前言
在golang中,我们比较熟悉的mysql相关的库就是database/sql,这是golang的内置库,该标准库没有具体实现,只列出第三方库需要实现的具体内容。也就是说,这个库只是定义了接口,并没有具体的实现。Go语言为开发数据库驱动定义了一些标准接口,使用标准接口开发的代码,在迁移数据库时,不需要做任何修改(当然双方数据库都遵守标准接口)。下面我将基于golang1.19的源码探究这个库的实现。
源码地址:https://github.com/golang/go/tree/release-branch.go1.19/src/database/sql
一、整体目录结构
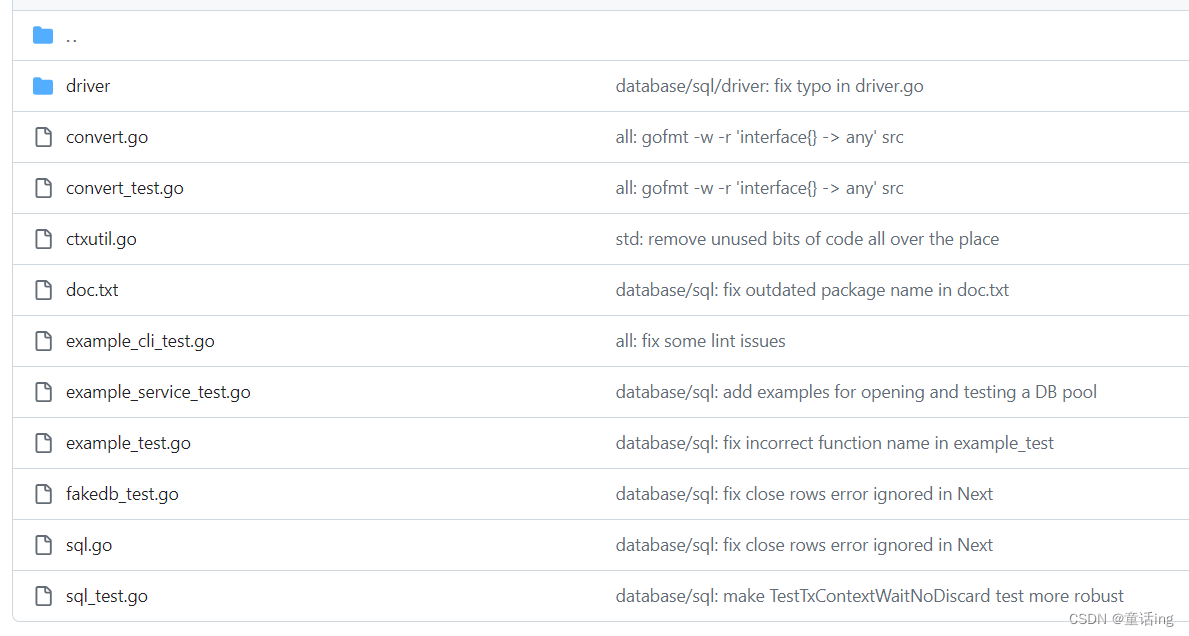
整个目录结构就是这样,包含两个包:sql和driver,这两个包必须一起配合着使用,sql包中主要包含着数据库具体实例、驱动的注册、结果集读取、转换各种定义类型结构等。driver包中主要是与数据库打交道的部分,增删改查的接口定义就在这里面。
sql包:
driver包:
二、driver包
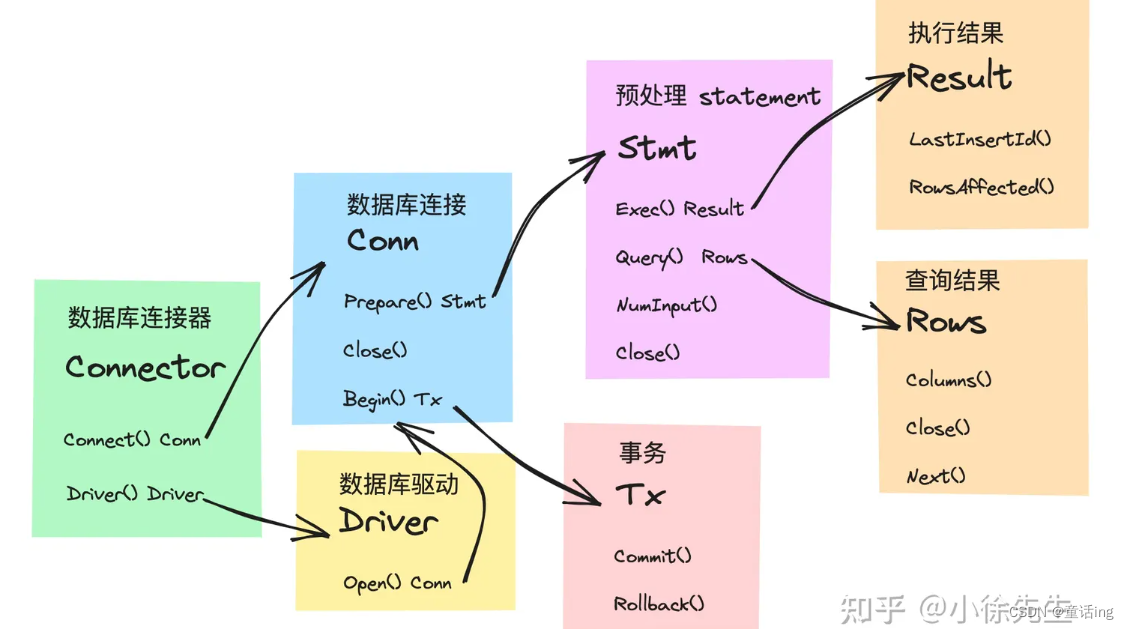
在driver包中,主要有如下的接口定义:
Connector:抽象的数据库连接器,需要具备创建数据库连接以及返回从属的数据库驱动的能力。Driver:抽象的数据库驱动,具备创建数据库连接的能力。Conn:抽象的数据库连接,具备预处理 sql 以及开启事务的能力。Tx:抽象的事务,具备提交和回滚的能力。Statement:抽象的请求预处理状态. 具备实际执行 sql 并返回执行结果的能力。Result/Row:抽象的 sql 执行结果。
1、驱动相关driver.Driver
Driver是一个数据库驱动的接口,定义了 Open(name string) ,该方法返回一个数据库的Conn接口:
// Driver is the interface that must be implemented by a database
// driver.
//
// Database drivers may implement DriverContext for access
// to contexts and to parse the name only once for a pool of connections,
// instead of once per connection.
type Driver interface {
// Open returns a new connection to the database.
// The name is a string in a driver-specific format.
//
// Open may return a cached connection (one previously
// closed), but doing so is unnecessary; the sql package
// maintains a pool of idle connections for efficient re-use.
//
// The returned connection is only used by one goroutine at a
// time.
Open(name string) (Conn, error)
}
在上面的源码中,我们可以清晰知道,Driver接口是必须要被所有的数据库驱动程序实现的,提供而一个Open方法用于返回一个连接,这个连接可能是缓存的有效的,也可能是新建的连接。同时也提供了一个DriverContext接口,数据库驱动程序可以实现DriverContext以访问上下文,并仅为连接池解析一次名称,而不是每个连接解析一次。
DriverContext接口提供了一个OpenConnector方法用于返回一个连接器,在连接器中去获取对应的连接。连接器接口Connector提供了两个方法,Connect和Driver,其中Connect用于获取连接,并且可以附带参数ctx,Driver用于获取当前这个连接器的的驱动程序。
// If a Driver implements DriverContext, then sql.DB will call
// OpenConnector to obtain a Connector and then invoke
// that Connector's Connect method to obtain each needed connection,
// instead of invoking the Driver's Open method for each connection.
// The two-step sequence allows drivers to parse the name just once
// and also provides access to per-Conn contexts.
type DriverContext interface {
// OpenConnector must parse the name in the same format that Driver.Open
// parses the name parameter.
OpenConnector(name string) (Connector, error)
}
// A Connector represents a driver in a fixed configuration
// and can create any number of equivalent Conns for use
// by multiple goroutines.
//
// A Connector can be passed to sql.OpenDB, to allow drivers
// to implement their own sql.DB constructors, or returned by
// DriverContext's OpenConnector method, to allow drivers
// access to context and to avoid repeated parsing of driver
// configuration.
//
// If a Connector implements io.Closer, the sql package's DB.Close
// method will call Close and return error (if any).
type Connector interface {
// Connect returns a connection to the database.
// Connect may return a cached connection (one previously
// closed), but doing so is unnecessary; the sql package
// maintains a pool of idle connections for efficient re-use.
//
// The provided context.Context is for dialing purposes only
// (see net.DialContext) and should not be stored or used for
// other purposes. A default timeout should still be used
// when dialing as a connection pool may call Connect
// asynchronously to any query.
//
// The returned connection is only used by one goroutine at a
// time.
Connect(context.Context) (Conn, error)
// Driver returns the underlying Driver of the Connector,
// mainly to maintain compatibility with the Driver method
// on sql.DB.
Driver() Driver
}
2、驱动连接:driver.Conn
在驱动连接driver.Conn中,包含着预处理结构statement、网络连接的关闭、以及开启一个事务的方式。
type Conn interface {
// Prepare returns a prepared statement, bound to this connection.
Prepare(query string) (Stmt, error)
// Close invalidates and potentially stops any current
// prepared statements and transactions, marking this
// connection as no longer in use.
//
// Because the sql package maintains a free pool of
// connections and only calls Close when there's a surplus of
// idle connections, it shouldn't be necessary for drivers to
// do their own connection caching.
//
// Drivers must ensure all network calls made by Close
// do not block indefinitely (e.g. apply a timeout).
Close() error
// Begin starts and returns a new transaction.
//
// Deprecated: Drivers should implement ConnBeginTx instead (or additionally).
Begin() (Tx, error)
}
Prepare:返回与当前连接相关的执行SQL语句的准备状态(Stmt),可以进行查询、删除等操作。
Close:关闭当前的链接,执行释放连接拥有的资源等清理工作。
Begin: // 返回一个代表事务处理的Tx,通过它可以进行查询、更新等操作,或者对事务进行回滚、递交。
新版本中,Begin方法已经不推荐了,被ConnBeginTx代替了, 新版本中的Begin方法多提供了入参ctx和额外的可选参数opts,便于扩展和控制。
// ConnBeginTx enhances the Conn interface with context and TxOptions.
type ConnBeginTx interface {
// BeginTx starts and returns a new transaction.
// If the context is canceled by the user the sql package will
// call Tx.Rollback before discarding and closing the connection.
//
// This must check opts.Isolation to determine if there is a set
// isolation level. If the driver does not support a non-default
// level and one is set or if there is a non-default isolation level
// that is not supported, an error must be returned.
//
// This must also check opts.ReadOnly to determine if the read-only
// value is true to either set the read-only transaction property if supported
// or return an error if it is not supported.
BeginTx(ctx context.Context, opts TxOptions) (Tx, error)
}
3、预处理结构:Stmt
// Stmt is a prepared statement. It is bound to a Conn and not
// used by multiple goroutines concurrently.
type Stmt interface {
// Close closes the statement.
//
// As of Go 1.1, a Stmt will not be closed if it's in use
// by any queries.
//
// Drivers must ensure all network calls made by Close
// do not block indefinitely (e.g. apply a timeout).
Close() error
// NumInput returns the number of placeholder parameters.
//
// If NumInput returns >= 0, the sql package will sanity check
// argument counts from callers and return errors to the caller
// before the statement's Exec or Query methods are called.
//
// NumInput may also return -1, if the driver doesn't know
// its number of placeholders. In that case, the sql package
// will not sanity check Exec or Query argument counts.
NumInput() int
// Exec executes a query that doesn't return rows, such
// as an INSERT or UPDATE.
//
// Deprecated: Drivers should implement StmtExecContext instead (or additionally).
Exec(args []Value) (Result, error)
// Query executes a query that may return rows, such as a
// SELECT.
//
// Deprecated: Drivers should implement StmtQueryContext instead (or additionally).
Query(args []Value) (Rows, error)
}
// StmtExecContext enhances the Stmt interface by providing Exec with context.
type StmtExecContext interface {
// ExecContext executes a query that doesn't return rows, such
// as an INSERT or UPDATE.
//
// ExecContext must honor the context timeout and return when it is canceled.
ExecContext(ctx context.Context, args []NamedValue) (Result, error)
}
// StmtQueryContext enhances the Stmt interface by providing Query with context.
type StmtQueryContext interface {
// QueryContext executes a query that may return rows, such as a
// SELECT.
//
// QueryContext must honor the context timeout and return when it is canceled.
QueryContext(ctx context.Context, args []NamedValue) (Rows, error)
}
Close:关闭当前的连接状态,但如果当前正在执行query,query还是会有效返回rows数据。
NumInput:返回当前预留参数的个数,当返回>=0时,数据库驱动会智能检查调用者的参数。 当数据库驱动包不知道预留参数的时候,返回-1。
Exec:执行Prepare准备好的SQL,传入参数执行Update/Insert等操作,返回Result数据,Result中包含最后插入的自增主键序号(LastInsertId)和受影响的行数(RowAffected)。
Query:执行Prepare准备好的SQL,传入需要的参数执行select操作,返回Rows结果集。
4、执行结果 driver.Result
// Result is the result of a query execution.
type Result interface {
// LastInsertId returns the database's auto-generated ID
// after, for example, an INSERT into a table with primary
// key.
LastInsertId() (int64, error)
// RowsAffected returns the number of rows affected by the
// query.
RowsAffected() (int64, error)
}
5、查询结果:driver.Rows
// Rows is an iterator over an executed query's results.
type Rows interface {
// 该函数返回查询数据库表的字段信息,这个返回的slice和SQL查询的字段一一对应,
// 而不是返回整张表的所有字段。
Columns() []string
// 用来关闭Rows迭代器
Close() error
// 该函数用来返回下一条数据,把数据赋值给dest .
// dest里面元素必须是driver.Value的值(string除外),返回的数据里面所有的 string 都必须转换成
// []byte.如果最后没有数据了,Next 函数返回 io.EOF。
Next(dest []Value) error
}
可以看到,在新版的源码中,Exec和Query已经被单独拎出去定义了接口,方法中只是为了增加ctx参数,这也是golang为了保持向下兼容而做的,试想,如果直接在原有的接口定义的加入ctx,升级golang版本的时候这块儿肯定得花很大功夫去改造。
6、driver.RowsAffected
RowsAffected 不是别的东西,实际上只是 int64 的别名,但它实现了Result接口,用于底层实现 Result 的表示方式,构建Exec方法返回的结果集。
// RowsAffected implements Result for an INSERT or UPDATE operation
// which mutates a number of rows.
type RowsAffected int64
var _ Result = RowsAffected(0)
func (RowsAffected) LastInsertId() (int64, error) {
return 0, errors.New("LastInsertId is not supported by this driver")
}
func (v RowsAffected) RowsAffected() (int64, error) {
return int64(v), nil
}
7、driver.Value
Value 其实是一个空接口,可以容纳任何的数据。
// diver 的 Value 是驱动必须能够操作的 Value,Value要么是nil,要么是下面任意一种:
//
// int64
// float64
// bool
// []byte
// string [*] 除了Rows.Next,返回的不能是string
// time.Time
//
type Value interface{}
8、Value定义转换相关
在driver/types.go中,还定义了ValueConverter将一个普通的值(any)转换成driver.Value的接口、Valuer接口用于获取driver.Value等,就不逐个展开了。
// ValueConverter is the interface providing the ConvertValue method.
//
// Various implementations of ValueConverter are provided by the
// driver package to provide consistent implementations of conversions
// between drivers. The ValueConverters have several uses:
//
// - converting from the Value types as provided by the sql package
// into a database table's specific column type and making sure it
// fits, such as making sure a particular int64 fits in a
// table's uint16 column.
//
// - converting a value as given from the database into one of the
// driver Value types.
//
// - by the sql package, for converting from a driver's Value type
// to a user's type in a scan.
type ValueConverter interface {
// ConvertValue converts a value to a driver Value.
ConvertValue(v any) (Value, error)
}
// Valuer is the interface providing the Value method.
//
// Types implementing Valuer interface are able to convert
// themselves to a driver Value.
type Valuer interface {
// Value returns a driver Value.
// Value must not panic.
Value() (Value, error)
}
三、sql包
在sql包中,包含着我们最熟悉的Open方法,返回一个DB实例,这个DB实例,对应为数据库的具象化实例。内部维护着连接池相关的信息。
1、Open方法
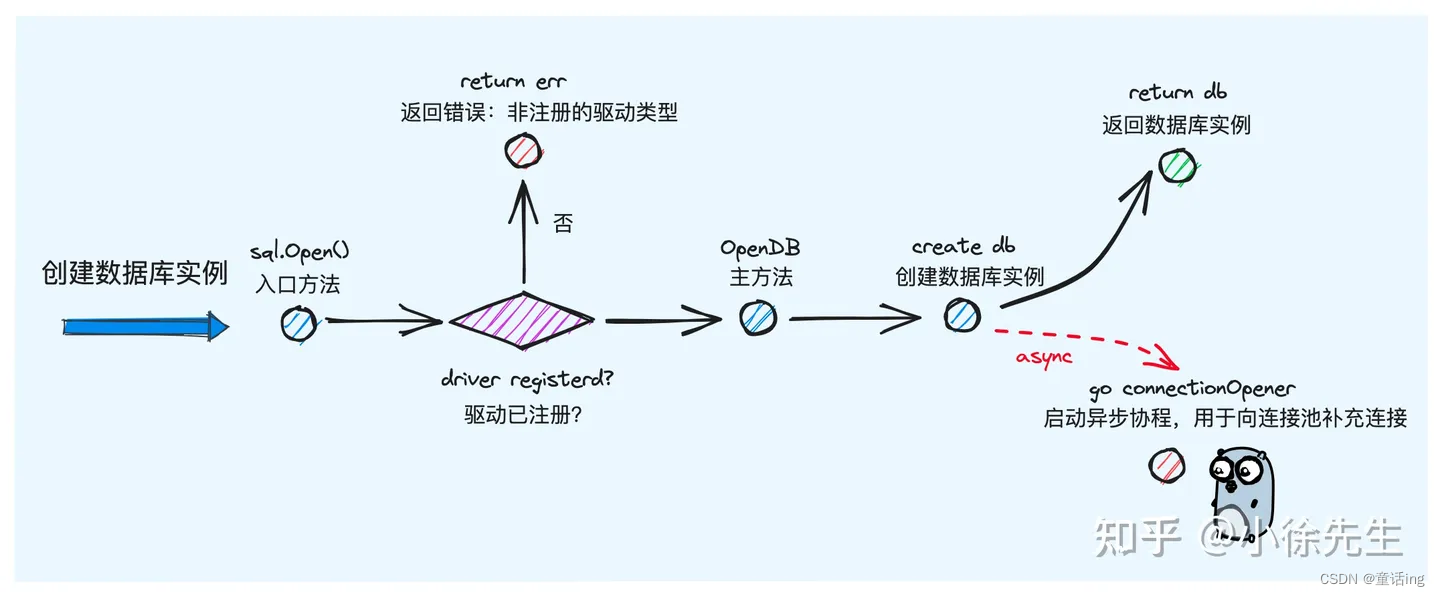
Open方法返回一个db实例,且这个DB实例是可以在多个gorountine中使用的,当调用Open方法的时候,会先从一个全局的驱动注册器(drivers)中获取对应的驱动,如果没注册对应的驱动,则会出错。如果这个驱动实现了DriverContext接口,则会调用OpenConnector方法创建一个对应的连接器,用于连接数据库。否则调用dsnConnector结构,组装返回一个对应的db实例。
// Open opens a database specified by its database driver name and a
// driver-specific data source name, usually consisting of at least a
// database name and connection information.
//
// Most users will open a database via a driver-specific connection
// helper function that returns a *DB. No database drivers are included
// in the Go standard library. See https://golang.org/s/sqldrivers for
// a list of third-party drivers.
//
// Open may just validate its arguments without creating a connection
// to the database. To verify that the data source name is valid, call
// Ping.
//
// The returned DB is safe for concurrent use by multiple goroutines
// and maintains its own pool of idle connections. Thus, the Open
// function should be called just once. It is rarely necessary to
// close a DB.
func Open(driverName, dataSourceName string) (*DB, error) {
driversMu.RLock()
driveri, ok := drivers[driverName]
driversMu.RUnlock()
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("sql: unknown driver %q (forgotten import?)", driverName)
}
if driverCtx, ok := driveri.(driver.DriverContext); ok {
connector, err := driverCtx.OpenConnector(dataSourceName)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return OpenDB(connector), nil
}
return OpenDB(dsnConnector{dsn: dataSourceName, driver: driveri}), nil
}
2、驱动注册:sql.Register
在各种驱动的实现中,一般都会在init方法中调用database/sql提供的注册方法注册对应的驱动。但同时只允许注册一种类型的驱动,否则会panic。
全局驱动注册器
driversMu sync.RWMutex
drivers = make(map[string]driver.Driver)
// 驱动注册
func Register(name string, driver driver.Driver) {
driversMu.Lock()
defer driversMu.Unlock()
if driver == nil {
panic("sql: Register driver is nil")
}
if _, dup := drivers[name]; dup {
panic("sql: Register called twice for driver " + name)
}
drivers[name] = driver
}
3、dsn驱动连接器:dsnConnector
该结构很简单的实现了两个方法,一个是调用驱动的Open方法创建一个连接,另一个则是返回当前的驱动实例。
sql.go dsn驱动连接器
type dsnConnector struct {
dsn string
driver driver.Driver
}
func (t dsnConnector) Connect(_ context.Context) (driver.Conn, error) {
return t.driver.Open(t.dsn)
}
func (t dsnConnector) Driver() driver.Driver {
return t.driver
}
3、OpenDB方法
从上面我们知道,最终获得连接器后,都会调用这个方法创建一个db实例返回。
// OpenDB opens a database using a Connector, allowing drivers to
// bypass a string based data source name.
//
// Most users will open a database via a driver-specific connection
// helper function that returns a *DB. No database drivers are included
// in the Go standard library. See https://golang.org/s/sqldrivers for
// a list of third-party drivers.
//
// OpenDB may just validate its arguments without creating a connection
// to the database. To verify that the data source name is valid, call
// Ping.
//
// The returned DB is safe for concurrent use by multiple goroutines
// and maintains its own pool of idle connections. Thus, the OpenDB
// function should be called just once. It is rarely necessary to
// close a DB.
func OpenDB(c driver.Connector) *DB {
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
db := &DB{
connector: c,
openerCh: make(chan struct{}, connectionRequestQueueSize),
lastPut: make(map[*driverConn]string),
connRequests: make(map[uint64]chan connRequest),
stop: cancel,
}
go db.connectionOpener(ctx)
return db
}
同时,我们还注意到,OpenDB方法中,除了正常的构建一个DB实例外,还起了一个协程,并且传入ctx作为入参,这个协程主要作用就是在接收到通道 openerCh 有数据(在真正执行query、exec时候发现连接不够用或者driver.ErrBadConn错误时候给这个通道发送消息)的时候,调用openNewConnection创建一个新的连接。传入ctx主要是为了便于控制协程的退出。因此从这里我们知道,连接池中的连接并不是一开始就创建好了的,而是在真正执行sql的时候才会创建,因此,不必担心调用多次Open方法创建多个DB实例会导致创建很多连接。
// Runs in a separate goroutine, opens new connections when requested.
func (db *DB) connectionOpener(ctx context.Context) {
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return
case <-db.openerCh:
db.openNewConnection(ctx)
}
}
}
///openNewConnection//
// Open one new connection
func (db *DB) openNewConnection(ctx context.Context) {
// maybeOpenNewConnections has already executed db.numOpen++ before it sent
// on db.openerCh. This function must execute db.numOpen-- if the
// connection fails or is closed before returning.
ci, err := db.connector.Connect(ctx)
db.mu.Lock()
defer db.mu.Unlock()
if db.closed {
if err == nil {
ci.Close()
}
db.numOpen--
return
}
if err != nil {
db.numOpen--
db.putConnDBLocked(nil, err)
db.maybeOpenNewConnections()
return
}
dc := &driverConn{
db: db,
createdAt: nowFunc(),
returnedAt: nowFunc(),
ci: ci,
}
if db.putConnDBLocked(dc, err) {
db.addDepLocked(dc, dc)
} else {
db.numOpen--
ci.Close()
}
}
/maybeOpenNewConnections///
// Assumes db.mu is locked.
// If there are connRequests and the connection limit hasn't been reached,
// then tell the connectionOpener to open new connections.
func (db *DB) maybeOpenNewConnections() {
numRequests := len(db.connRequests)
if db.maxOpen > 0 {
numCanOpen := db.maxOpen - db.numOpen
if numRequests > numCanOpen {
numRequests = numCanOpen
}
}
for numRequests > 0 {
db.numOpen++ // optimistically
numRequests--
if db.closed {
return
}
db.openerCh <- struct{}{}
}
}
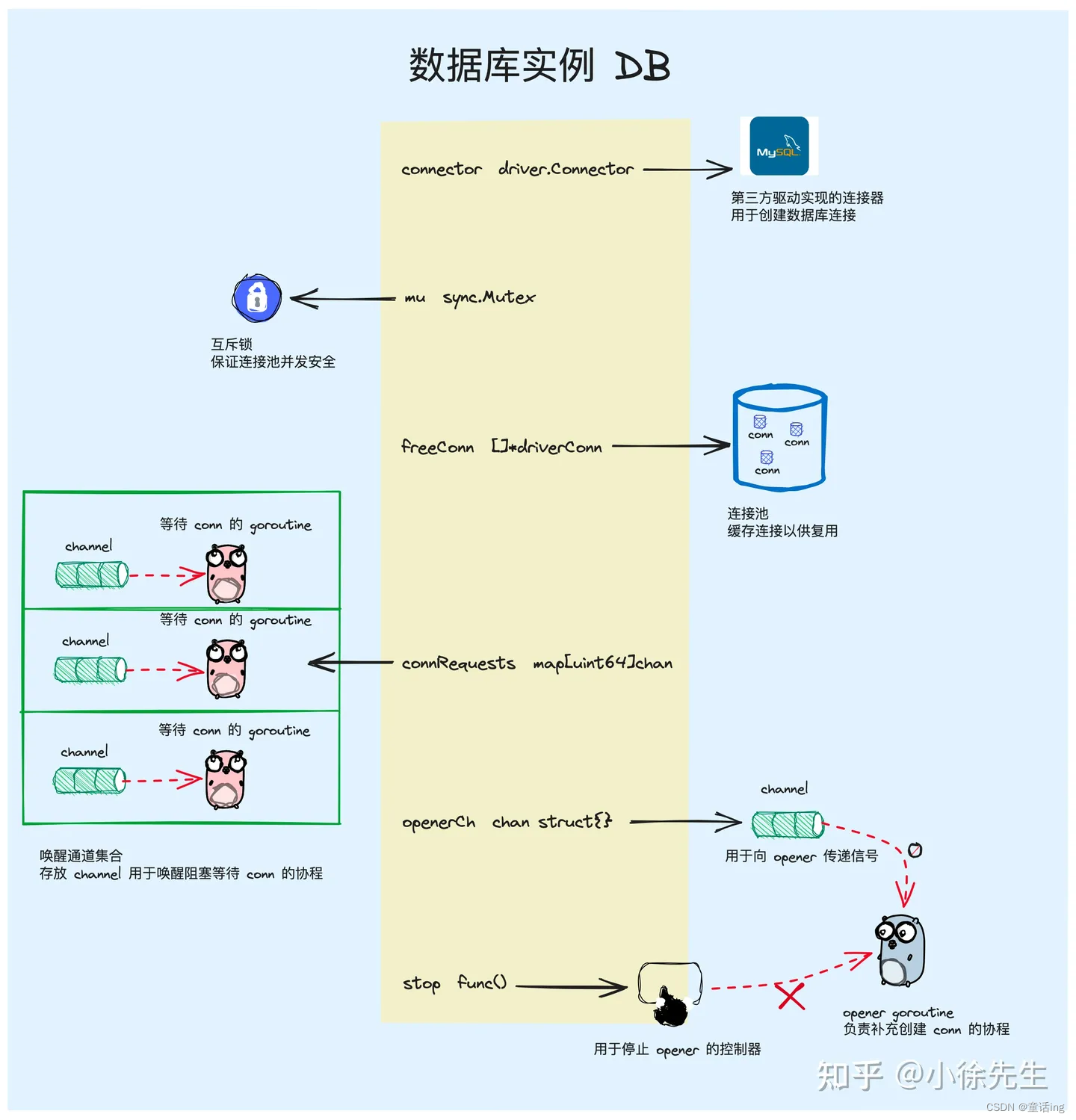
4、数据库实例:sql.DB
整个DB实例是sql包中非常核心的部分,其中有几个主要的字段,其他字段大部分都是和连接池参数相关的,整体围绕着连接池进行设计,方便复用连接:
connector:用于创建数据库连接的抽象连接器,由第三方数据库提供具体实现。freeConn:数据库连接池,缓存可用的连接以供后续复用。connRequests:唤醒通道集合,和阻塞等待连接的协程是一对一的关系。openerCh:创建连接信号通道. 用于向连接创建协程 opener goroutine 发送信号。stop:连接创建协程 opener goroutine 的终止器,用于停止该协程。
// DB is a database handle representing a pool of zero or more
// underlying connections. It's safe for concurrent use by multiple
// goroutines.
//
// The sql package creates and frees connections automatically; it
// also maintains a free pool of idle connections. If the database has
// a concept of per-connection state, such state can be reliably observed
// within a transaction (Tx) or connection (Conn). Once DB.Begin is called, the
// returned Tx is bound to a single connection. Once Commit or
// Rollback is called on the transaction, that transaction's
// connection is returned to DB's idle connection pool. The pool size
// can be controlled with SetMaxIdleConns.
type DB struct {
// Atomic access only. At top of struct to prevent mis-alignment
// on 32-bit platforms. Of type time.Duration.
waitDuration int64 // Total time waited for new connections.
connector driver.Connector
// numClosed is an atomic counter which represents a total number of
// closed connections. Stmt.openStmt checks it before cleaning closed
// connections in Stmt.css.
numClosed uint64
mu sync.Mutex // protects following fields
freeConn []*driverConn // free connections ordered by returnedAt oldest to newest
connRequests map[uint64]chan connRequest
nextRequest uint64 // Next key to use in connRequests.
numOpen int // number of opened and pending open connections
// Used to signal the need for new connections
// a goroutine running connectionOpener() reads on this chan and
// maybeOpenNewConnections sends on the chan (one send per needed connection)
// It is closed during db.Close(). The close tells the connectionOpener
// goroutine to exit.
openerCh chan struct{}
closed bool
dep map[finalCloser]depSet
lastPut map[*driverConn]string // stacktrace of last conn's put; debug only
maxIdleCount int // zero means defaultMaxIdleConns; negative means 0
maxOpen int // <= 0 means unlimited
maxLifetime time.Duration // maximum amount of time a connection may be reused
maxIdleTime time.Duration // maximum amount of time a connection may be idle before being closed
cleanerCh chan struct{}
waitCount int64 // Total number of connections waited for.
maxIdleClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to idle count.
maxIdleTimeClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to idle time.
maxLifetimeClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to max connection lifetime limit.
stop func() // stop cancels the connection opener.
}
DB结构主要作用如下:
DB实例中关乎我们sql执行的最重要的两个方法Exec和Query,下面将介绍它们。
5、ExecContext
ExecContext主要用于执行delete、update、insert等语句,可以看到,在该方法中会对连接进行重试,如果连接过期了(exec方法返回了driver.ErrBadConn错误),那么将会重试。重试过程中携带的连接建立策略是cachedOrNewConn,如果重试次数达到上限并且连接被标记为isBadConn (一般是mysql server主动断开连接使得连接失效),那么将直接调用exec方法,将连接的建立策略修改为alwaysNewConn。
// ExecContext executes a query without returning any rows.
// The args are for any placeholder parameters in the query.
func (db *DB) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error) {
var res Result
var err error
var isBadConn bool
for i := 0; i < maxBadConnRetries; i++ {
res, err = db.exec(ctx, query, args, cachedOrNewConn)
isBadConn = errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn)
if !isBadConn {
break
}
}
if isBadConn {
return db.exec(ctx, query, args, alwaysNewConn)
}
return res, err
}
连接建立策略
- alwaysNewConn:表示强制请求建立一个新的数据库连接。
- cachedOrNewConn:表示从连接池中获取,如果没有,那么将会阻塞等待连接可用;或者也可以请求创建一个新的连接。
// connReuseStrategy determines how (*DB).conn returns database connections.
type connReuseStrategy uint8
const (
// alwaysNewConn forces a new connection to the database.
alwaysNewConn connReuseStrategy = iota
// cachedOrNewConn returns a cached connection, if available, else waits
// for one to become available (if MaxOpenConns has been reached) or
// creates a new database connection.
cachedOrNewConn
)
/ 核心exec方法
func (db *DB) exec(ctx context.Context, query string, args []any, strategy connReuseStrategy) (Result, error) {
dc, err := db.conn(ctx, strategy)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return db.execDC(ctx, dc, dc.releaseConn, query, args)
}
6、QueryContext
Query方法也是类似,这里不再赘述。
// QueryContext executes a query that returns rows, typically a SELECT.
// The args are for any placeholder parameters in the query.
func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error) {
var rows *Rows
var err error
var isBadConn bool
for i := 0; i < maxBadConnRetries; i++ {
rows, err = db.query(ctx, query, args, cachedOrNewConn)
isBadConn = errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn)
if !isBadConn {
break
}
}
if isBadConn {
return db.query(ctx, query, args, alwaysNewConn)
}
return rows, err
}
核心query
func (db *DB) query(ctx context.Context, query string, args []any, strategy connReuseStrategy) (*Rows, error) {
dc, err := db.conn(ctx, strategy)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return db.queryDC(ctx, nil, dc, dc.releaseConn, query, args)
}
在 queryDC 、execDC方法中,主要都是依赖于具体的驱动实现来完成请求的执行,主要完成下面几个动作:
- 首先通过连接将 sql 预处理成 statement。
- 向数据库发包执行请求,并返回对应的结果。
- 最后需要将连接放回连接池,倘若连接池已满或者连接已过期,则需要关闭连接。
// queryDC executes a query on the given connection.
// The connection gets released by the releaseConn function.
// The ctx context is from a query method and the txctx context is from an
// optional transaction context.
func (db *DB) queryDC(ctx, txctx context.Context, dc *driverConn, releaseConn func(error), query string, args []any) (*Rows, error) {
queryerCtx, ok := dc.ci.(driver.QueryerContext)
var queryer driver.Queryer
if !ok {
queryer, ok = dc.ci.(driver.Queryer)
}
if ok {
var nvdargs []driver.NamedValue
var rowsi driver.Rows
var err error
withLock(dc, func() {
nvdargs, err = driverArgsConnLocked(dc.ci, nil, args)
if err != nil {
return
}
rowsi, err = ctxDriverQuery(ctx, queryerCtx, queryer, query, nvdargs)
})
if err != driver.ErrSkip {
if err != nil {
releaseConn(err)
return nil, err
}
// Note: ownership of dc passes to the *Rows, to be freed
// with releaseConn.
rows := &Rows{
dc: dc,
releaseConn: releaseConn,
rowsi: rowsi,
}
rows.initContextClose(ctx, txctx)
return rows, nil
}
}
var si driver.Stmt
var err error
withLock(dc, func() {
si, err = ctxDriverPrepare(ctx, dc.ci, query)
})
if err != nil {
releaseConn(err)
return nil, err
}
ds := &driverStmt{Locker: dc, si: si}
rowsi, err := rowsiFromStatement(ctx, dc.ci, ds, args...)
if err != nil {
ds.Close()
releaseConn(err)
return nil, err
}
// Note: ownership of ci passes to the *Rows, to be freed
// with releaseConn.
rows := &Rows{
dc: dc,
releaseConn: releaseConn,
rowsi: rowsi,
closeStmt: ds,
}
rows.initContextClose(ctx, txctx)
return rows, nil
}
7、连接建立:db.conn
从上面我们知道,无论是query还是exec,都会进行连接的建立,并且还有策略的区别。下面我们将进行两种策略下连接建立的探索。
从上面我们知道,连接的获取有两种策略,一种是alwaysNewConn,一种是cachedOrNewConn。
- 在cachedOrNewConn策略下,a:如果有空闲连接可用,那么将从连接池中获取连接并调用expire方法检查连接是否有效,如果失效就返回driver.ErrBadConn,接下来会调用resetSession方法,检查这个连接是否需要重置session信息,如果需要则重置,重制失败并且返回driver.ErrBadConn会关闭当前连接,然后再进行重试。b:如果没有连接可用,且连接达到上限
db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen,则会将当前协程挂起,建立对应的 channel 添加到 connRequests map 中,等待有连接释放时被唤醒。 - 在alwaysNewConn策略下,a:如果没有连接可用,且连接达到上限
db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen,则会将当前协程挂起,建立对应的 channel 添加到 connRequests map 中,等待有连接释放时被唤醒。b:如果连接数未达上限,则会调用第三方驱动的 connector 完成新连接的创建。
// conn returns a newly-opened or cached *driverConn.
func (db *DB) conn(ctx context.Context, strategy connReuseStrategy) (*driverConn, error) {
db.mu.Lock()
if db.closed {
db.mu.Unlock()
return nil, errDBClosed
}
// Check if the context is expired.
select {
default:
case <-ctx.Done():
db.mu.Unlock()
return nil, ctx.Err()
}
lifetime := db.maxLifetime
// Prefer a free connection, if possible.
last := len(db.freeConn) - 1
if strategy == cachedOrNewConn && last >= 0 {
// Reuse the lowest idle time connection so we can close
// connections which remain idle as soon as possible.
conn := db.freeConn[last]
db.freeConn = db.freeConn[:last]
conn.inUse = true
if conn.expired(lifetime) {
db.maxLifetimeClosed++
db.mu.Unlock()
conn.Close()
return nil, driver.ErrBadConn
}
db.mu.Unlock()
// Reset the session if required.
if err := conn.resetSession(ctx); errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn) {
conn.Close()
return nil, err
}
return conn, nil
}
// Out of free connections or we were asked not to use one. If we're not
// allowed to open any more connections, make a request and wait.
if db.maxOpen > 0 && db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen {
// Make the connRequest channel. It's buffered so that the
// connectionOpener doesn't block while waiting for the req to be read.
req := make(chan connRequest, 1)
reqKey := db.nextRequestKeyLocked()
db.connRequests[reqKey] = req
db.waitCount++
db.mu.Unlock()
waitStart := nowFunc()
// Timeout the connection request with the context.
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
// Remove the connection request and ensure no value has been sent
// on it after removing.
db.mu.Lock()
delete(db.connRequests, reqKey)
db.mu.Unlock()
atomic.AddInt64(&db.waitDuration, int64(time.Since(waitStart)))
select {
default:
case ret, ok := <-req:
if ok && ret.conn != nil {
db.putConn(ret.conn, ret.err, false)
}
}
return nil, ctx.Err()
case ret, ok := <-req:
atomic.AddInt64(&db.waitDuration, int64(time.Since(waitStart)))
if !ok {
return nil, errDBClosed
}
// Only check if the connection is expired if the strategy is cachedOrNewConns.
// If we require a new connection, just re-use the connection without looking
// at the expiry time. If it is expired, it will be checked when it is placed
// back into the connection pool.
// This prioritizes giving a valid connection to a client over the exact connection
// lifetime, which could expire exactly after this point anyway.
if strategy == cachedOrNewConn && ret.err == nil && ret.conn.expired(lifetime) {
db.mu.Lock()
db.maxLifetimeClosed++
db.mu.Unlock()
ret.conn.Close()
return nil, driver.ErrBadConn
}
if ret.conn == nil {
return nil, ret.err
}
// Reset the session if required.
if err := ret.conn.resetSession(ctx); errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn) {
ret.conn.Close()
return nil, err
}
return ret.conn, ret.err
}
}
db.numOpen++ // optimistically
db.mu.Unlock()
ci, err := db.connector.Connect(ctx)
if err != nil {
db.mu.Lock()
db.numOpen-- // correct for earlier optimism
db.maybeOpenNewConnections()
db.mu.Unlock()
return nil, err
}
db.mu.Lock()
dc := &driverConn{
db: db,
createdAt: nowFunc(),
returnedAt: nowFunc(),
ci: ci,
inUse: true,
}
db.addDepLocked(dc, dc)
db.mu.Unlock()
return dc, nil
}
8、连接重置:resetSession
resetSession方法是用于重置数据库会话的方法。当调用resetSession方法时,会话将被重置为初始状态,包括清除任何未提交的事务、关闭任何打开的连接以及清除任何会话级别的设置。这可以帮助确保会话处于干净的状态,以便进行下一个操作或查询。
// resetSession checks if the driver connection needs the
// session to be reset and if required, resets it.
func (dc *driverConn) resetSession(ctx context.Context) error {
dc.Lock()
defer dc.Unlock()
if !dc.needReset {
return nil
}
if cr, ok := dc.ci.(driver.SessionResetter); ok {
return cr.ResetSession(ctx)
}
return nil
}
9、连接池相关可配置参数
func (db *DB) SetConnMaxIdleTime(d time.Duration) // 空闲连接生存的最长时间
func (db *DB) SetConnMaxLifetime(d time.Duration) // 连接存活的最长时间,也就是这个连接能够重复使用的最长时间。设置为0表示永久复用,但可能真正执行的时候会收到BadConn的错误日志,因为mysql server可能设置了wait_timeout、超时后将主动断开这个连接。
func (db *DB) SetMaxOpenConns(n int) // 最大连接数
func (db *DB) SetMaxIdleConns(n int) // 最大空闲连接数,最大不能超过MaxOpenConns
10、可监控指标
在sql包中还有一个结构叫DBStats,其中的字段主要都是描述整体连接的一些使用情况,并且可以通过Stats方法能够获取这些指标,方便我们对这块儿进行一些监控等。
// DBStats contains database statistics.
type DBStats struct {
MaxOpenConnections int // Maximum number of open connections to the database.
// Pool Status
OpenConnections int // The number of established connections both in use and idle.
InUse int // The number of connections currently in use.
Idle int // The number of idle connections.
// Counters
WaitCount int64 // The total number of connections waited for.
WaitDuration time.Duration // The total time blocked waiting for a new connection.
MaxIdleClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetMaxIdleConns.
MaxIdleTimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxIdleTime.
MaxLifetimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxLifetime.
}
// Stats returns database statistics.
func (db *DB) Stats() DBStats {
wait := atomic.LoadInt64(&db.waitDuration)
db.mu.Lock()
defer db.mu.Unlock()
stats := DBStats{
MaxOpenConnections: db.maxOpen,
Idle: len(db.freeConn),
OpenConnections: db.numOpen,
InUse: db.numOpen - len(db.freeConn),
WaitCount: db.waitCount,
WaitDuration: time.Duration(wait),
MaxIdleClosed: db.maxIdleClosed,
MaxIdleTimeClosed: db.maxIdleTimeClosed,
MaxLifetimeClosed: db.maxLifetimeClosed,
}
return stats
}
最后,我们借助参考中的第二篇文献中的两张图总结请求的执行流程、连接获取。
- 创建数据库实例
 * 请求执行流程
* 请求执行流程
- 数据库连接的获取
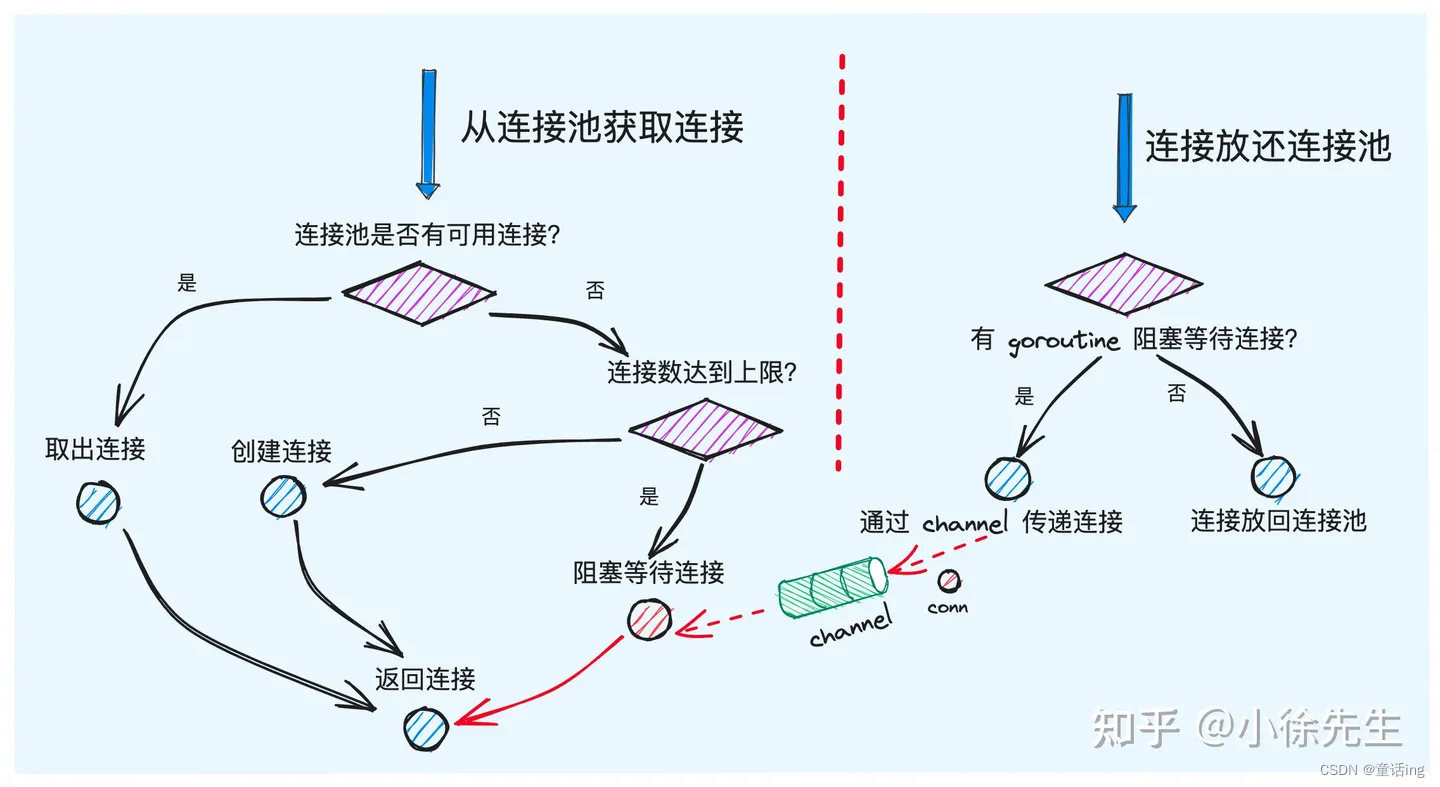
- 连接的清理
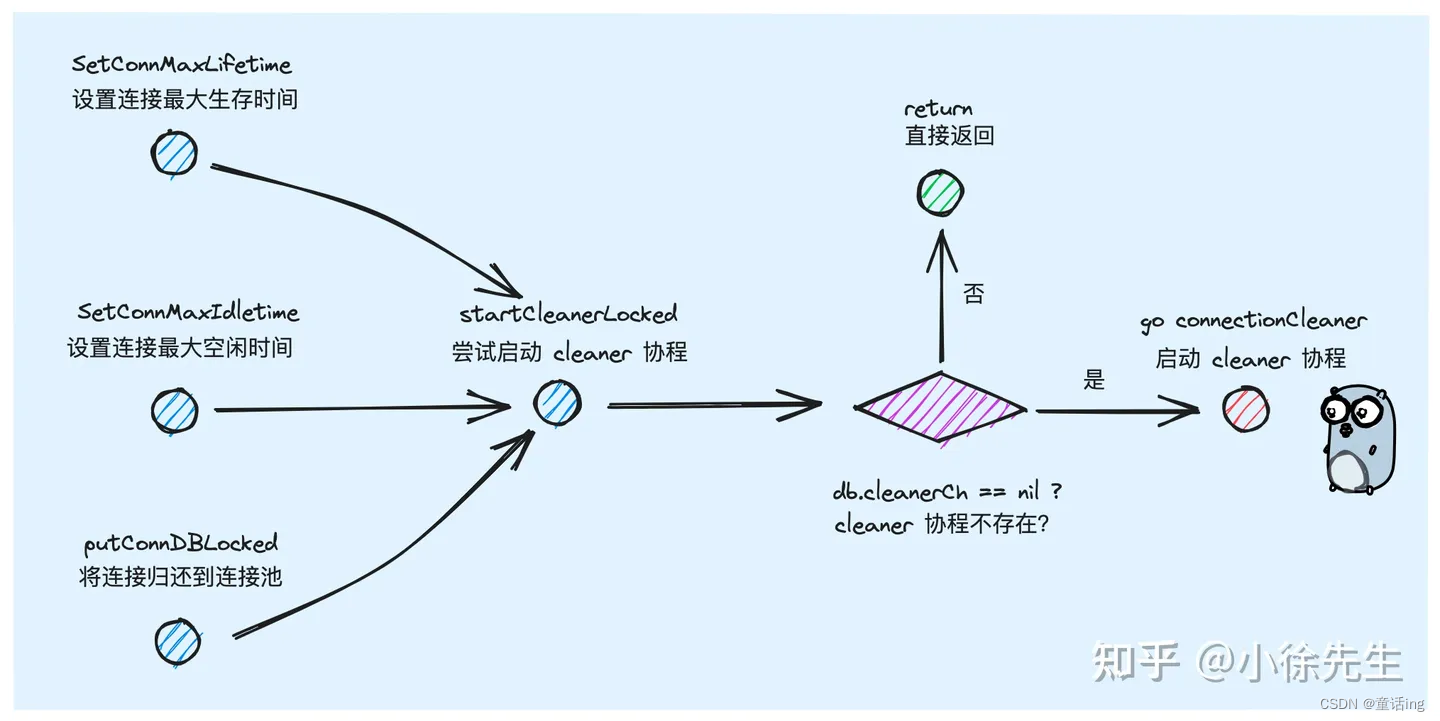
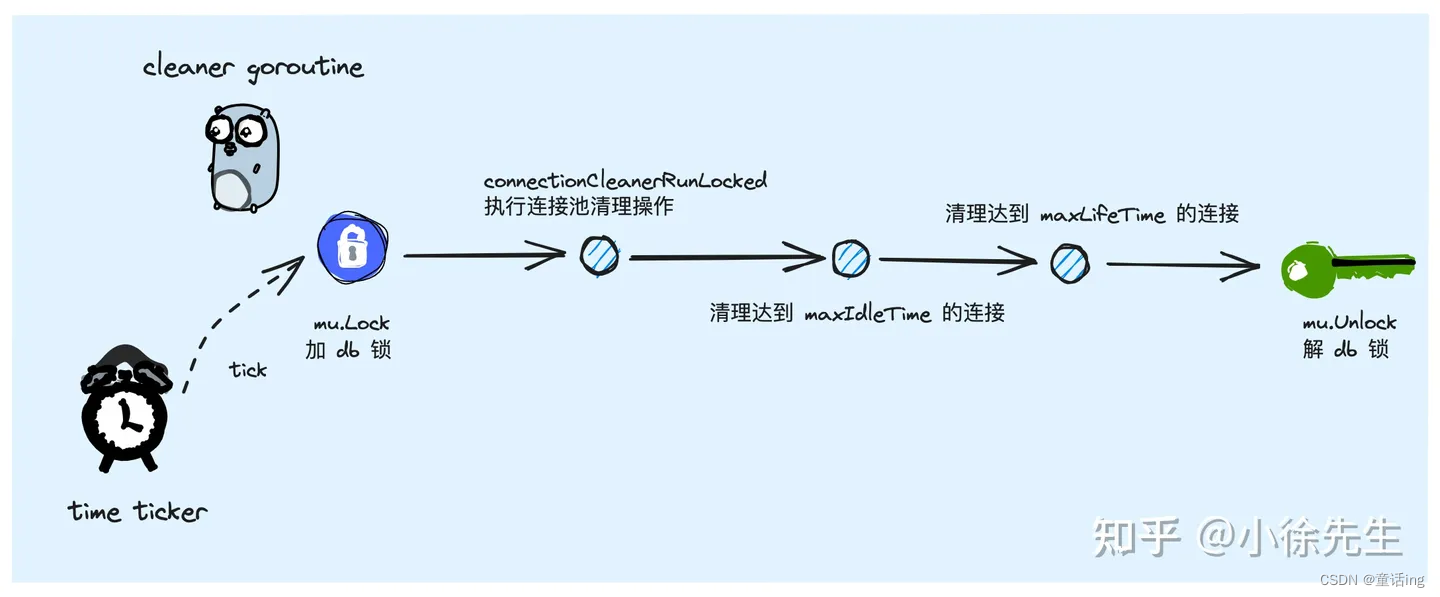
二、结语
本章中我们基于go1.19阅读了golang中database/sql的源码,了解了整个database/sql最大的特点就是定义接口,不做具体实现,从而让使用方去方便使用不同的驱动实现。同时提供了DB实例,内置连接池,方便管理连接的创建和销毁。
最后,非常感谢知乎小徐大佬的图,画的太赞了,传送链接:Golang sql 标准库源码解析
三、参考
1、Go database/sql连接池 - 源码学习
2、强烈推荐看这篇:Golang sql 标准库源码解析