1.自动类型转换与强制类型转换
1.自动类型转换:类型范围小的变量,可以直接赋值给类型范围大的变量。
2.表达式的自动类型转换:
在表达式中,小范围类型的变量会自动转换成当前较大范围的类型再运算。
byte, short, char---->int---->long---->float---->double
注意事项:
表达式的最终结果类型由表达式中的最高类型决定。
在表达式中,byte、short、char是直接转换成int类型参与运算的。
测试:
public class HelloMajunjun{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 25; byte b = a System.out.println(b);//会报错 } }
问题:
类型范围大的数据或变量,不能直接赋值给类型范围小的变量,会报错
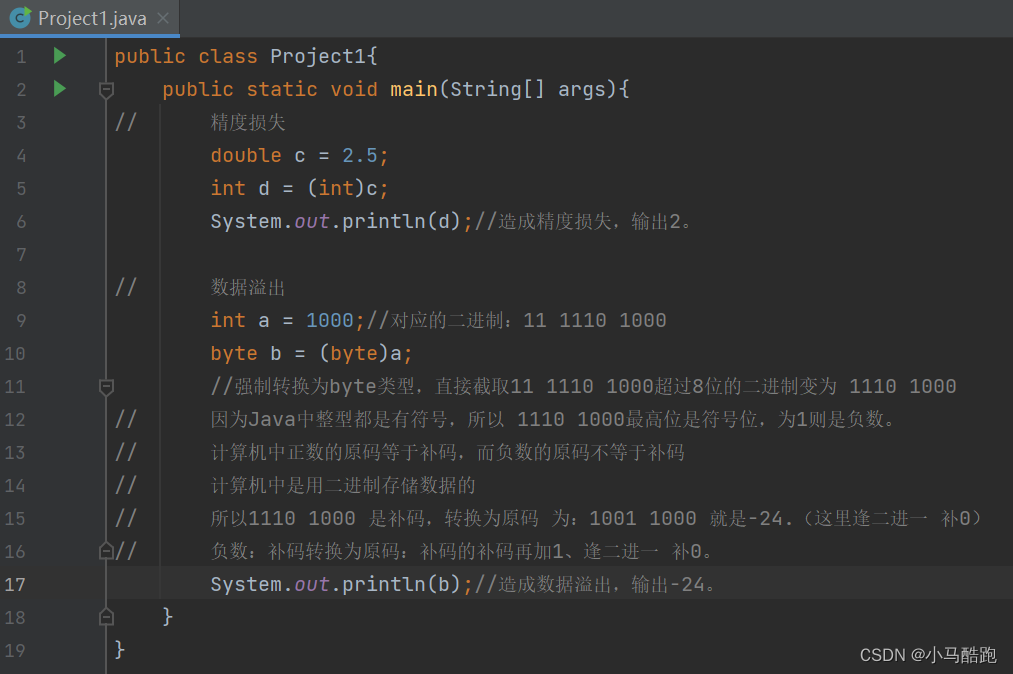
强制类型转换:
1.可以理解为自动类型转换的逆过程。是将大容量的数据类型转换为小容量的数据类型。
2.需要将数据从高精度数据类型转换为低精度数据类型。(即高精度类型的数据不能直接赋值给低精度数据)
3.使用风险:
(1)精度损失(2)数据溢出
3.运算符:+、-、*、/、%
1.数据拆分:
public class Project1{
public static void main(String[] args){
// 数据拆分:个位、十位、百位分别输出
int data = 356;
// 个位
int get = data % 10;
System.out.println(get);
// 十位
int get1 = data / 10 % 10;
System.out.println(get1);
// 百位
int get2 = data / 100;
System.out.println(get2); } }
2. + 加号做连接符:
技巧:能算就算,不能算就在一起。
+ 做连接符使用
int e = 8;
System.out.println('e');
System.out.println(e + 'e');
System.out.println(e + 20);//28
System.out.println(e + "inter");//8inter
System.out.println(e + "" +17);//817
System.out.println(10 + "inter" + e);//10inter8
System.out.println(e + 'e' + "inter");//109inter
System.out.println("inter" + e + 'e');//inter8e
System.out.println("inter" + (e + 'e'));//inter109
3. 自增、自减
++、- -运算符:
++、--在变量前面:先加、减后运算
int g = 100;
int rs = ++g;
System.out.println(g);//101
System.out.println(rs);//101
// ++、--在变量后面:先运算后加、减
int h = 10;
int res = h++;
System.out.println(h);
System.out.println(res);
案例:
// 案例
int l =15;
int m =12;
int ro = l++ + --m + --l + ++l - m-- + m++ + ++m + l--;
// l 15 16 15 16 15
// m 12 11 10 11 12
// ro 15 11 15 16 -11 10 12 16
System.out.println(l);// 15
System.out.println(m);// 12
System.out.println(ro);// 84
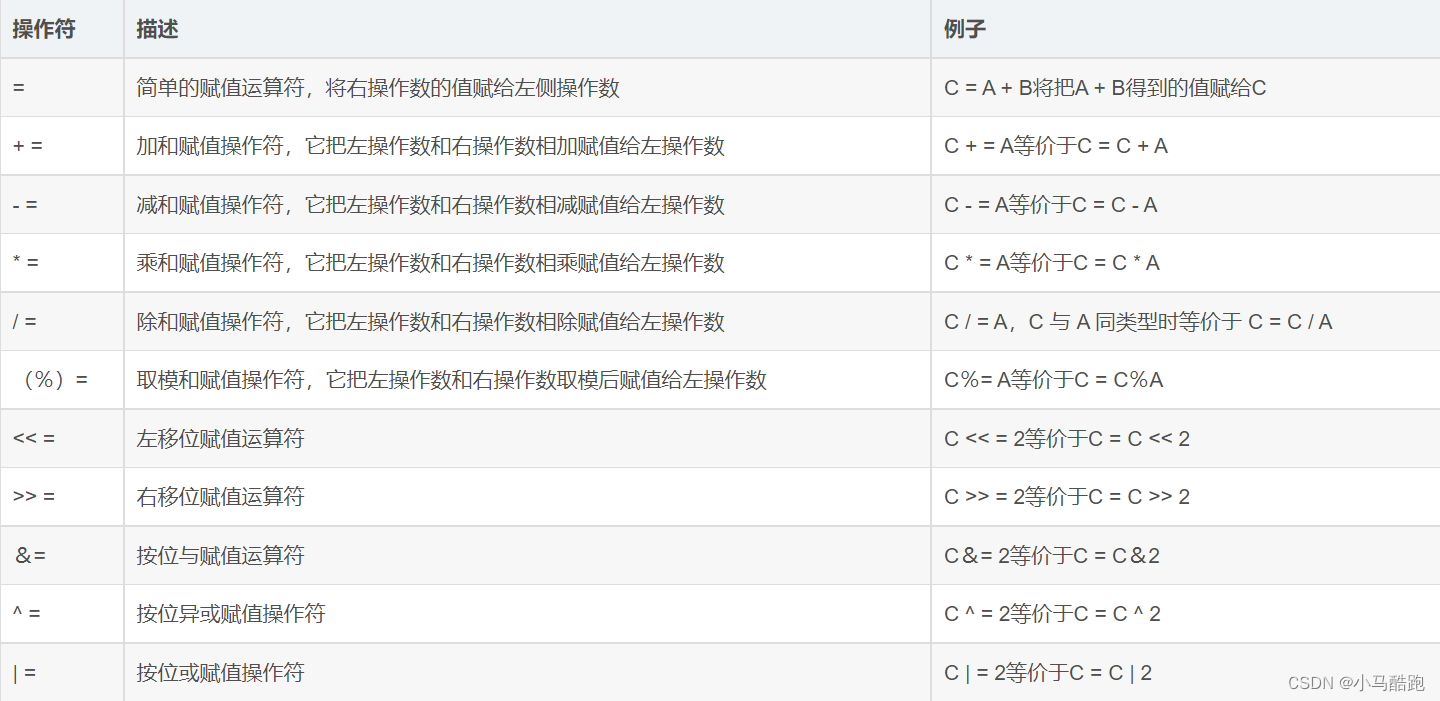
4.赋值运算符:
=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=,
5.逻辑运算符:
//逻辑运算符
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 与(and) 或(or) 非(取反)
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("a && b:"+(a&&b) ); //逻辑与运算:两个变量都为真,结果才为true System.out.println("a || b:"+(a||b)); //逻辑或运算:两个变量有一个为真,则结果才为true System.out.println("! (a && b):"+!(a&&b)); //如果是真,则为假,如果是假则为真。 //短路运算 int c = 5;
boolean d = (c<4)&&(c++<4);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(c); } }
总结:逻辑运算符:

6.三元运算符:
基本语法
语法:条件表达式?表达式1:表达式2;
运算规则:
1、如果条件表达式为true,运算后的结果是表达式1;
2、如果条件表达式为false,运算后的结果是表达式2;
// 三元运算符:
int as = 99;
int bs = 10;
int result = as > bs ? as++ : bs--; //表达式1 先赋值后自增
System.out.println(result);//输出99
System.out.println("a = " + as);//输出 100
System.out.println("b = " + bs);//输出10
// 判断最大值
int an = 56;
int bn = 122;
int cn = 100;
int max1 = an > bn ? an : bn;
int max2 = max1 > cn ? max1 : cn;
//推荐使用第一种
System.out.println(max2);
//三元嵌套
int max3 = an > bn ? an > cn ? an : cn : bn > cn ? bn : cn;
System.out.println(max3);