对目录进行 “文件编程”
1.打开opendir
opendir
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
功能:
打开一个目录文件关联一个目录流
参数:
@name 要打开的目录名字字符串
返回值:
成功 目录流指针
失败 NULL 并且 errno会被设置
2.读写
目录没有写操作
读目录
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* Inode number */ Index Node Number
off_t d_off; /* Not an offset; see below */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* Type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* Null-terminated filename */
};
".."
"."
".bashrc"
DT_BLK This is a block device.
DT_CHR This is a character device.
DT_DIR This is a directory.
DT_FIFO This is a named pipe (FIFO).
DT_LNK This is a symbolic link.
DT_REG This is a regular file.
DT_SOCK This is a UNIX domain socket.
DT_UNKNOWN The file type could not be determined.
功能:
从dirp中读取目录项,返回对应一个结构体
参数:
@dirp 要操作的目录流指针
返回值:
成功 读到的某一个目录项的结构体指针
失败 NULL && errno
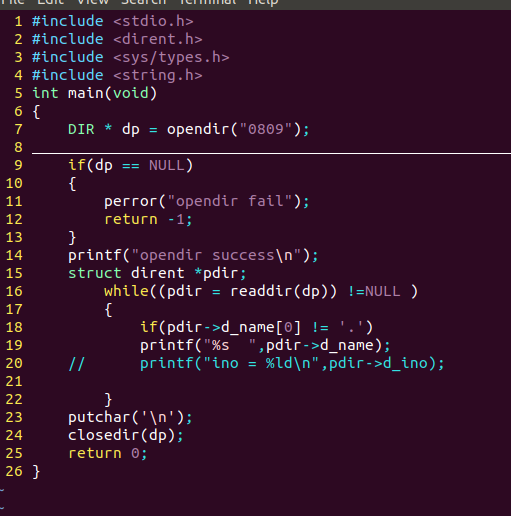
练习:
读取某个目录 打印目录下的所有文件的
名字 和 inode编号
3.关闭
closedir
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
功能:
关闭目录流
参数:
dirp ---目录流指针
返回值
成功 0
失败 -1 并且 errno 会被设置
linux下,文件名以 '.' 开头的,叫隐藏文件
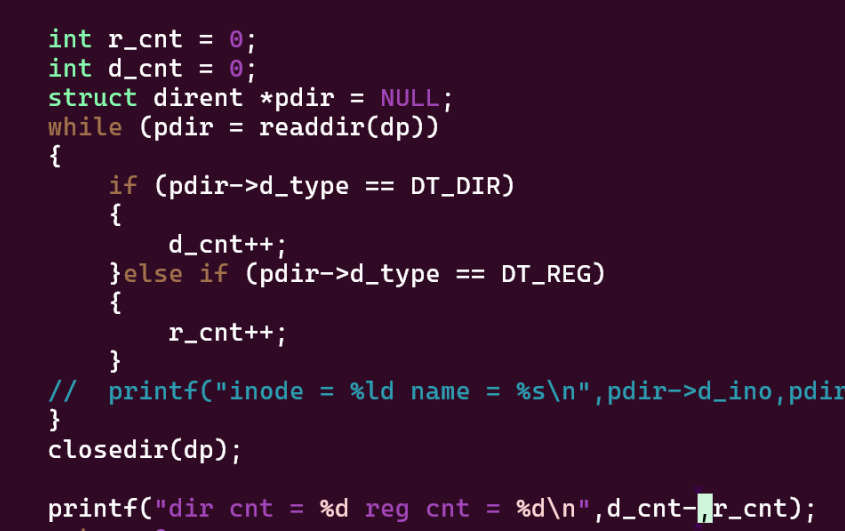
练习:
统计某个目录下 目录文件 和 普通文件 的个数
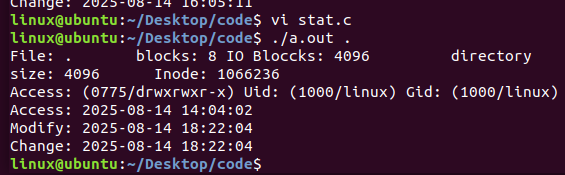
4.stat
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
功能:
获得文件的状态信息
bruce@brucePc:~/linux_code/0814$ stat .
File: .
Size: 4096 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 directory
Device: 830h/2096d Inode: 121289 Links: 3
Access: (0755/drwxr-xr-x) Uid: ( 1000/ bruce) Gid: ( 1000/ bruce)
Access: 2025-08-14 11:31:47.652320067 +0800
Modify: 2025-08-14 11:31:21.764339358 +0800
Change: 2025-08-14 11:31:21.764339358 +0800
Birth: -
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
* 自 Linux 2.6 起,内核支持以下时间戳字段的纳秒级精度。有关 Linux 2.6 之前的详情,请参阅 NOTES。 */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
返回值:
成功 0
失败 -1 &&errno
练习:编写实现stat
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <filename>\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
struct stat st;
if (stat(argv[1],&st) < 0)
{
perror("stat fail!\n");
return -1;
}
char type_name[7][20] = {"socket",
"symbolic",
"regular",
"block",
"directory",
"character",
"FIFO"};
char type[7] = {'s','l','-','b','d','c','p'};
printf("File: %s\n",argv[1]);
int i = 0;
switch (st.st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFSOCK:
i = 0;
break;
case S_IFLNK:
i = 1;
break;
case S_IFREG:
i = 2;
break;
case S_IFBLK:
i = 3;
break;
case S_IFDIR:
i = 4;
break;
case S_IFCHR:
i = 5;
break;
case S_IFIFO:
i = 6;
break;
}
printf("Size: %ld\tBlocks: %ld\tIO Blocks: %ld\t %s\n",st.st_size,st.st_blocks,st.st_blksize,type_name[i]);
printf("Device: %ld\t Inode: %ld\t Links: %ld\n",st.st_dev,st.st_ino,st.st_nlink);
printf("Access: (%#o/",(st.st_mode&S_IRWXU)|(st.st_mode&S_IRWXG)|(st.st_mode&S_IRWXO));
putchar(type[i]);
st.st_mode&S_IRUSR?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWUSR?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXUSR?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IRGRP?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWGRP?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXGRP?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IROTH?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWOTH?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXOTH?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
putchar(')');
printf(" Uid: (%d) Gid: (%d)\n",st.st_uid,st.st_gid);
struct tm *ptm = localtime(&(st.st_atim.tv_sec));
printf("Access: %04d-%02d-%2d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",ptm->tm_year+1900,ptm->tm_mon+1,ptm->tm_mday,ptm->tm_hour,ptm->tm_min,ptm->tm_sec);
ptm = localtime(&st.st_mtim.tv_sec);
printf("Modify: %04d-%02d-%2d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",ptm->tm_year+1900,ptm->tm_mon+1,ptm->tm_mday,ptm->tm_hour,ptm->tm_min,ptm->tm_sec);
ptm = localtime(&st.st_ctim.tv_sec);
printf("Change: %04d-%02d-%2d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",ptm->tm_year+1900,ptm->tm_mon+1,ptm->tm_mday,ptm->tm_hour,ptm->tm_min,ptm->tm_sec);
return 0;
}