文章目录
大纲
html:负责框架结构
css:负责样式修饰
js:负责行为交互,动态效果。是逻辑语言。
JavaScrip:动态,脚本语言,解释执行,不需要编译。单线程语言(不支持多线程)
(动态语言:能够在程序运行期间动态的改变,变量没有数据类型)
JavaScrip和Java有什么关系?
雷锋和雷峰塔的关系。即一点关系没有
在网页中引入js方式(都很常见)
1、写在js标记内:在onxxxx事件中、href.通常写js片段
2、页内js:可以写在head中,或者boday内
3.引入外部js文件
以上三种形式都常见
三种引入方式的代码示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js</title>
<!-- 2、页内引入 -->
<script>
console.log('ddd');
</script>
<!-- 3、引入外部文件 -->
<script src="./js/index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 第一种引入方式:on...后面跟js,比如以下内容:
onclick:单击按钮时,后面可以写js语句 -->
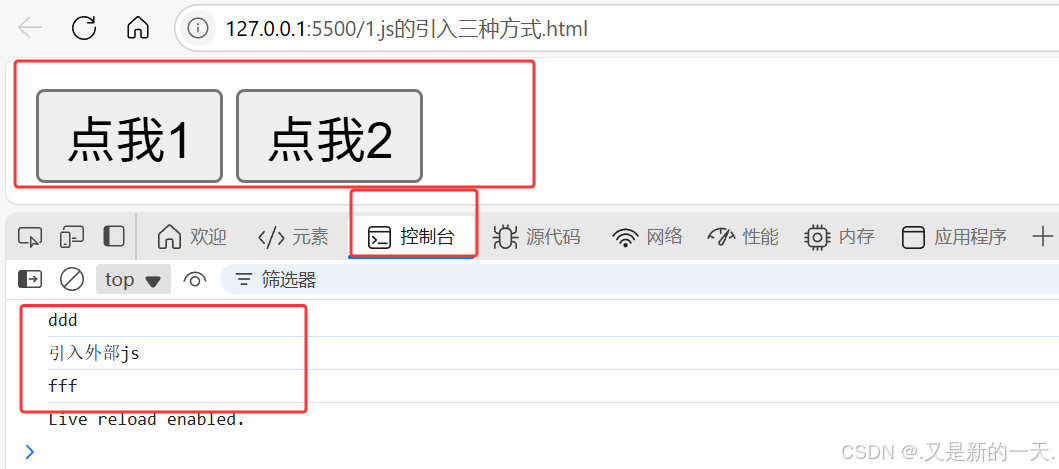
<input type="button" value="点我1" onclick="alert('你好')">
<!-- 在控制台输出内容你好,右键检查选控制台 -->
<input type="button" value="点我2" onclick="console.log('你好')">
<!-- 第二种引入方式:页内js:<script></script>,执行有顺序 -->
<script>
console.log('fff');
</script>
<!-- 第三种:引入外部js文件 -->
</body>
</html>
外部js:
console.log('引入外部js');
输出结果展示:
js版本,发展史
目前流行数字版本:5和6(es5和es6----Ecma Script)
js语法
一、定义变量和常量
变量:let
常量:const
控制台输出:console.log
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js语法</title>
<script>
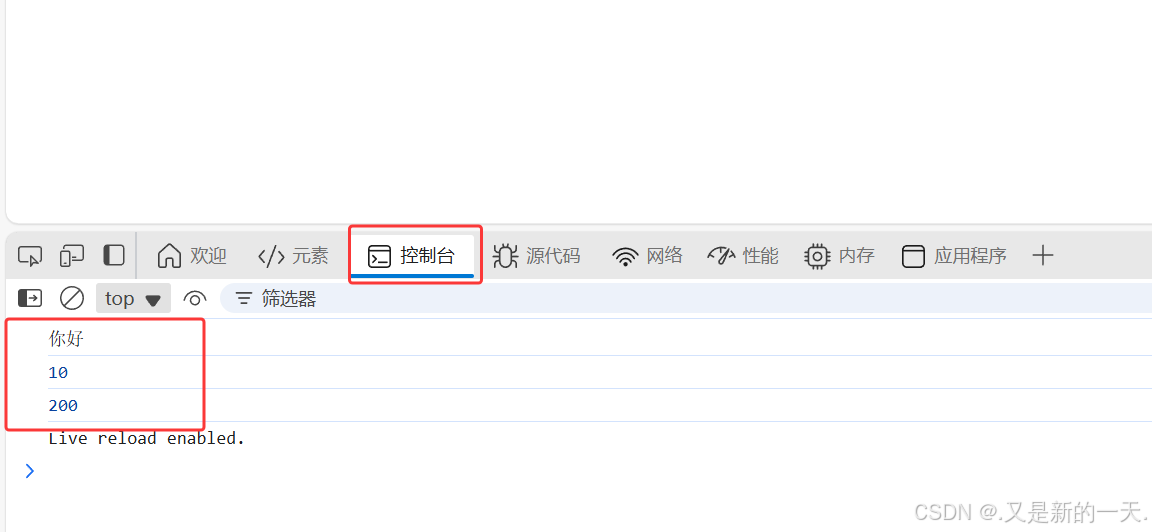
//控制台输出:浏览器右键检查
console.log('你好 ');
// 定义变量 :
let a = 10;
console.log(a);//10
//定义常量
const b = 200;
console.log(b);//200
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
展示结果:
二、js的数据类型P:原始数据类型和引入数据类型
原始数据类型(primitive):
number:数字类型,不分整数小数
string:字符串
boolean:布尔值
null :引用类型的一个值表示为指向任何对象。
undefined:表示未定义。
symbol:新提出的,使用频率极低
三、运算符
1、/和%
2、比较运算符:=== ! ==
== 值相等但忽略类型
===值和类型都相等
3、逻辑运算符
4、赋值运算符
5、位运算符
6、条件运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 算法运算符
let a = 30;
let b = 20;
console.log(a/b);//1.5
// 本身没有整除,整除的实现:
console.log(parseInt(a/b));//强制转为整数:1
console.log(Math.floor(a/b));//小于结果的最大整数:1
console.log(a%b)//取余:js支持取余操作 :10
//比较运算符:
aa="30";
bb=30;
console.log(aa==bb)//==值相等但忽略类型true
console.log(aa===bb)//===值和类型都相等false
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、表达式
js中的表达式和java没有任何区别
五、流程控制
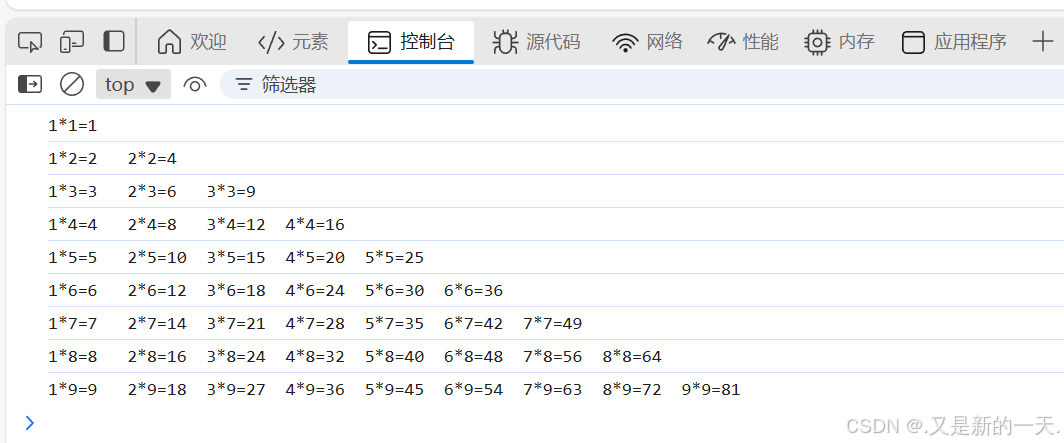
打印九九乘法表:
把int换成let
把输出语句换成console.log即可
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 打印九九乘法表 -->
<script>
for(let i=1;i<=9;i++){
let out = "";
for(let j=1;j<=i;j++){
out +=j+"*"+i+"="+j*i+"\t"
}
console.log(out);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
数组(引用数据类型)
在Js中,数组是万能数据结构,可以无限。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>数组</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let arr = [];//语法糖写法
let a = new Array();//原始写法,不需要写大小,会自动扩展
let arr2 = [1,2,3,4,5];
arr[4] = 50;
arr2[4] = 50;
console.log(arr[4]==arr2[4]);//true
console.log(arr2);//1,2,3,4,50
//数组的属性:
console.log(arr2.length);//5
arr2.push(6);//入栈,尾部压入
console.log(arr2);//1,2,3,4,50,6
let t = arr2.pop();//出栈,在尾部弹出一个元素
console.log(t);//6
console.log(arr2);//1,2,3,4,50
arr2.unshift(100);//在arr2头部压入一个元素100
console.log(arr2);//100,1,2,3,4,50
t=arr2.shift();//arr2头部弹出一个元素
console.log(t);//100
console.log(arr2);//1,2,3,4,50
// 数组的平方:
arr2 = arr2.map(it=>it*it);
console.log(arr2);//1,4,9,16,2500
</script>
</body>
</html>
函数
在js中,函数是一等公民。
函数定义示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 定义函数
function sum(a,b){
return a+b;
}
//调用函数
let result = sum(19,11);
console.log(result);//30
</script>
</body>
</html>
函数在函数中可以嵌套定义函数
代码示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 定义函数
function sum(a,b){
return a+b;
}
//调用函数
let result = sum(19,11);
console.log(result);//30
//函数嵌套函数
function quickSort(nums) {
sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1)
//快排的具体实现:
function sort(array, low, high) {
if (low >= high) {
return
}
let pl = low;
let pr = high;
let pivot = array[low];
while (pl < pr) {
while (pl < pr && array[pr] >= pivot) {
pr--
}
while (pl < pr && array[pl] <= pivot) {
pl++
}
if (pl !== pr) {
const t = array[pl]
array[pl] = array[pr]
array[pr] = t
}
}
if (pl !== low) {
array[low] = array[pl]
array[pl] = pivot
}
sort(array, low, pl - 1)
sort(array, pl + 1, high)
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
函数表达式,函数可以作为一个值赋值给变量。匿名函数可以作为值
立即执行表达式。
箭头函数
具体代码实现:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//函数表达式:属于语句,要顺序执行的,且变量a是有作用域的
//当作变量来理解,在使用上面都一样
let a = function(a,b){
return a+b;
}
console.log(a(10,20));//30
//函数的定义:没有顺序
function sum(a,b){
return a+b;
}
console.log(sum(10,20));//30
// 立即执行函数表达式:
(function(name){
console.log("hello" + name);
})("张三")//hello张三
// 箭头函数,也叫lambda表达式
let fun = (a,b)=>a+b;
console.log(fun(10,20));//30
</script>
</body>
</html>
1、句末分号是可选的,前提是不能出现语法歧义
面向对象(基于原型的)
在js中,对象就是键值对的集合
js是支持面向对象的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>面向对象</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let obj = new Object();
//语法糖
let o = {};
o.name = "张三";;
o.age = 20;
o.sayhello = function{
console.log("ddd"+this.age);
}
o.sayhello();
//创建了一个类型,相当构造函数
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
let p = new Person("张三");
console.log(p.name);
</script>
</body>
</html>