MySQL的安装就不讲述了, 本篇文章着重讲解sql优化
本篇是对B站颜群老师视频讲解的笔记梳理, 感兴趣的可以去看下老师的原视频: SQL优化
MySQL原理
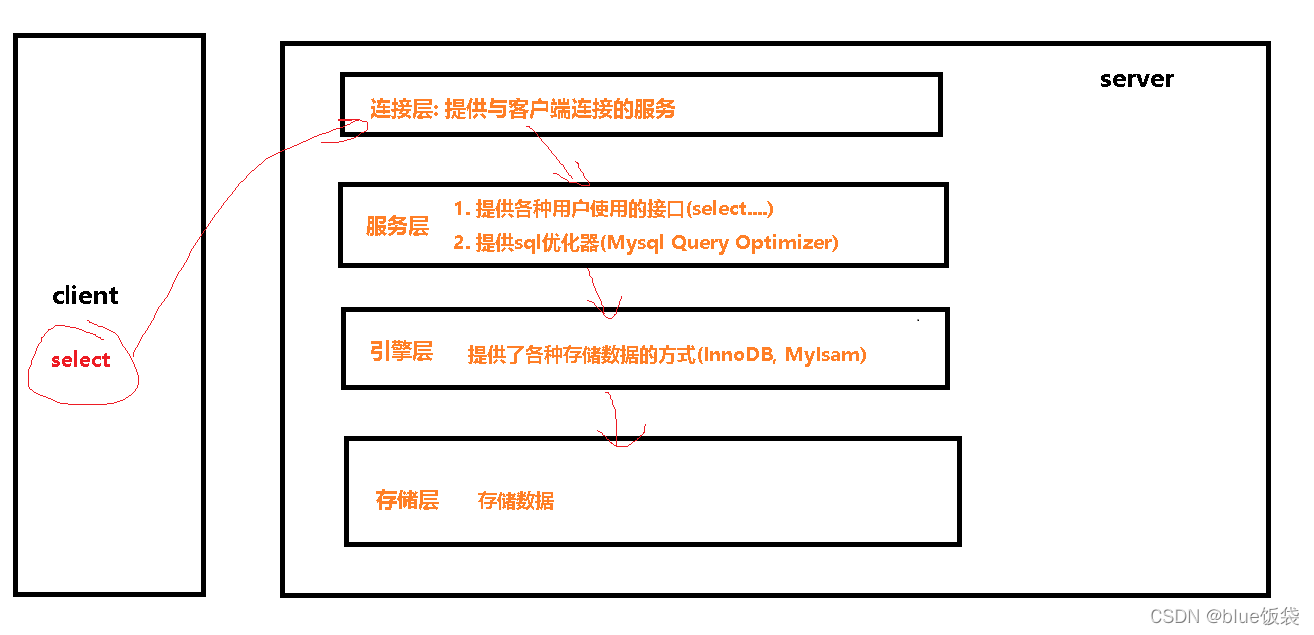
1. MySQL逻辑分层: 连接层->服务层->引擎层->存储层(如图)
- 连接层:提供与客户端连接的服务
- 服务层:提供各种用户使用的接口(select…)/提供各种sql优化器(mysql query optimizer)
- 引擎层:提供了各种存储数据的方式(InnoDB和MyIsam)
- 存储层:存储数据
- InnoDB引擎(默认使用): 事务优先, 适合高并发操作, 采用的是行锁
- MyISAM: 性能优先, 采用的是表锁
2. 查看数据库引擎
支持哪些引擎的命令
show engines;
查看当前使用的引擎
show variables like '%storage_engine%';
指定数据库对象的引擎
create table tb(....)
ENGINE=MYISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=1
DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8MB4;
3.SQL优化
3.1 原因: 性能低, 执行时间太长, 等待时间太久, SQL语句欠佳(连接查询), 索引失效, 服务器参数设置不合理(缓冲, 线程数…)
- SQL的编写过程:
select distinct...from...join...on...where...group by...having...order by...limit...
- SQL的解析过程
from...on...join...where...group by...having...select distinct...order by...limit...
- SQL优化,主要是优化索引
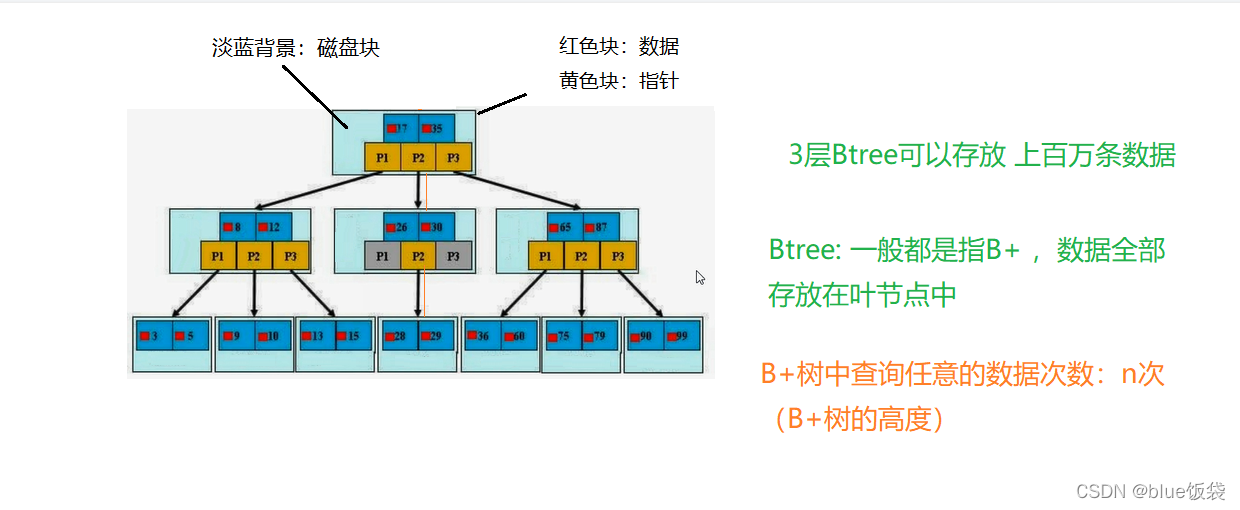
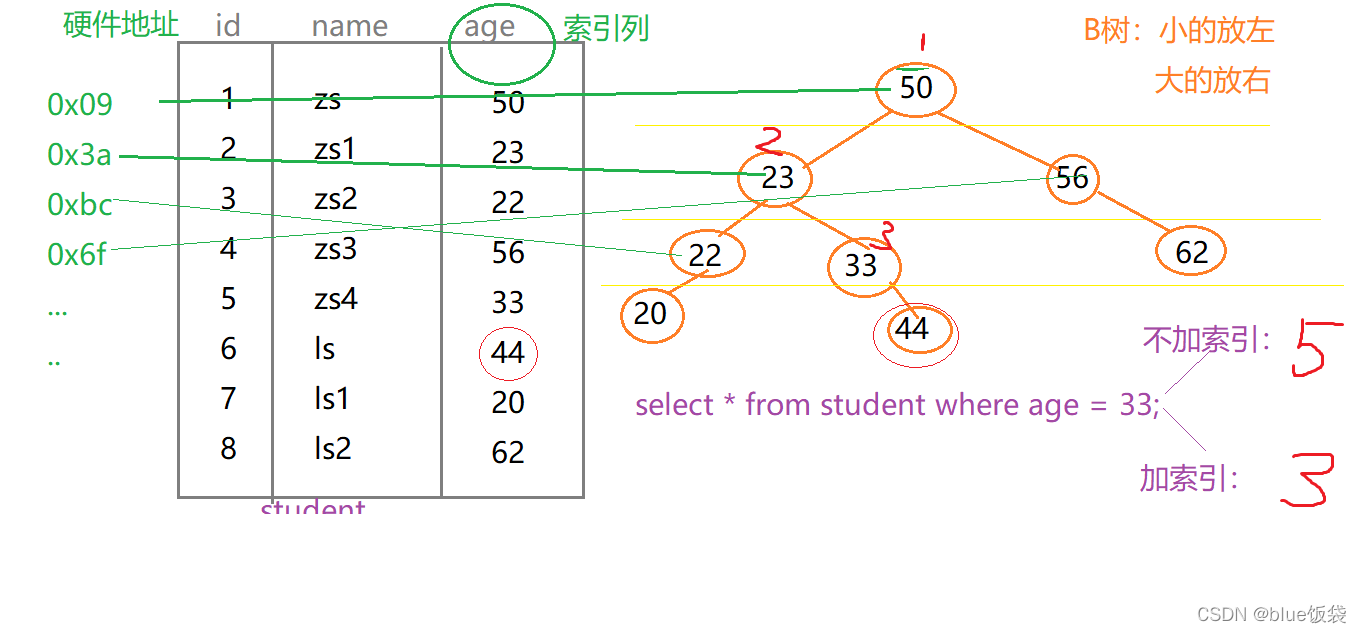
索引相当于书的目录, 是帮助mysql高效获取数据的数据结构(树: B树, Hash树)
- 索引的弊端
- 索引本身很大, 可以存放在内存/硬盘(一般为硬盘)
- 索引不是所有情况都适用(少量数据/频繁更新的字段/很少使用的字段并不适合索引)
- 索引会降低增删改的效率
- 索引的优势
- 提高查询效率, 降低IO使用率
- 降低CPU使用率(…order by age desc, 因为B树索引本身就是一个好排序的结构, 因此可以在排序时直接使用)
4. 索引
4.1 索引分类
- 主键索引: 不能重复, 不能是null, 是一种约束, 例如id
- 唯一索引: 不能重复, 可以是null, 是一种索引
- 单值索引: 单列, 一个表可以有多个单值索引
- 复合索引: 多个列构成的索引, 相当于二级目录
附: 主键索引和唯一索引的区别
- 主键是一种约束, 而唯一索引是一种索引, 二者在本质上市不同的
- 主键可以被其他表作为外键引用, 而唯一索引不能
- 主键列不允许空值, 唯一索引列允许空值
- 一张表里可以多个唯一索引, 但是只有一个主键
- 主键创建后一定包含一个唯一索引, 而唯一索引不一定是主键
4.2 创建索引
- 方式一: create 索引类型 索引名 on 表(字段)
单值索引 : create index dept_index on tb(dept);
唯一索引: create unique index name_index on tb(name);
复合索引: create index dept_name_index on tb(dept,name);
- 方式二: alter table 表名 索引类型 索引名(字段)
单值索引: alter table tb add index dept_index(dept);
唯一索引: alter table tb add unique index name_index(name);
复合索引: alter table tb add index dept_name_index(dept,name);
4.3 删除索引
drop index 索引名 on 表名;
drop index name_index on tb;
4.4 查询索引
show index from 表名;
show index from 表名 \G
5. SQL性能问题
- 分析SQL的执行计划: explain, 可以模拟sql优化器执行SQL语句, 从而让开发人员知道自己编写的SQL状况
- MySQL查询优化器会干扰我们的优化
- 优化方法, 官网https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/optimize-overview.html
- 查询执行计划: explain + SQL语句, 如图:
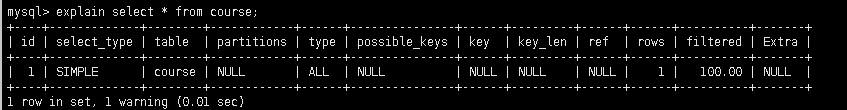
- 字段详解
id: 编号
select_type: 查询类型
table: 表名
partitions: 分区
type: 类型
possible_keys: 预测使用到的索引
key: 实际使用到的索引
key_len: 实际使用到的索引长度
ref: 表之间的引用
rows: 通过索引查询到的数据量
filtered: 返回结果的行数占读取行数的百分比
Extra: 额外的信息
5.1 准备数据
课程表
create table course(
cid int(3),
cname varchar(20),
tid int(3)
);
教师表
create table teacher(
tid int(3),
tname varchar(20),
tcid int(3)
);
教师信息表
create table teacher_card(
tcid int(3),
tcdesc varchar(200)
);
插入数据
insert into course values(1,'java',1);
insert into course values(2,'html',1);
insert into course values(3,'sql',2);
insert into course values(4,'web',3);
insert into teacher values(1,'tz',1);
insert into teacher values(2,'tw',2);
insert into teacher values(3,'tl',3);
insert into teacher_card values(1,'tzdesc') ;
insert into teacher_card values(2,'twdesc') ;
insert into teacher_card values(3,'tldesc') ;
5.2 执行过程分析
5.2.1 id
select tc.tcdesc from course c join teacher t on c.tid = t.tid join teacher_card tc on t.tcid = tc.tcid where c.cid = 2 or tc.tcid = 3
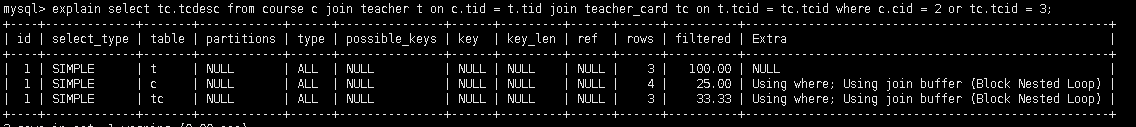
id值相同, 从上往下顺序执行, t - c -tc
表的执行顺序, 因数量的个数改变而改变的原因: 笛卡尔积
a b c
4 3 2 = 2*3*4 = 6*4 = 24
= 3*4*2 = 12*2 = 24
查询原则: 数据小的表, 优先查询
id值不同: id值越大, 越优先查询(本质: 在嵌套时, 先查内层, 再查外层)
子查询 + 多表: 查询教授SQL课程的老师的描述
-- 查询教授sql的老师tid
select tid from course where cname = 'sql';
-- 查询该老师的tcid
select tcid from teacher where tid = (select tid from course where cname = 'sql');
-- 查询该tcid对应老师的描述
select tcdesc from teacher_card where tcid = (select tcid from teacher where tid = (select tid from course where cname = 'sql'));
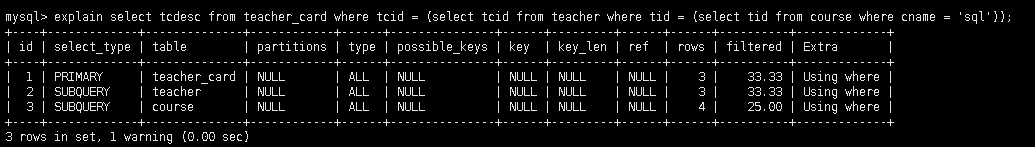
id值有相同, 又有不同; id值越大越优先, id值相同, 从上往下顺序执行
5.2.2 select_type: 查询类型
PRIMARY: 包含子查询SQL中的主查询(最外层)
SUBQUERY:包含子查询SQL中的子查询(非最外层)
SIMPLE:简单查询(不包含子查询, union)
DERIVED: 衍生查询(使用到了临时表)
UNION:
- 在from子查询中只有一张表
explain select cr.cname from(select * from course where tid in (1,2)) cr;
- 在from子查询中, 如果有table1 union table2, 则table1就是derived, table2就是union
explain select cr.cname from (select * from course where tid = 1 union select * from course where tid = 2) cr;
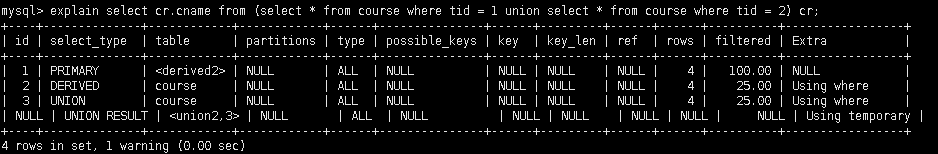
UNION RESULT:告知开发人员, 哪些表之间存在union查询
5.2.3 type: 索引类型, 类型
级别对比: system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL
其中, system,const只是理想情况, 实际能达到ref > range
5.2.3.1 system(忽略): 只有一条数据的系统表, 或衍生表只有一条数据的主查询
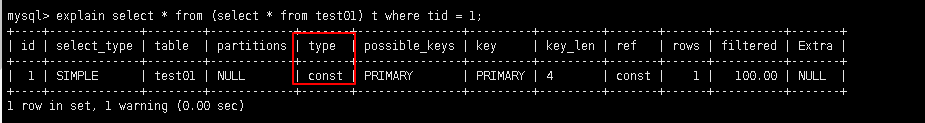
5.2.3.2 const: 仅仅能查到一条数据的sql, 用于primary key 或 unique 索引(类型与索引类型有关)
-- 建表插入数据
create table test01(
tid int(3),
tname varchar(20)
);
insert into test01 values(1,'a');
commit;
-- 增加索引并解析
alter table test01 add constraint tid_pk primary key(tid) ;
explain select * from (select * from test01) t where tid = 1;
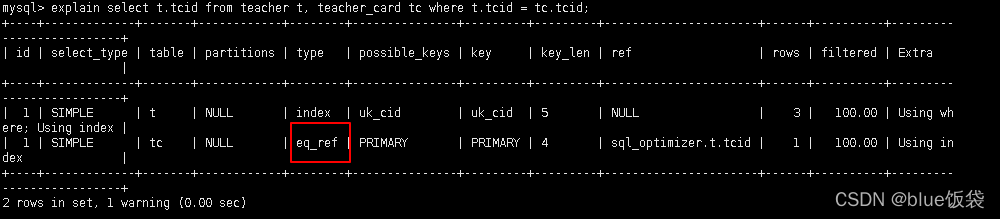
5.2.3.3 eq_ref: 唯一性索引, 对于每个索引键的查询, 返回匹配唯一行数据(有且只有1个, 不能多, 不能0), 常见于唯一索引和主键索引
lalter table teacher_card add constraint pk_tcid primary key(tcid);
alter table teacher add constraint uk_tcid unique index(tcid);
explain select t.tcid from teacher t, teacher_card tc where t.tcid = tc.tcid;
以上SQL, 用到的索引是t.tcid, 即teacher表中的tcid字段;
除非teacher表的数据个数与连接查询的数据个数一致, 则有可能满足eq_ref级别, 否则无法满足
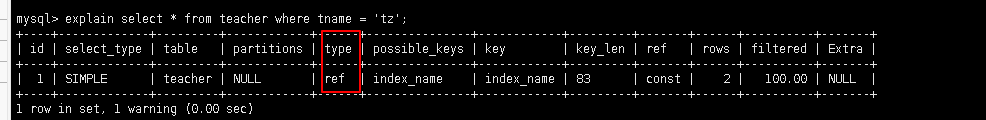
5.2.3.4 ref: 非唯一性索引, 对于每个索引键的查询, 返回匹配的所有行(0条或多条)
准备数据:
insert into teacher values(4,'tz',4);
insert into teacher_card values(4,'tz222');
测试:
alter table teacher add index index_name(tname);
explain select * from teacher where tname = 'tz';
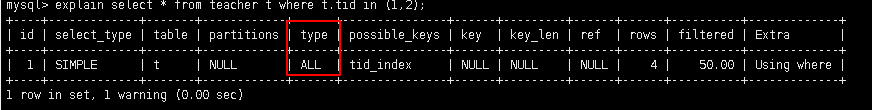
5.2.3.5 range: 检索指定范围的行, where后面是一个范围查询(between, >, <, >=, <=)
alter table teacher add index tid_index(tid);
explain select * from teacher t where t.tid in (1,2);
explain select * from teacher t where t.tid < 3;
特殊: in有时候会失效, 从而转为无索引 all

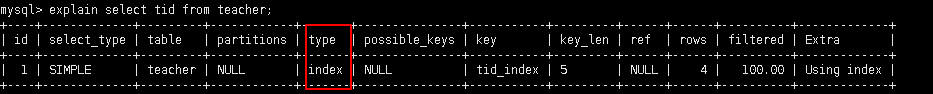
5.2.3.6 index: 查询全部索引中数据
explain select tid from teacher;
tid是索引, 只需要扫描索引表,不需要所有表中的数据
5.2.3.7 all: 查询全部表中的数据
explain select cid from course;
cid 不是索引, 需要全表扫描
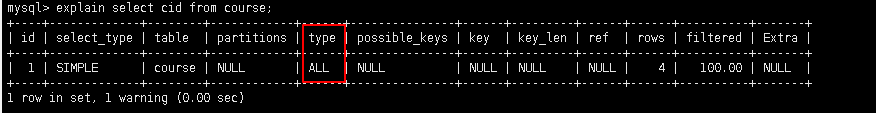
5.2.4 possible_keys: 可能用到的索引, 是一种预测, 不准
alter table course add index index_cname_index(cname);
如果possible_keys/key是null, 则说明没用索引
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacher_card tc, course c, teacher t where c.tid = t.tid and t.tcid = tc.tcid and c.cname = 'sql';
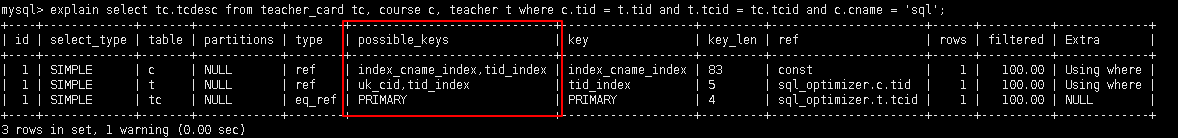
5.2.5 key: 实际使用到的索引(具体可参考上面的)
5.2.6 key_len: 索引的长度
作用: 用于判断复合索引是否被完全使用(a,b,c)
create table test_kl(
name char(20) not null default ''
);
alter table test_kl add index index_name(name);
explain select * from test_kl where name = '';
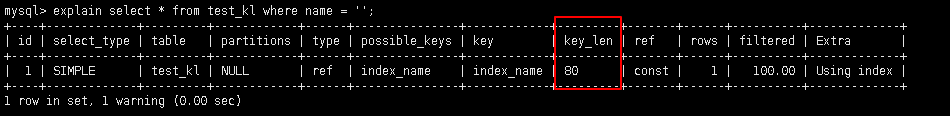
在utf8mb4编码中, 一个字符占4个字节
alter table test_kl add column name1 char(20); -- name1可以为null
-- 如果索引字段可以为null, 则会使用1个字节用于标识
explain select * from test_kl where name1 = ''; -- null
-- 增加一个符合索引
alter table test_kl add index name_name1_index(name,name1);
explain select * from test_kl where name1 = ''; -- null
explain select * from test_kl where name = ''; -- 80
-- 可以为null
alter table test_kl add column name2 varchar(20);
alter table test_kl add index name2_index(name2);
-- 83 = 20 * 4 = 80 + 1(null) + 2(2个字节标识可变长度)
explain select * from test_kl where name2 = '';
5.2.7 ref: 注意与type中的ref值区分
作用: 指明当前所参照的字段
select ...where a.c = b.x;(其中b.x可以是常量, const)
alter table course add index tid_index(tid);
explain select * from course c, teacher t where c.tid = t.tid and t.tname = 'tw';
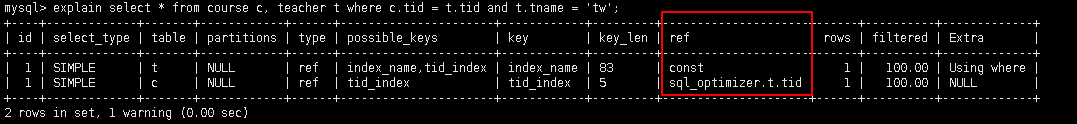
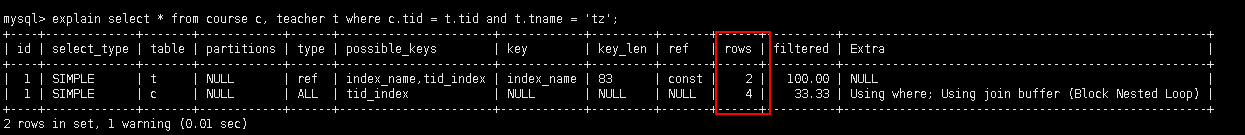
5.2.8 rows: 被索引优化查询的数据条数(实际通过索引而查询到的数据条数)
explain select * from course c, teacher t where c.tid = t.tid and t.tname = 'tz';
5.2.9 Extra: 额外的
5.2.9.1 using filesort: 性能消耗大, 需要额外的一次排序(查询), 常见于order by语句中
排序:先查询
单值索引
create table test02(
a1 char(3),
a2 char(3),
a3 char(3),
index idx_a1(a1),
index idx_a2(a2),
index idx_a3(a3)
);
explain select * from test02 where a1 = '' order by a1;
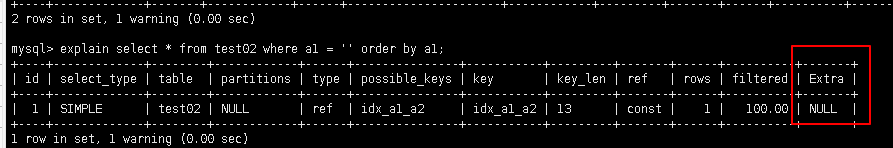
explain select * from test02 where a1 = '' order by a2; -- using filesort
小结: 避免using filesort 的出现, where哪些字段, 就order by哪些字段
复合索引
drop index idx_a1 on test02;
drop index idx_a2 on test02;
drop index idx_a3 on test02;
alter table test02 add index idx_a1_a2_a3(a1,a2,a3);
explain select * from test02 where a1 = '' order by a3; -- 跨列使用
explain select * from test02 where a2 = '' order by a3; -- 跨列使用
explain select * from test02 where a1 = '' order by a2; -- 有序使用
explain select * from test02 where a2 = '' order by a1; -- 无序使用
小结: 避免using filesort的方法, where和order by 按照复合索引的顺序使用, 不要跨列或者无序使用
5.2.9.2 using temporary: 性能损耗大, 用到了临时表, 一般出现在group by语句中
explain select a1 from test02 where a1 in ('1','2','3') group by a1;
explain select a1 from test02 where a1 in ('1','2','3') group by a2; -- using temporary

规避原则: 查询哪些列, 就根据哪些列group by
5.2.9.3 using index: 性能提升, 索引覆盖
原因: 不读取源文件, 只从索引文件中获取数据(不需要回表查询), 只要使用到的列全部在索引中, 就是索引覆盖
例如: test02表中有一个复合索引(a1, a2, a3)
explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1 = '' or a2 = ''; -- using index
drop index idx_a1_a2_a3 on test02;
alter table test02 add index idx_a1_a2(a1,a2);
explain select a1,a3 from test02 where a1 = '' or a3 = '';
-- 如果用到了索引覆盖(using index), 会对possible_keys 和key造成影响:
-- a. 如果没有where, 则索引只出现在key中;
-- b. 如果有where, 则索引出现在key和possible_keys中
explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1 = '' or a2 = '';
explain select a1,a2 from test02;
5.2.9.4 using where(需要回表查询)
假设age是索引列, 但查询语句select age, name from …where age = … 此语句中必须回原表查Name, 因此会显示using where
explain select a1,a3 from test02 where a3 = ''; -- a3需要回表查询
5.2.9.5 impossible where : where 子句永远为false
explain select * from test02 where a1 = 'x' and a1 = 'y';
6. 优化案例(单表优化, 双表优化, 三表优化)
6.1 单表优化
create table book(
bid int(4) primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
authorid int(4) not null,
publicid int(4) not null,
typeid int(4) not null
);
insert into book values(1,'tjava',1,1,2);
insert into book values(2,'tc',2,1,2);
insert into book values(3,'wx',3,2,1);
insert into book values(4,'math',4,2,3);
6.1.1 查询authorid 为1并且 typeid 为2或3的bid
explain select bid from book where authorid = 1 and (typeid in (2,3)) order by typeid desc;
-- 优化,加索引
alter table book add index idx_bta(bid,authorid,typeid);
-- 虽然是using index, 但是也有回表查询的情况

-- 索引一旦进行升级优化, 需要将之前废弃的索引删掉,防止干扰
drop index idx_bta on book;
-- 根据sql实际解析的顺序, 调整索引的顺序
alter table book add index idx_atb(authorid,typeid,bid);
-- 再次优化(之前是index级别): 因为范围查询in有时候会失效, 因此交换索引的顺序,将typeid in(2,3)放在最后
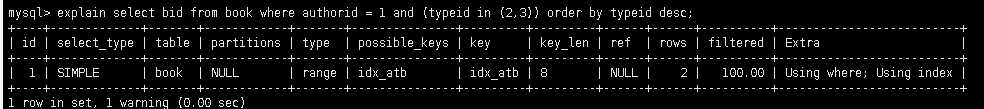
6.1.2 小结
- 最佳左前缀, 保证索引定义与使用的顺序一致性
- 索引需要逐步优化
- 将含in的范围查询放在where条件的最后, 防止索引失效
6.1.3 本例中同时出现了using where(需要回原表); using index(不需要回原表);
原因:
where authorid = 1 and typeid in (2, 3)中, authorid 在索引(authorid,typeid,bid)中, 因此不需要回原表(直接在索引表中就能查到); 而typeid虽然也在索引(authorid,typeid,bid)中, 但是含in的范围查询以及or的条件连接查询已经使该typeid索引失效, 因此相当于没有typeid这个索引, 所以需要回原表(using where)
例如以下没有了in, 则不会出现using where
explain select bid from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2 order by typeid desc;
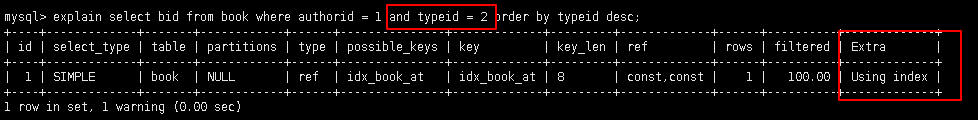
还可以通过key_len属性证明in可以使索引失效
6.2 双表优化
create table teacher2(
tid int(4) primary key,
cid int(4) not null
);
insert into teacher2 values(1,2);
insert into teacher2 values(2,1);
insert into teacher2 values(3,3);
create table course2(
cid int(4),
cname varchar(20)
);
insert into course2 values(1,'java');
insert into course2 values(2,'python');
insert into course2 values(3,'kotlin');
6.2.1 左连接
explain select * from teacher2 t left join course2 c on t.cid = c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
Q: 索引往哪张表加?
A: 小表驱动大表, 索引建立在经常使用的字段上(本题t.cid = c.cid可知, cid字段使用频繁, 因此给该字段加上索引), 一般情况下, 对于左外连接, 给左表加索引, 右外连接, 给右表加索引
小表: 10条数据
大表: 300条数据
where 小表 x10 = 大表y300 ; – 循环了10次
大表y 300 = 小表x 10; – 循环了300次
select ...where 小表.x10=大表.x300 ;
for(int i=0;i<小表.length10;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<大表.length300;j++)
{
...
}
}
select ...where 大表.x300=小表.x10 ;
for(int i=0;i<大表.length300;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<小表.length10;j++)
{
...
}
}
-- 以上2个for循环, 最终都会循环3000次;但是对于双层循环来说, 一般建议将数据量小的循环放外层, 数据量大的循环放内层
-- 当编写...on t.cid = c.cid时, 将数据量小的表放左边(假设此时t表数据量小)
alter table teacher2 add index index_teacher2_cid(cid) ;
alter table course2 add index index_course2_cname(cname);
Using join buffer:extra中的一个选项,作用:Mysql引擎使用了 连接缓存。
6.3 三张表优化A B C
a. 小表驱动大表
b. 索引建立在经常查询的字段上
create table test03(
a1 int(4) not null,
a2 int(4) not null,
a3 int(4) not null,
a4 int(4) not null
);
alter table test03 add index idx_a1_a2_a3_4(a1,a2,a3,a4) ;
-- 推荐写法,因为索引的使用顺序(where后面的顺序), 和复合索引的顺序保持一致
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1 = 1 and a2 = 2 and a3 = 3 and a4 = 4;
-- 虽然编写顺序和索引顺序不一致, 但是sql在真正执行前, 经过了sql优化器的调整,结果与上条是一致的
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a4 = 1 and a2 = 2 and a3 = 3 and a1 = 4;
-- 以上两个sql, 使用了全部的复合索引
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1 = 1 and a2 = 2 and a4 = 4 order by a3;
-- 以上sql用到了a1,a2两个索引,该两个字段不需要回表查询using index; 而a4因为跨列使用,造成该索引失效,需要回表查询, 因此是where;以上可以通过key_len验证
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1 = 1 and a4 = 4 order by a3;
-- 以上sql出现了using filesort(文件排序, "多了一次额外的查找排序";) 不要跨列使用(where和order by拼起来, 不要跨列使用)
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1 = 1 and a4 = 4 order by a2, a3;
-- 以上sql不会出现using filesort
c. 总结
- 如果(a,b,c,d)复合索引和使用的顺序全部一致, 且不跨列使用, 则复合索引全部使用, 如果部分一致(且不跨列使用), 则使用的部分索引. 例如:
select a,c where a =... and b = ... and c = ... where 和order by拼起来, 不需要跨列使用usring temporary: 需要额外多使用一张表, 一般出现在group by语句中, 已经有表了, 但是不适用, 必须再来一张表
explain select * from test03 where a2 = 2 and a4 = 4 group by a2,a4; -- 没有using temporary
explain select * from test03 where a2 = 2 and a4 = 4 group by a3;
- 解析过程:
from...on...join...where...group by...having...select...distinct...order by...limit...
7.避免索引失效的一些原则
7.1 复合索引
- 不要跨列使用或者无序使用
- 尽量使用全索引匹配
7.2 不要在索引上进行任何操作(计算, 函数, 类型转换), 否则索引失效
select ... where A.x = ...; -- 假设A.x是索引
-- 不要进行对索引进行操作, 如下
select .. where A.x * 3 = ...;
explain select * from book where authorid = 3 and typeid = 2;
-- 以上sql用到了'a','t'2个索引
explain select * from book where authorid = 3 and typeid * 2 = 2;
-- 以上sql用到了'a'1个索引
explain select * from book where authorid * 2 = 3 and typeid = 2;
-- 以上sql用到了0个索引, 对于复合索引,如果左边失效,右侧全部失效
-- 单索引(不适用最佳左前缀)
drop index idx_atb on book;
alter table book add index idx_authorid(authorid);
alter table book add index idx_typeid(typeid);
explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2;
7.3 复合索引不能使用"!=“, “is (not) null”, 否则自身以及右侧索引全部失效, 如果复合索引中有”>", 则自身以及右侧索引全部失效
explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2;
explain select * from book where authorid != 1 and typeid = 2;
explain select * from book where authorid != 1 and typeid != 2;
-- sql优化,是一种概率层面的优化. 至于是否实际使用了我们的优化, 需要通过explain进行推测
-- 体验概率情况(>,<,=):原因是服务层中有sql优化器,可能会影响我们的优化
drop index idx_authorid on book;
drop index idx_typeid on book;
alter table book add index idx_book_at(authorid,typeid);
explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2; -- 复合索引at全部使用
explain select * from book where authorid > 1 and typeid = 2; -- 复合索引如果有>, 则自身和右侧索引全部失效
explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid > 2; -- 复合索引全部使用
-- 明显的概率问题 --
explain select * from book where authorid < 1 and typeid = 2; -- 复合索引只用到了1个索引
explain select * from book where authorid < 10 and typeid = 2; -- 复合索引全部失效
7.4 补救: 尽量使用索引覆盖(using index)
-- 假设表中有复合索引(a,b,c), 尽量以下面这种方式去写
select a,b,c from ... where a = ... and b = ...and c = ...;
7.5 like尽量以"常量"开头, 不要以"%"开头, 否则索引失效
select * from ... where name like '%x%'; -- name索引失效
explain select * from teacher where tname like '%x%'; -- tname索引失效
explain select * from teacher where tname like 'x%';
explain select tname from teacher where tname like '%x%'; -- 如果必须要用like'%X%'进行模糊查询, 可以使用索引覆盖挽救一部分.
7.6 尽量不要使用类型转换(显示/隐式), 否则索引失效
explain select * from teacher where tname = 'abc';
explain select * from teacher where tname = 123; -- 程序底层将123 -> '123', 进行了类型转换, 因此索引失效
7.7 尽量不要使用or, 否则会使索引失效
explain select * from teacher where tname = '' or tcid > 1; -- or左侧的tname将失效
8. 一些其他的优化方法
8.1 exist和in
select ... from table where exists (子查询);
select ... from table where column in (子查询);
-- 如果主查询的数据集大, 则使用in, 效率高
-- 如果子查询的数据集大, 则使用exists, 效率高
-- exists语法: 将主查询的结果, 放到子查询结果中去校验(看子查询是否有数据,如果有数据, 则校验成功), 如果符合校验, 则保留数据
select tname from teacher where exists (select * from teacher);
-- 等价于 select tname from teacher
select tname from teacher where exists (select * from teacher where tid = 9999);
-- in语法
select ... from table where id in (1,3,5);
8.2 order by 优化
using filesort 有两种算法(根据io的次数, io消耗性能): 单路排序, 双路排序
MySQL4.1 之前默认使用双路排序,:
双路排序: 扫描2次磁盘
- 从磁盘读取排序字段, 对排序字段进行排序(在buffer中进行的排序)
- 扫描其他字段
MySQL4.1之后默认使用单路排序: 只读一次(全部字段), 在buffer中进行排序, 但这种单路排序会有一定的隐患(不一定真的是单路1次io, 有可能多次io).
原因:`如果数据量特别大, 则无法将所有字段的数据一次性读取完毕, 因此会进行单路排序; 单路排序在使用时, 如果数据量大, 可以考虑调整buffer的大小
set max_length_for_sort_data = 1024; -- 单位为byte
如果max_length_for_sort_data值太低, 则mysql会自动从单路切换到双路(太低: 需要排序的字段的总大小超过了max_length_for_sort_data定义的字节数)
提高order by 查询的策略:
- 选择使用单路还是双路, 调整buffer容量的大小
- 避免
select * ...... - 复合索引: 不要跨列使用, 避免using filesort
- 保证全部的排序字段, 排序的一致性(都是升序或者降序)