线程局部存储
线程局部存储是指对象内存在线程开始后分配,线程结束后回收;且每个线程都有该对象自己的实例。
线程本身是操作系统的概念,线程局部存储这个功能离不开操作系统支持。不同操作系统对线程局部存储的实现有不同,使用的系统 API 也有区别。
1. Windows原生API实现
#include <windows.h>
DWORD g_tlsIndex; // TLS槽索引
// 初始化TLS系统
void InitTLS() {
g_tlsIndex = TlsAlloc(); // 分配TLS索引
}
// 线程函数
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc(LPVOID lpParam) {
int* pData = new int(42);
TlsSetValue(g_tlsIndex, pData); // 设置线程私有数据
int* ret = (int*)TlsGetValue(g_tlsIndex); // 获取数据
// 使用数据...
delete pData;
return 0;
}
// 清理资源
void Cleanup() {
TlsFree(g_tlsIndex);
}
2. Linux pthread实现
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_key_t g_key; // TLS键
// 析构函数(线程退出时自动调用)
void Destructor(void* data) {
delete static_cast<int*>(data);
}
void InitPthreadTLS() {
pthread_key_create(&g_key, Destructor); // 创建带析构的键
}
void* ThreadProc(void* arg) {
int* pData = new int(42);
pthread_setspecific(g_key, pData); // 设置数据
int* ret = static_cast<int*>(pthread_getspecific(g_key));
// 使用数据...
return nullptr;
}
void CleanupPthread() {
pthread_key_delete(g_key);
}
3. C++11标准化实现
基础声明方式
thread_local int g_tlsVar = 0; // 外部链接
struct Widget {
static thread_local std::string s_cache; // 类静态成员
};
thread_local std::string Widget::s_cache = "init"; // 类外定义
void ThreadTask() {
thread_local std::vector<int> localVec; // 自动初始化
localVec.push_back(42);
// 线程退出时自动析构
}
初始化特性验证
struct Tracer {
Tracer() { std::cout << "构造于" << std::this_thread::get_id() << '\n'; }
~Tracer() { std::cout << "析构于" << std::this_thread::get_id() << '\n'; }
};
void TestInit() {
thread_local Tracer t; // 每个线程首次调用时构造
}
// 启动3个线程各调用TestInit()两次
// 输出结果:每个线程只输出一次构造/析构
关键特性验证代码
a. 地址运行时计算验证
thread_local int tlsVar;
static int staticVar;
int main() {
constexpr const int* pStatic = &staticVar; // 编译期确定
// constexpr const int* pTls = &tlsVar; // 编译错误!地址运行时确定
std::cout << "TLS地址:" << &tlsVar << '\n'; // 每次运行不同
}
b. 跨线程访问风险演示
thread_local std::string tlsStr;
void MaliciousThread() {
std::string* p = &tlsStr; // 获取TLS变量地址
// 将p传递给其他线程...
}
void AttackThread(std::string* p) {
// 当原线程退出后访问:
p->append("boom"); // 未定义行为!可能崩溃
}
典型应用场景
a. 线程安全版errno实现
thread_local int tls_errno = 0;
int thread_safe_api() {
if(failure) {
tls_errno = EAGAIN; // 仅影响当前线程
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
void ThreadWorker() {
if(thread_safe_api() == -1) {
std::cout << "线程" << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "错误码:" << tls_errno << '\n';
}
}
b. 线程局部缓存池
class ThreadCache {
public:
static thread_local ThreadCache instance;
void* Alloc(size_t size) { /* ... */ }
void Dealloc(void* ptr) { /* ... */ }
private:
ThreadCache() = default; // 禁止外部构造
std::vector<void*> blocks_;
};
thread_local ThreadCache ThreadCache::instance; // 每个线程独立实例
void ProcessRequest() {
void* mem = ThreadCache::instance.Alloc(1024);
// 使用内存...
ThreadCache::instance.Dealloc(mem);
}
各平台历史实现对比
| 平台 | 关键字/API | 特性 |
|---|---|---|
| GCC | __thread |
基础类型支持,无析构函数 |
| Clang | __thread |
同GCC |
| MSVC | __declspec(thread) |
支持类类型,但有构造限制 |
| C++11 | thread_local |
完整对象生命周期管理 |
| Windows | TlsAlloc/TlsSetValue |
手动内存管理,最大支持1088个索引 |
| Linux | pthread_key_create |
带析构函数,默认1024个键 |
thread_local
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
// 输出同步互斥锁(确保多线程下的输出完整性)
std::mutex g_out_lock;
/// @brief 引用计数器(演示thread_local特性)
struct RefCount {
// 构造函数:记录创建时的线程和函数信息
RefCount(const std::string& f) // 改为直接接收string避免悬垂指针
: i(0), func(f) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_out_lock);
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "|" << func
<< ": 构造函数 i(" << i << ")\n";
}
// 析构函数:展示对象生命周期结束
~RefCount() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_out_lock);
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "|" << func
<< ": 析构函数 i(" << i << ")\n";
}
// 增加引用计数并打印日志
void inc() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_out_lock);
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "|" << func
<< ": 引用计数+1 i(" << i << "->" << i+1 << ")\n";
++i;
}
int i;
std::string func; // 使用string副本避免指针失效
};
// 线程局部存储测试函数
void foo(const char* f) {
// 先构造完整字符串再传递(确保生命周期)
const std::string func = std::string(f) + "#foo";
thread_local RefCount tv(func); // 每个线程独享的静态对象
tv.inc();
}
void bar(const char* f) {
const std::string func = std::string(f) + "#bar";
thread_local RefCount tv(func);
tv.inc();
}
// 测试线程1:连续调用foo
void threadfunc1() {
const char* func = "threadfunc1";
foo(func); // 首次调用初始化thread_local
foo(func); // 后续调用复用对象
foo(func);
}
// 测试线程2:与线程1相同模式
void threadfunc2() {
const char* func = "threadfunc2";
foo(func);
foo(func);
foo(func);
}
// 测试线程3:混合调用foo和bar
void threadfunc3() {
const char* func = "threadfunc3";
foo(func); // 初始化foo的thread_local
bar(func); // 初始化bar的thread_local
bar(func); // 复用bar的对象
}
int main() {
std::thread t1(threadfunc1);
std::thread t2(threadfunc2);
std::thread t3(threadfunc3);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}
代码行为解释
thread_local特性演示
thread_local RefCount tv(...);- 每个线程首次访问时初始化
- 线程结束时自动销毁
- 不同线程拥有独立实例
典型输出示例
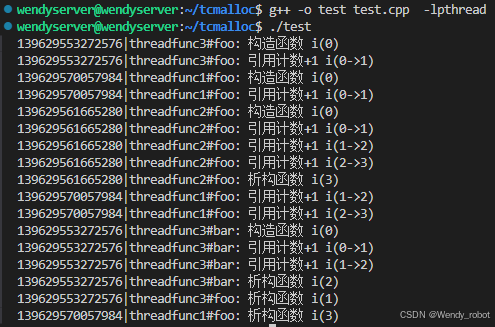
线程执行模式
- 线程1/2:连续调用foo,共3次inc()
- 线程3:调用foo(1次) + bar(2次)
- 每个thread_local对象在对应函数首次调用时创建
关键概念说明
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| thread_local | 线程局部存储,每个线程有独立实例,首次访问时构造,线程退出时销毁 |
| lock_guard | RAII锁管理,确保离开作用域时自动释放互斥锁 |
| 构造函数/析构函数 | 展示thread_local对象的生命周期管理 |
| 引用计数 | 通过inc()方法演示对象被重复使用的状态变化 |