目录
InitializingBean 和 init-method
描述一下 Bean 的 生命周期
导图
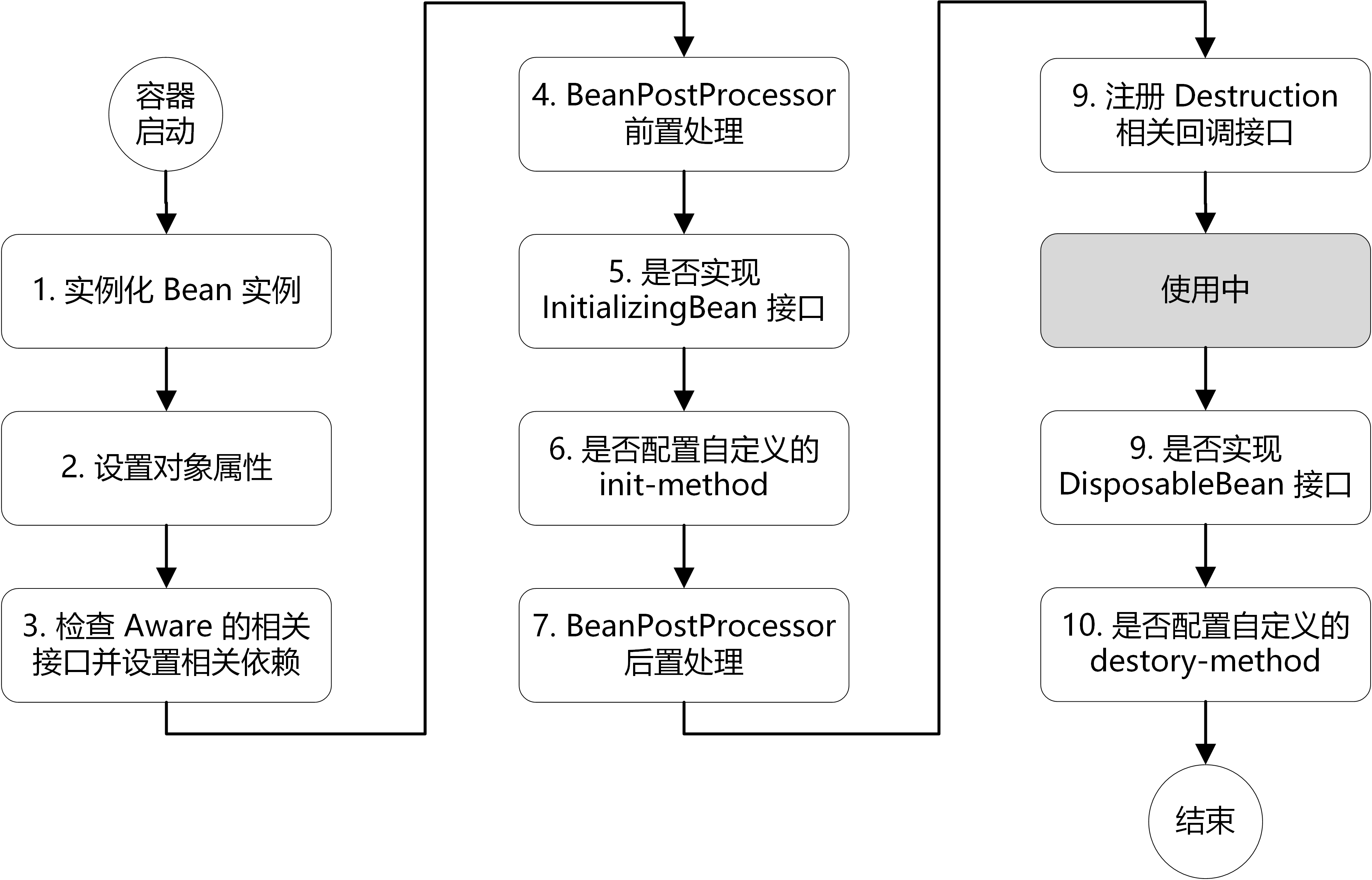
步骤
总体上可以分为五步
- 首先是 Bean 的实例化
- Bean 在进行实例化后 , 进行属性赋值
- 接着初始化 Bean
- 使用 Bean
- Bean 销毁
第一步 实例化
首先是实例化一个 Bean 对象
主要使用的 createBeanInstance()方法实现
将 bean 挂载到一个包装器上 BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}createBeanInstance()方法 是用来实例化 bean 的
伪代码逻辑
通过反射(无参构造函数)拿到 工厂方法拿到 动态代理...
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// 1. 解析bean的class类型
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 2. 检查是否指定了工厂方法
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 3. 处理有参构造函数
if (args != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, args);
}
// 4. 处理无参构造函数
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, args);
}
// 5. 默认使用无参构造函数实例化
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}第二步 属性赋值
使用 populateBean() 方法 进行赋值
// 2. 属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);我来详细讲一下这个populateBean 方法
我们把 beanname 还有一个刚刚的 beanwapper 包装器传入populateBean() 方法
- 前置处理:
-
- 允许 BeanPostProcessor 干预属性注入流程(如 @Autowired 字段注入)
- 属性值准备:
-
- 获取配置的属性值(XML / 注解)
- 处理自动装配(byName/byType)
- 应用 BeanPostProcessor 修改属性值(如 @Value 解析)
- 属性注入:
-
- 解析属性值(处理对其他 bean 的引用)
- 类型转换(字符串 → 目标类型)
- 通过 BeanWrapper 完成最终注入
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
// 1. 检查 BeanWrapper 是否为空
if (bw == null) {
return;
}
// 2. 允许 BeanPostProcessor 在属性注入前修改 bean(如 @Autowired 字段注入)
boolean continuePopulation = true;
if (hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (processor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor;
// 例如:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 会在此处理 @Autowired 字段
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continuePopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continuePopulation) {
return;
}
// 3. 获取配置的属性值(来自 XML 或注解)
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null;
// 4. 处理自动装配(byName/byType)
int autowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (autowireMode == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
autowireMode == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// 按名称自动装配:例如 <property name="userService"/>
if (autowireMode == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// 按类型自动装配:例如 @Autowired UserService userService;
if (autowireMode == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
// 5. 应用 BeanPostProcessor 修改属性值(如 @Value 解析)
if (hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (processor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor;
// 例如:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理 @Resource
PropertyValues processedPvs = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (processedPvs != null) {
pvs = processedPvs;
}
}
}
}
// 6. 应用最终的属性值到 bean 实例
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
// 简化版:按名称自动装配
private void autowireByName(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
// 获取所有未设置值的属性
String[] propertyNames = getUnsatisfiedPropertyNames(bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
// 如果容器中有同名的 bean,则自动注入
if (containsBean(propertyName)) {
Object bean = getBean(propertyName);
pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
// 注册依赖关系
registerDependentBean(propertyName, beanName);
}
}
}
// 简化版:按类型自动装配
private void autowireByType(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
TypeConverter converter = getTypeConverter();
String[] propertyNames = getUnsatisfiedPropertyNames(bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
try {
// 获取属性类型
PropertyDescriptor pd = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
Class<?> propertyType = pd.getPropertyType();
// 查找匹配类型的 bean
Object autowiredValue = resolveDependencyByType(propertyType, beanName);
if (autowiredValue != null) {
pvs.add(propertyName, autowiredValue);
}
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException("自动装配失败: " + propertyName, ex);
}
}
}
// 简化版:应用属性值
private void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
TypeConverter converter = getTypeConverter();
BeanDefinitionValueResolver resolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(
this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// 解析所有属性值(处理引用、类型转换等)
List<PropertyValue> resolvedValues = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvs.getPropertyValues()) {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
// 解析可能的 bean 引用(如 ref="userService")
Object resolvedValue = resolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
// 类型转换(如 String → Integer)
Object convertedValue = convertIfNecessary(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
resolvedValues.add(new PropertyValue(propertyName, convertedValue));
}
// 应用解析后的属性值到 bean
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(resolvedValues));
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException("设置属性值失败", ex);
}
}第三步 初始化
初始化还是比较复杂的
大体上的逻辑
- 检查 aware 相关接口设置依赖
- BeanPostProcessor 前置处理
- 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
- 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行
- BeanPostProceesor 后置处理
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 3. 检查 Aware 相关接口并设置相关依赖
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
// 4. BeanPostProcessor 前置处理
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
// 5. 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
// 6. 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
// 7. BeanPostProceesor 后置处理
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}aware 接口
注入相关依赖
若 Spring 检测到 bean 实现了 Aware 接口,则会为其注入相应的依赖。所以通过让bean 实现 Aware 接口,则能在 bean 中获得相应的 Spring 容器资源。
Spring 中提供的 Aware 接口有:
- BeanNameAware:注入当前 bean 对应 beanName;
- BeanClassLoaderAware:注入加载当前 bean 的 ClassLoader;
- BeanFactoryAware:注入 当前BeanFactory容器 的引用。
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}以上是针对 BeanFactory 类型的容器,而对于 ApplicationContext 类型的容器,也提供了 Aware 接口,只不过这些 Aware 接口的注入实现,是通过 BeanPostProcessor 的方式注入的,但其作用仍是注入依赖。
- EnvironmentAware:注入 Enviroment,一般用于获取配置属性;
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware:注入 EmbeddedValueResolver(Spring EL解析器),一般用于参数解析;
- ApplicationContextAware(ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware):注入 ApplicationContext 容器本身。
// ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.java
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware)bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware)bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware)bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware)bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware)bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware)bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}BeanPostProcessor 接口
BeanPostProcessor 是 Spring 为修改 bean提供的强大扩展点,其可作用于容器中所有 bean,其定义如下:
常用场景有:
- 对于标记接口的实现类,进行自定义处理。例如3.1节中所说的ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,为其注入相应依赖;再举个例子,自定义对实现解密接口的类,将对其属性进行解密处理;
- 为当前对象提供代理实现。例如 Spring AOP 功能,生成对象的代理类,然后返回。
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
}
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
// 返回代理类
return proxy;
}
return null;
}InitializingBean 和 init-method
初始化拓展点
InitializingBean 接口
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}指定 init-method 方法,指定初始化方法:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="demo" class="com.chaycao.Demo" init-method="init()"/>
</beans>第四步使用
第五步使用后销毁
类似于 InitializingBean() 和 init-method()