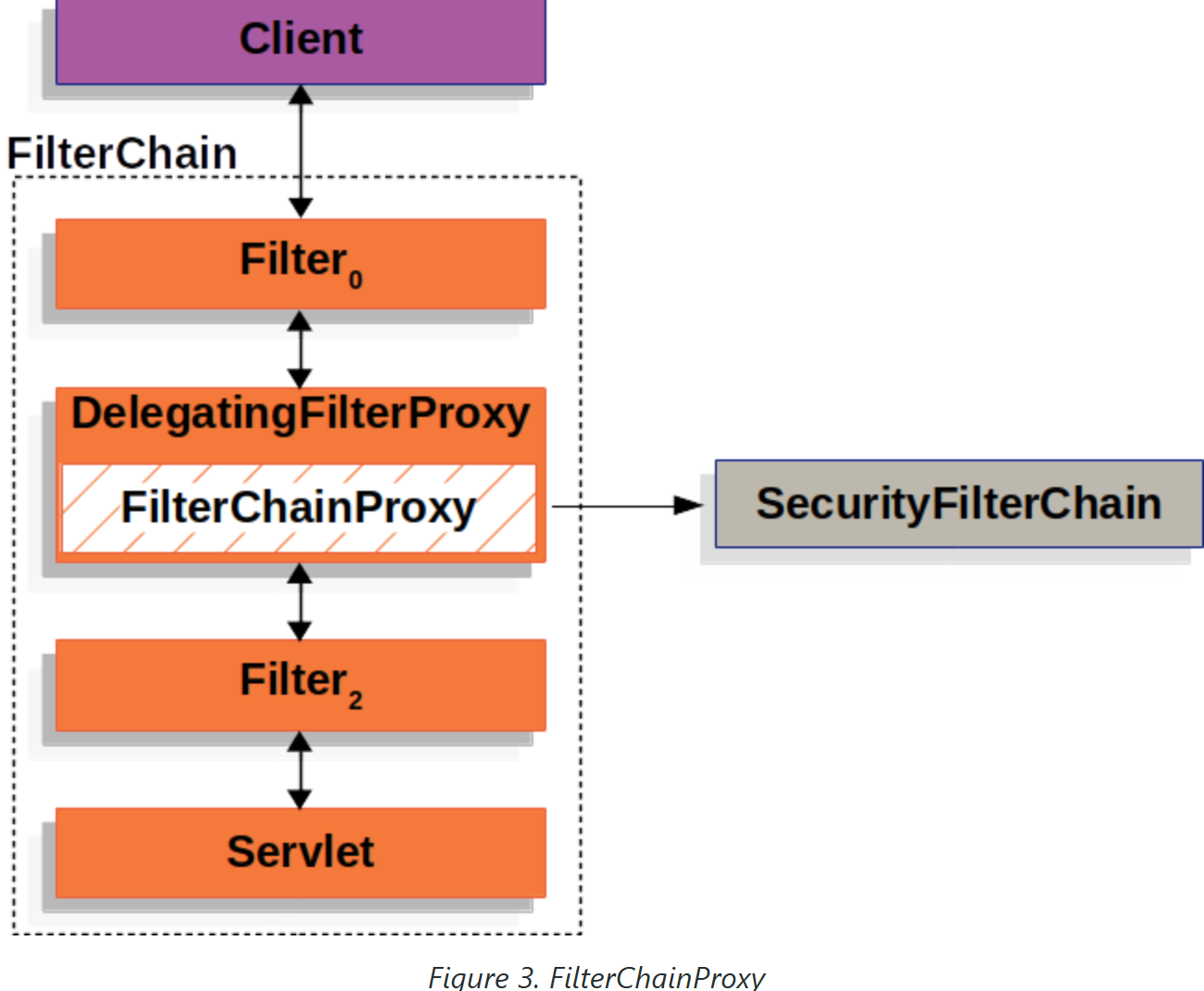
4.4、SecurityFilterChain
SecurityFilterChain 由 FilterChainProxy 用于确定当前请求应调用哪些 Spring Security Filter实例。
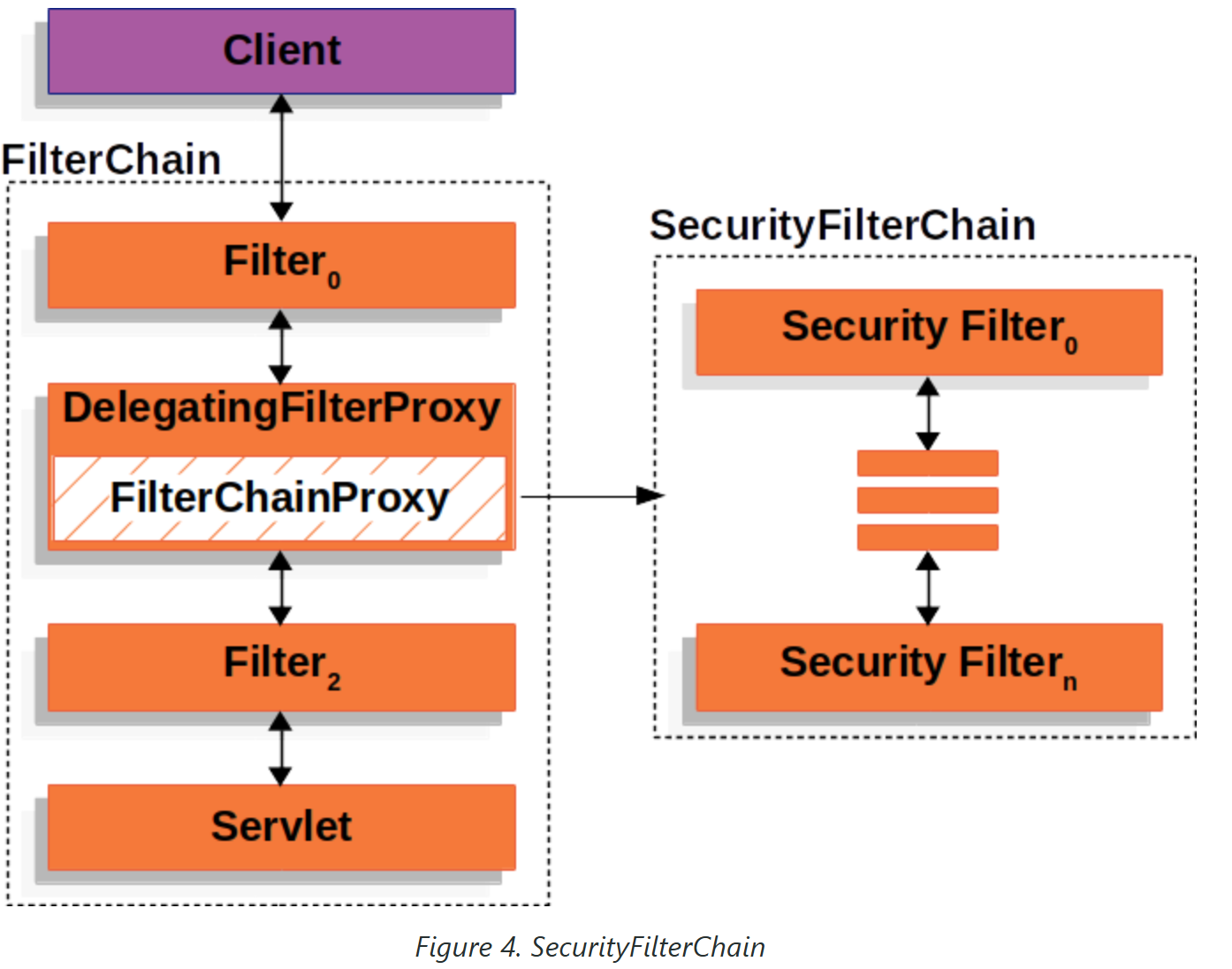
SecurityFilterChain中的安全过滤器通常是Bean,但它们是在FilterChainProxy而不是DelegatingFilterProxy中注册的。FilterChainProxy提供了许多直接向Servlet容器或DelegatingFilterProxy注册的优点。首先,它为Spring Security的所有Servlet支持提供了一个起点。因此,如果您试图对Spring Security的Servlet支持进行故障排除,在FilterChainProxy中添加调试点是一个很好的起点。
其次,由于FilterChainProxy是Spring Security使用的核心,它可以执行不被视为可选的任务。例如,它清除SecurityContext以避免内存泄漏。它还应用了Spring Security的HttpFirewall来保护应用程序免受某些类型的攻击。
此外,它在确定何时应调用SecurityFilterChain方面提供了更大的灵活性。在Servlet容器中,仅根据URL调用Filter实例。但是,FilterChainProxy可以通过使用RequestMatcher接口根据HttpServletRequest中的任何内容来确定调用。
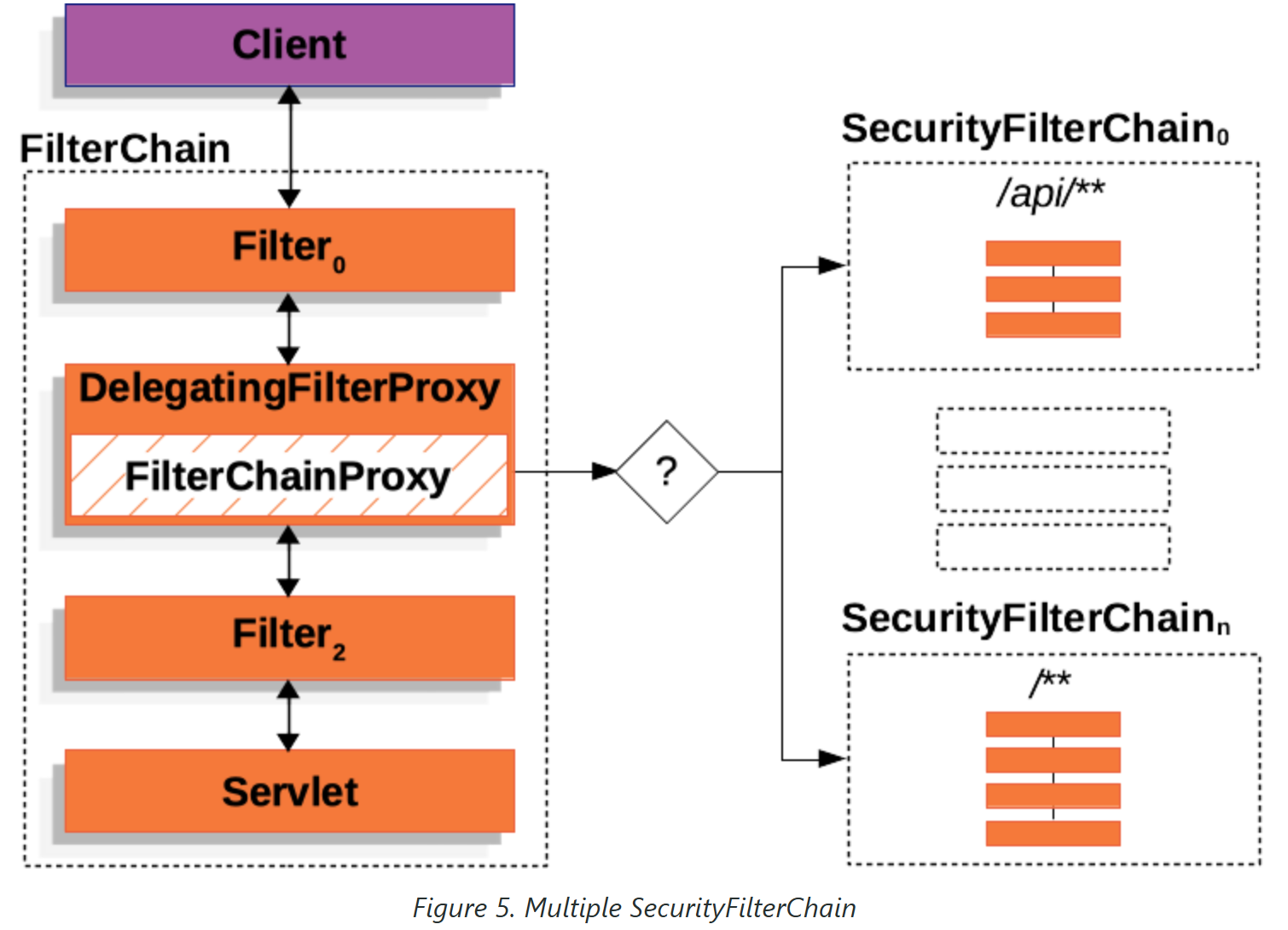
可以有多个SecurityFilterChain的配置,FilterChainProxy决定使用哪个SecurityFilterChain。如果请求的URL是/api/messages/,它首先匹配SecurityFilterChain0的模式/api/**,因此只调用SecurityFilterChain 0。假设没有其他SecurityFilterChain实例匹配,那么将调用SecurityFilterChain n。
5、程序的启动和运行
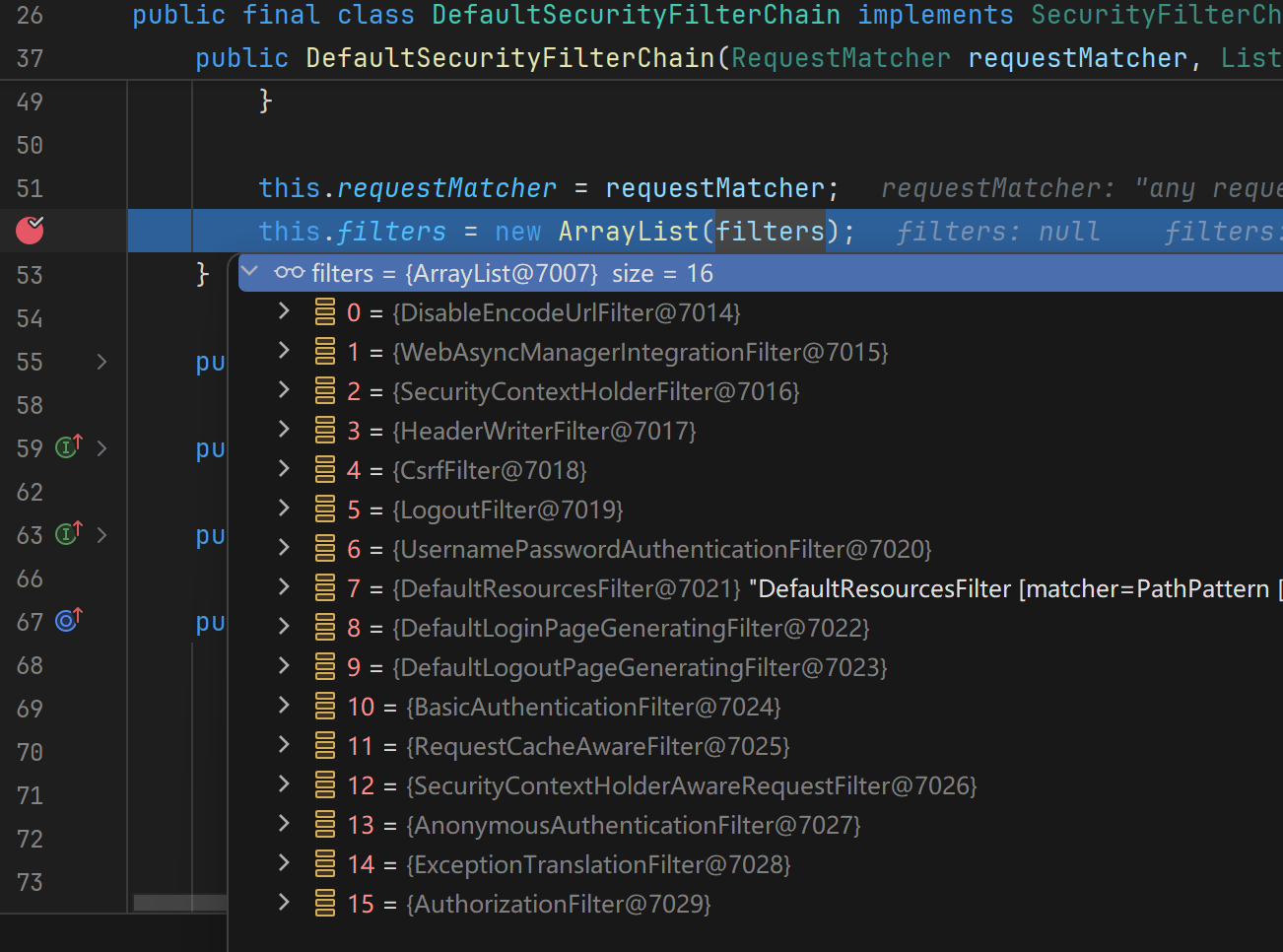
5.1、DefaultSecurityFilterChain
SecurityFilterChain接口的实现,加载了默认的16个Filter
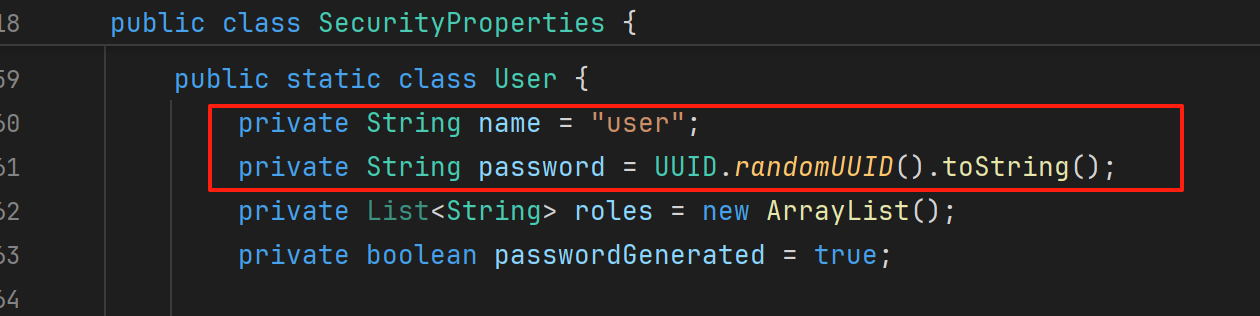
5.2、SecurityProperties
默认情况下Spring Security将初始的用户名和密码存在了SecurityProperties类中。这个类中有一个静态内部类User,配置了默认的用户名(name = "user")和密码(password = uuid)
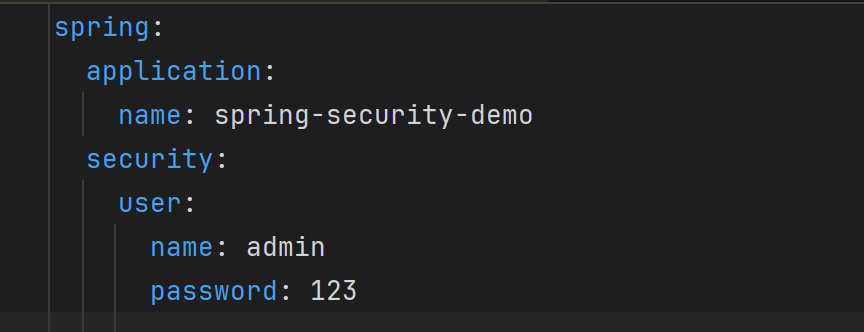
我们也可以将用户名、密码配置在SpringBoot的配置文件中:在application.yml中配置自定义用户名和密码
二、Spring Security自定义配置
1、基于内存的用户认证
1.1、创建自定义配置
实际开发的过程中,我们需要应用程序更加灵活,可以在SpringSecurity中创建自定义配置文件
官方文档:Java Configuration :: Spring Security
UserDetailsService 用来管理用户信息,InMemoryUserDetailsManager是UserDetailsService的一个实现,用来管理基于内存的用户信息。
创建一个WebSecurityConfig文件:
定义一个@Bean,类型是UserDetailsService,实现是InMemoryUserDetailsManager
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
//创建基于内存的用户信息管理器
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
//使用manager管理UserDetails对象
manager.createUser(
//创建UserDetails对象
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER").build());
return manager;
}
}1.2、基于内存的用户认证流程
- 程序启动时:
- 创建
InMemoryUserDetailsManager对象 - 创建
User对象,封装用户名密码 - 使用InMemoryUserDetailsManager
将User存入内存
- 创建
- 校验用户时:
- SpringSecurity自动使用
InMemoryUserDetailsManager的loadUserByUsername方法从内存中获取User对象 - 在
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器中的attemptAuthentication方法中将用户输入的用户名密码和从内存中获取到的用户信息进行比较,进行用户认证
- SpringSecurity自动使用
2、基于数据库的用户认证
2.1、基于数据库的用户认证流程
程序启动时:
创建
DBUserDetailsManager类,实现接口 UserDetailsManager, UserDetailsPasswordService在应用程序中初始化这个类的对象
校验用户时:
SpringSecurity自动使用
DBUserDetailsManager的loadUserByUsername方法从数据库中获取User对象在
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器中的attemptAuthentication方法中将用户输入的用户名密码和从数据库中获取到的用户信息进行比较,进行用户认证
2.2、定义DBUserDetailsManager
public class DBUserDetailsManager implements UserDetailsManager, UserDetailsPasswordService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails updatePassword(UserDetails user, String newPassword) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void createUser(UserDetails user) {
}
@Override
public void updateUser(UserDetails user) {
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(String username) {
}
@Override
public void changePassword(String oldPassword, String newPassword) {
}
@Override
public boolean userExists(String username) {
return false;
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
LambdaUpdateWrapper<User> wrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(User::getUsername, username);
User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");
}else {
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword(),
user.getEnabled(),
true, //用户账号是否未过期
true, //用户凭证是否未过期
true, //用户是否未被锁定
authorities);
}
}
}
2.3、初始化UserDetailsService
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
DBUserDetailsManager manager = new DBUserDetailsManager();
return manager;
}
}或者直接在DBUserDetailsManager类上添加@Component注解
@Component
public class DBUserDetailsManager implements UserDetailsManager, UserDetailsPasswordService {2.3、SpringSecurity的默认配置
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//对所有请求都开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
//已认证的请求会被自动授权
.authenticated()
)
//使用表单授权方式
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
//使用HTTP 基本授权方式
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}2.4、添加用户
@PostMapping("/add")
public void add(@RequestBody User user){
userService.saveUserDetails(user);
}@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements IUserService {
@Resource
private DBUserDetailsManager dbUserDetailsManager;
@Override
public void saveUserDetails(User user) {
UserDetails userDetails = org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username(user.getUsername()) //自定义用户名
.password(user.getPassword()) //自定义密码
.build();
dbUserDetailsManager.createUser(userDetails);
}
}DBUserDetailsManager
@Override
public void createUser(UserDetails userDetails) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(userDetails.getUsername());
user.setPassword(userDetails.getPassword());
user.setEnabled(true);
userMapper.insert(user);
}3、密码加密算法
官方网站:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/features/authentication/password-storage.html
3.1、密码加密方式
明文密码:
最初,密码以明文形式存储在数据库中。但是恶意用户可能会通过SQL注入等手段获取到明文密码,或者程序员将数据库数据泄露的情况也可能发生。
Hash算法:
Spring Security的PasswordEncoder接口用于对密码进行单向转换,从而将密码安全地存储。对密码单向转换需要用到哈希算法,例如MD5、SHA-256、SHA-512等,哈希算法是单向的,只能加密,不能解密。
因此,数据库中存储的是单向转换后的密码,Spring Security在进行用户身份验证时需要将用户输入的密码进行单向转换,然后与数据库的密码进行比较。
因此,如果发生数据泄露,只有密码的单向哈希会被暴露。由于哈希是单向的,并且在给定哈希的情况下只能通过暴力破解的方式猜测密码。
彩虹表:
恶意用户创建称为彩虹表的查找表。
彩虹表就是一个庞大的、针对各种可能的字母组合预先生成的哈希值集合,有了它可以快速破解各类密码。越是复杂的密码,需要的彩虹表就越大,主流的彩虹表都是100G以上,目前主要的算法有LM, NTLM, MD5, SHA1, MYSQLSHA1, HALFLMCHALL, NTLMCHALL, ORACLE-SYSTEM, MD5-HALF。
加盐密码:
为了减轻彩虹表的效果,开发人员开始使用加盐密码。不再只使用密码作为哈希函数的输入,而是为每个用户的密码生成随机字节(称为盐)。盐和用户的密码将一起经过哈希函数运算,生成一个唯一的哈希。盐将以明文形式与用户的密码一起存储。然后,当用户尝试进行身份验证时,盐和用户输入的密码一起经过哈希函数运算,再与存储的密码进行比较。唯一的盐意味着彩虹表不再有效,因为对于每个盐和密码的组合,哈希都是不同的。
自适应单向函数:
随着硬件的不断发展,加盐哈希也不再安全。原因是,计算机可以每秒执行数十亿次哈希计算。这意味着我们可以轻松地破解每个密码。
现在,开发人员开始使用自适应单向函数来存储密码。使用自适应单向函数验证密码时,故意占用资源(故意使用大量的CPU、内存或其他资源)。自适应单向函数允许配置一个“工作因子”,随着硬件的改进而增加。我们建议将“工作因子”调整到系统中验证密码需要约一秒钟的时间。这种权衡是为了让攻击者难以破解密码。
自适应单向函数包括bcrypt、PBKDF2、scrypt和argon2。
3.2、PasswordEncoder
BCryptPasswordEncoder
使用广泛支持的bcrypt算法来对密码进行哈希。为了增加对密码破解的抵抗力,bcrypt故意设计得较慢。和其他自适应单向函数一样,应该调整其参数,使其在您的系统上验证一个密码大约需要1秒的时间。BCryptPasswordEncoder的默认实现使用强度10。建议您在自己的系统上调整和测试强度参数,以便验证密码时大约需要1秒的时间。
Argon2PasswordEncoder
使用Argon2算法对密码进行哈希处理。Argon2是密码哈希比赛的获胜者。为了防止在自定义硬件上进行密码破解,Argon2是一种故意缓慢的算法,需要大量内存。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。当前的Argon2PasswordEncoder实现需要使用BouncyCastle库。
Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder
使用PBKDF2算法对密码进行哈希处理。为了防止密码破解,PBKDF2是一种故意缓慢的算法。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。当需要FIPS认证时,这种算法是一个很好的选择。
SCryptPasswordEncoder
使用scrypt算法对密码进行哈希处理。为了防止在自定义硬件上进行密码破解,scrypt是一种故意缓慢的算法,需要大量内存。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。
3.3、密码加密测试
public class TestPassword {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 工作因子,默认值是10,最小值是4,最大值是31,值越大运算速度越慢
PasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(4);
//明文:"password"
//密文:result,即使明文密码相同,每次生成的密文也不一致
String result = encoder.encode("password");
System.out.println(result);
//密码校验
Assert.isTrue(encoder.matches("password", result), "密码不一致");
}
}3.4、DelegatingPasswordEncoder
表中存储的密码形式:
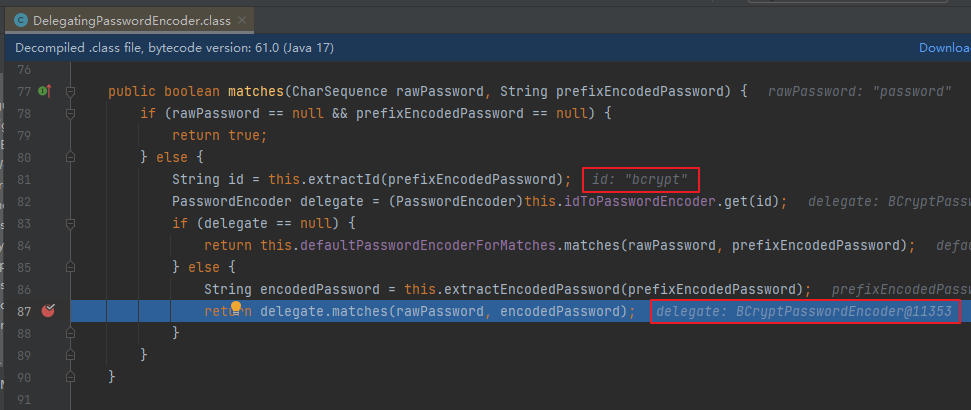
{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW通过如下源码可以知道:可以通过
{bcrypt}前缀动态获取和密码的形式类型一致的PasswordEncoder对象目的:方便随时做密码策略的升级,兼容数据库中的老版本密码策略生成的密码
4、自定义登录页
4.1、创建Controller和登录页
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "login";
}
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>登录</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录</h1>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
错误的用户名和密码.</div>
<!--method必须为"post"-->
<!--th:action="@{/login}" ,
使用动态参数,表单中会自动生成_csrf隐藏字段,用于防止csrf攻击
login: 和登录页面保持一致即可,SpringSecurity自动进行登录认证-->
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<!--name必须为"username"-->
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名"/>
</div>
<div>
<!--name必须为"password"-->
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码"/>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="登录" />
</form>
</body>
</html>4.2、配置SecurityFilterChain
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//对所有请求都开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
//已认证的请求会被自动授权
.authenticated()
)
//使用表单授权方式
.formLogin(form -> form
.loginPage("/login").permitAll() //登录页面无需授权即可访问
.usernameParameter("username") //自定义表单用户名参数,默认是username
.passwordParameter("password") //自定义表单密码参数,默认是password
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //登录处理url,默认是/login
.defaultSuccessUrl("/") //登录成功的返回地址
.failureUrl("/login?error") //登录失败的返回地址
);
//关闭CSRF保护
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable);
return http.build();
}
}三、前后端分离
1、用户认证流程
登录成功后调用:AuthenticationSuccessHandler
登录失败后调用:AuthenticationFailureHandler
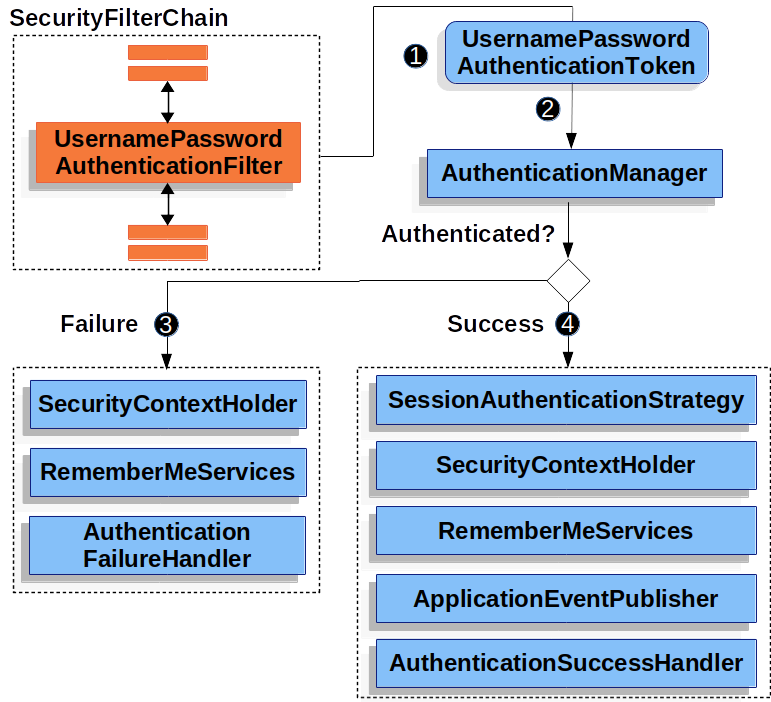
2、认证成功响应
/**
* 认证成功的响应
* 成功结果处理
*/
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取用户身份信息
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code",0);
result.put("message", "登录成功");
result.put("data", principal);
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
//返回响应
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain配置
http.formLogin(form -> {
form.successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler());
}); //认证成功时的处理3、认证失败响应
/**
* 失败结果处理
*/
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取错误信息
String localizedMessage = exception.getLocalizedMessage();
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", -1);
result.put("message", localizedMessage);
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain配置
http.formLogin(form -> {
form.failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler());
}); //认证失败时的处理4、注销响应
/**
* 注销结果处理
*/
public class MyLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", 0);
result.put("msg", "注销成功");
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain配置
http.logout(logout -> {
logout.logoutSuccessHandler(new MyLogoutSuccessHandler()); //注销成功时的处理
});5、请求未认证接口
官网:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/authentication/architecture.html
public class MyAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取错误信息: Full authentication is required to access this resource
// String localizedMessage = authException.getLocalizedMessage();
String localizedMessage = "请先登录后再访问";
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", -1);
result.put("message", localizedMessage);
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain配置
//错误处理
http.exceptionHandling(exception -> {
exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint());//请求未认证的接口
});6、跨域
跨域全称是跨域资源共享(Cross-Origin Resources Sharing,CORS),它是浏览器的保护机制,只允许网页请求统一域名下的服务,同一域名指=>协议、域名、端口号都要保持一致,如果有一项不同,那么就是跨域请求。在前后端分离的项目中,需要解决跨域的问题。
在SpringSecurity中解决跨域很简单,在配置文件中添加如下配置即可
http.cors(Customizer.withDefaults()); //开启跨域7、身份认证
在Spring Security框架中,SecurityContextHolder、SecurityContext、Authentication、Principal和Credential是一些与身份验证和授权相关的重要概念。它们之间的关系如下:
SecurityContextHolder:SecurityContextHolder 是 Spring Security 存储已认证用户详细信息的地方。
SecurityContext:SecurityContext 是从 SecurityContextHolder 获取的内容,包含当前已认证用户的 Authentication 信息。
Authentication:Authentication 表示用户的身份认证信息。它包含了用户的Principal、Credential和Authority信息。
Principal:表示用户的身份标识。它通常是一个表示用户的实体对象,例如用户名。Principal可以通过Authentication对象的getPrincipal()方法获取。
Credentials:表示用户的凭证信息,例如密码、证书或其他认证凭据。Credential可以通过Authentication对象的getCredentials()方法获取。
GrantedAuthority:表示用户被授予的权限
总结起来,SecurityContextHolder用于管理当前线程的安全上下文,存储已认证用户的详细信息,其中包含了SecurityContext对象,该对象包含了Authentication对象,后者表示用户的身份验证信息,包括Principal(用户的身份标识)和Credential(用户的凭证信息)。
7.1、在Controller中获取用户信息
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/")
public Map<String, Object> index() {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();//存储认证对象的上下文
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();//认证对象
String username = authentication.getName();//用户名
Object principal =authentication.getPrincipal();//身份
Object credentials = authentication.getCredentials();//凭证(脱敏)
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();//权限
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(principal);
System.out.println(credentials);
System.out.println(authorities);
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", 0);
result.put("data", username);
return result;
}
}7.2、会话并发处理
实现接口SessionInformationExpiredStrategy
/**
* 会话并发处理
* 后登录的账号会使先登录的账号失效
*/
public class MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy {
@Override
public void onExpiredSessionDetected(SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException, ServletException {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", -1);
result.put("msg", "该账号已从其他设备登录");
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
HttpServletResponse response = event.getResponse();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain配置
//会话管理
http.sessionManagement(session -> {
session
.maximumSessions(1)
.expiredSessionStrategy(new MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy());
});8、授权
官网:Authorize HttpServletRequests :: Spring Security
8.1、用户-权限-资源
配置权限:SecurityFilterChain
//开启授权保护
http.authorizeRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//具有USER_LIST权限的用户可以访问/user/list
.requestMatchers("/user/list").hasAuthority("USER_LIST")
//具有USER_ADD权限的用户可以访问/user/add
.requestMatchers("/user/add").hasAuthority("USER_ADD")
//对所有请求开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
//已认证的请求会被自动授权
.authenticated()
);授予权限
DBUserDetailsManager中的loadUserByUsername方法:
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
authorities.add(()->"USER_LIST");
authorities.add(()->"USER_ADD");8.2、用户-角色-资源
需求:角色为ADMIN的用户才可以访问/user/**路径下的资源
配置角色:SecurityFilterChain
//开启授权保护
http.authorizeRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//具有管理员角色的用户可以访问/user/**
.requestMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
//对所有请求开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
//已认证的请求会被自动授权
.authenticated()
);授予角色:DBUserDetailsManager中的loadUserByUsername方法:
return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
.withUsername(user.getUsername())
.password(user.getPassword())
.roles("ADMIN")
.build();8.3、未授权响应
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
//创建结果对象
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", -1);
result.put("message", "没有权限");
//转换成json字符串
String json = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(result);
//返回响应
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().println(json);
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
}SecurityFilterChain
http.exceptionHandling(exception -> {
exception.accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler());//请求未授权的接口
}
);8.5、基于方法授权(注解授权)
官网:Method Security :: Spring Security
在配置文件中添加如下注解
@EnableMethodSecurity常用的注解例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin")
public class AdminController {
//用户必须有 ADMIN 角色 并且 用户名是 admin 才能访问此方法
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and authentication.name == 'admim'")
@GetMapping("/list")
public String getList(){
return "admin-list";
}
//用户必须有 ADMIN 角色 或者有 admin:update 权限 才能访问此方法
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('admin:update') || hasRole('ADMIN')")
@GetMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "admin-update";
}
}
8.6、自定义动态配置接口权限(*)
动态资源权限:通过从数据库加载 URL 与权限的映射关系,替代硬编码的@hasAuthority('')配置。
从 Spring Security 6.0 开始,FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource确实已被标记为 deprecated(过时),官方推荐使用更灵活的RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager和AuthorizationManager组合来实现动态权限控制。
创建自定义MyAuthorizationManager实现动态权限判断:
@Component
public class MyAuthorizationManager implements AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> {
// 缓存URL与权限的映射关系
private final Map<String, List<String>> urlPermCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 初始化权限缓存(项目启动时加载)
@PostConstruct
public void initPermCache() {
refreshPermCache();
}
// 刷新权限缓存(可通过接口触发实时更新)
public void refreshPermCache() {
urlPermCache.clear();
//todo 从数据库查询所有URL权限映射
// List<Map<String, String>> urlPerms = permissionMapper.selectAllUrlPerms();
List<Map<String, String>> urlPerms = new ArrayList<>();
urlPerms.add(Map.of("url", "/admin/list", "perm_code", "admin:list"));
urlPerms.add(Map.of("url", "/admin/add", "perm_code", "admin:add"));
urlPerms.add(Map.of("url", "/user/list", "perm_code", "user:list"));
for (Map<String, String> map : urlPerms) {
String url = map.get("url");
String permCode = map.get("perm_code");
urlPermCache.computeIfAbsent(url, k -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(permCode);
}
}
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication,
RequestAuthorizationContext context) {
// 1. 获取当前请求URL
String requestUrl = context.getRequest().getRequestURI();
// 2. 匹配URL对应的权限要求
List<String> requiredPerms = getRequiredPermissions(requestUrl);
// 3. 如果不需要特定权限,直接允许访问
if (requiredPerms.isEmpty()) {
return new AuthorizationDecision(true);
}
// 4. 检查用户是否拥有所需权限
Authentication auth = authentication.get();
if (auth == null || !auth.isAuthenticated()) {
return new AuthorizationDecision(false);
}
// 5. 权限匹配逻辑
boolean hasPermission = auth.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.anyMatch(requiredPerms::contains);
return new AuthorizationDecision(hasPermission);
}
// 根据URL获取所需权限
private List<String> getRequiredPermissions(String requestUrl) {
AntPathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
// 遍历缓存的URL模式,匹配当前请求
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : urlPermCache.entrySet()) {
if (pathMatcher.match(entry.getKey(), requestUrl)) {
return entry.getValue();
}
}
// 未匹配到的URL默认需要认证(可根据业务调整)
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}SecurityFilterChain
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Resource
private MyAuthorizationManager myAuthorizationManager;//开启授权保护
http.authorizeHttpRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//对所有请求都开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
.access(myAuthorizationManager)
);@hasRole('') 动态权限配置类似@hasAuthority(''),可仿照以上代码编写。
配置类:WebSecurityConfig
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Resource
private MyAuthorizationManager myAuthorizationManager;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//开启授权保护
http.authorizeHttpRequests(
authorize -> authorize
//对所有请求都开启授权保护
.anyRequest()
.access(myAuthorizationManager)
);
//使用表单授权方式
http.formLogin(form -> form
.loginPage("/login").permitAll() //登录页面无需授权即可访问
.usernameParameter("username") //自定义表单用户名参数,默认是username
.passwordParameter("password") //自定义表单密码参数,默认是password
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //登录处理url,默认是/login
.defaultSuccessUrl("/") //登录成功的返回地址
.failureUrl("/login?error") //登录失败的返回地址
.successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
.failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler())
)
.logout(logout -> {
logout.logoutSuccessHandler(new MyLogoutSuccessHandler());
})
.exceptionHandling(exception -> {
exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint());//请求未认证的接口
exception.accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler());//请求未授权的接口
}
)
.cors(Customizer.withDefaults()) //开启跨域
//会话管理
.sessionManagement(session -> {
session.maximumSessions(1)
.expiredSessionStrategy(new MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy());
})
;
//关闭CSRF保护
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable);
return http.build();
}
}