文章目录
前言
在现代应用开发中,高效可靠的Excel处理能力已成为企业级应用的刚需。本文介绍的Excel工具类基于阿里巴巴EasyExcel技术栈,提供从基础数据导入导出、多Sheet复杂报表生成到枚举类型自动转换的一站式解决方案。通过简洁的API设计和严谨的内存管理,开发者可轻松应对各种Excel处理场景,避免重复造轮子,显著提升开发效率。
一、依赖坐标
核心依赖
<!--表格处理——easyexcel-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok(简化代码结构) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Web(文件上传支持) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
依赖说明
| 依赖 | 核心功能 | 版本要求 | 优势特性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EasyExcel | Excel 读写操作 | ≥3.3.2 | 低内存占用、高性能处理 |
| Lombok | 简化代码结构(非必需) | - | 减少样板代码 |
| Spring Web | 文件上传支持(非必需) | - | 简化 Web 集成 |
二、工具类:ExcelUtil
核心功能设计
| 方法名 | 参数 | 功能描述 | 返回值示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
importExcel |
file=订单.xlsx, clazz=Order.class |
导入订单数据到Order对象列表 | List<Order> |
exportSingle |
baseName="订单", sheet=orderSheet |
导出订单数据到单Sheet文件 | /exports/订单_20240520.xlsx |
exportMulti |
baseName="报表", sheets=[sheet1,sheet2] |
导出多Sheet财务报表 | /exports/报表_20240520.xlsx(多sheet) |
Sheet数据封装类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class Sheet<T> {
private final String name; // Sheet名称
private final List<T> data; // 数据列表
private final Class<T> clazz;// 数据模型类
}
完整代码
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.WriteSheet;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Excel 工具类
*/
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Component
public class ExcelUtil {
// 默认导出目录(可自定义)
@Value("${vehicle.export}")//这里通过配置文件配置,然后用spring提供的value注解注入的,也可以直接指定
private String defaultExportDir;
/**
* 导入整张表
*/
public <T> List<T> importExcel(MultipartFile file, Class<T> clazz) throws IOException {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("上传的文件为空");
}
return EasyExcel.read(file.getInputStream())
.head(clazz)
.sheet()
.doReadSync();
}
/**
* 导出单个 Sheet
*/
public Path exportSingle(String baseName, Sheet<?> sheet) throws IOException {
String filepath = generateUniqueFileName(baseName);
EasyExcel.write(filepath, sheet.getClazz()).sheet(sheet.getName()).doWrite(sheet.getData());
return Path.of(filepath);
}
/**
* 导出多个 Sheet
*/
public Path exportMulti(String baseName, List<Sheet<?>> sheets) throws IOException {
String filepath = generateUniqueFileName(baseName);
// 创建 ExcelWriter
ExcelWriter writer = EasyExcel.write(filepath).build();
// 写入每个 sheet
for (int i = 0; i < sheets.size(); i++) {
Sheet<?> sheet = sheets.get(i);
WriteSheet writeSheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet(i, sheet.getName())
.head(sheet.getClazz())
.build();
writer.write(sheet.getData(), writeSheet);
}
// 手动关闭 ExcelWriter
writer.finish();
return Path.of(filepath);
}
/**
* 生成带时间戳的唯一文件名(避免覆盖)
*/
private String generateUniqueFileName(String baseName) throws IOException {
// 确保目录存在
File dir = new File(defaultExportDir);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
// 使用时间戳和随机数生成唯一文件名
String timestamp = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss"));
String randomSuffix = java.util.UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4); // 随机后缀,避免极小概率的冲突
return String.format("%s%s_%s_%s.xlsx", defaultExportDir, baseName, timestamp, randomSuffix);
}
/**
* Sheet 数据封装类
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
public static class Sheet<T> {
private final String name;
private final List<T> data;
private final Class<T> clazz;
}
}
三、测试
1.实体类
// 测试实体类 - 用户
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class User {
@ExcelProperty("用户ID")
private Long id;
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("邮箱")
private String email;
@ExcelProperty("注册日期")
private LocalDate registerDate;
}
// 测试实体类 - 产品
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class Product {
@ExcelProperty("产品ID")
private String productId;
@ExcelProperty("产品名称")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("价格")
private Double price;
@ExcelProperty("库存数量")
private Integer stock;
}
2.前置操作
private ExcelUtil excelUtil;
private List<User> testUsers;
private List<Product> testProducts;
// 导出目录 - src/test/resources/excel
private static final String EXPORT_DIR = "src/test/resources/excel/";
@BeforeEach
void setUp() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
// 初始化ExcelUtil,设置导出目录
excelUtil = new ExcelUtil();
//反射获取数据
Field field = ExcelUtil.class.getDeclaredField("defaultExportDir");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(excelUtil, EXPORT_DIR);
// 准备测试用户数据
testUsers = new ArrayList<>();
testUsers.add(new User(1L, "张三", "zhangsan@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 15)));
testUsers.add(new User(2L, "李四", "lisi@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 3, 22)));
testUsers.add(new User(3L, "王五", "wangwu@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 30)));
// 准备测试产品数据
testProducts = new ArrayList<>();
testProducts.add(new Product("P001", "笔记本电脑", 5999.0, 120));
testProducts.add(new Product("P002", "智能手机", 3999.0, 200));
testProducts.add(new Product("P003", "平板电脑", 2999.0, 150));
}
3.单Sheet导出
/**
* 测试单Sheet导出功能
* 文件将导出到 src/test/resources/excel 目录
*/
@Test
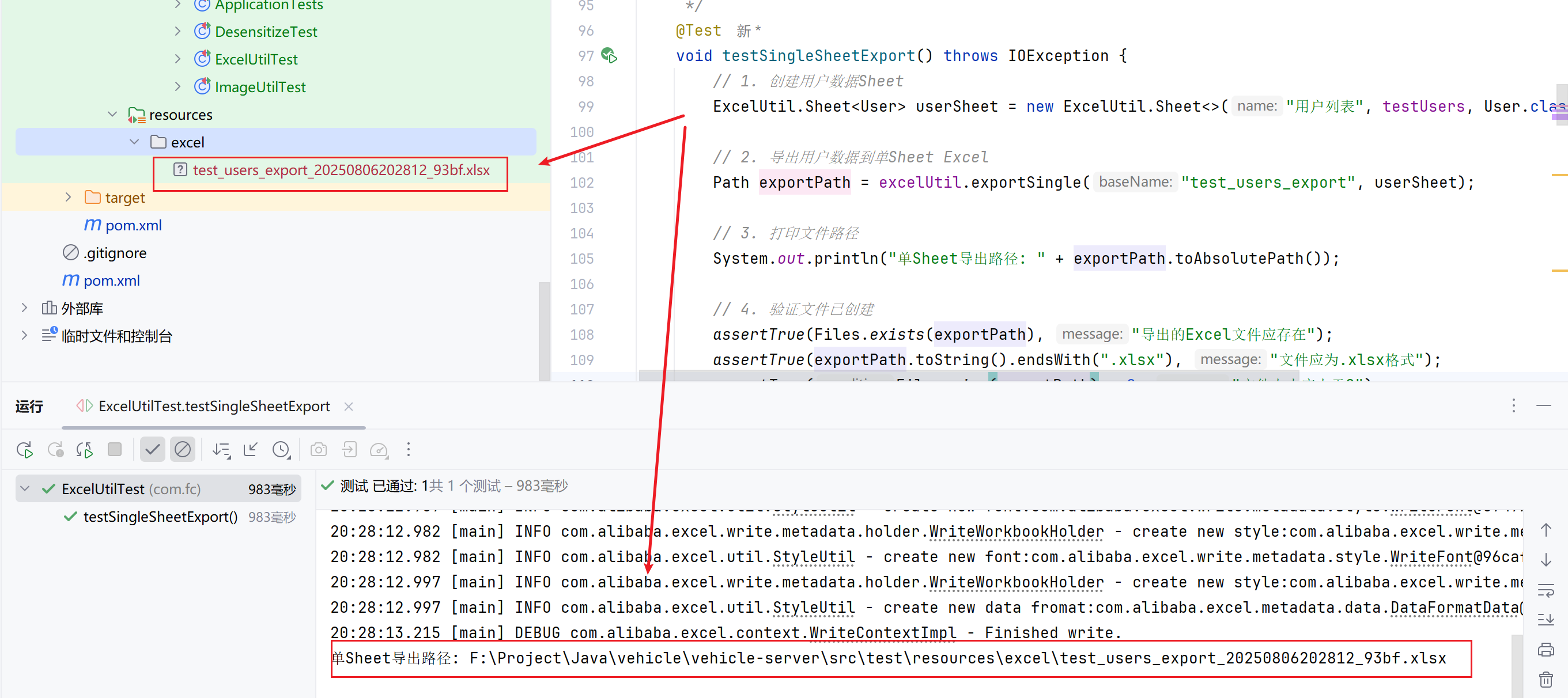
void testSingleSheetExport() throws IOException {
// 1. 创建用户数据Sheet
ExcelUtil.Sheet<User> userSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("用户列表", testUsers, User.class);
// 2. 导出用户数据到单Sheet Excel
Path exportPath = excelUtil.exportSingle("test_users_export", userSheet);
// 3. 打印文件路径
System.out.println("单Sheet导出路径: " + exportPath.toAbsolutePath());
// 4. 验证文件已创建
assertTrue(Files.exists(exportPath), "导出的Excel文件应存在");
assertTrue(exportPath.toString().endsWith(".xlsx"), "文件应为.xlsx格式");
assertTrue(Files.size(exportPath) > 0, "文件大小应大于0");
}
4.单Sheet导入
修改文件名成刚生成的文件
/**
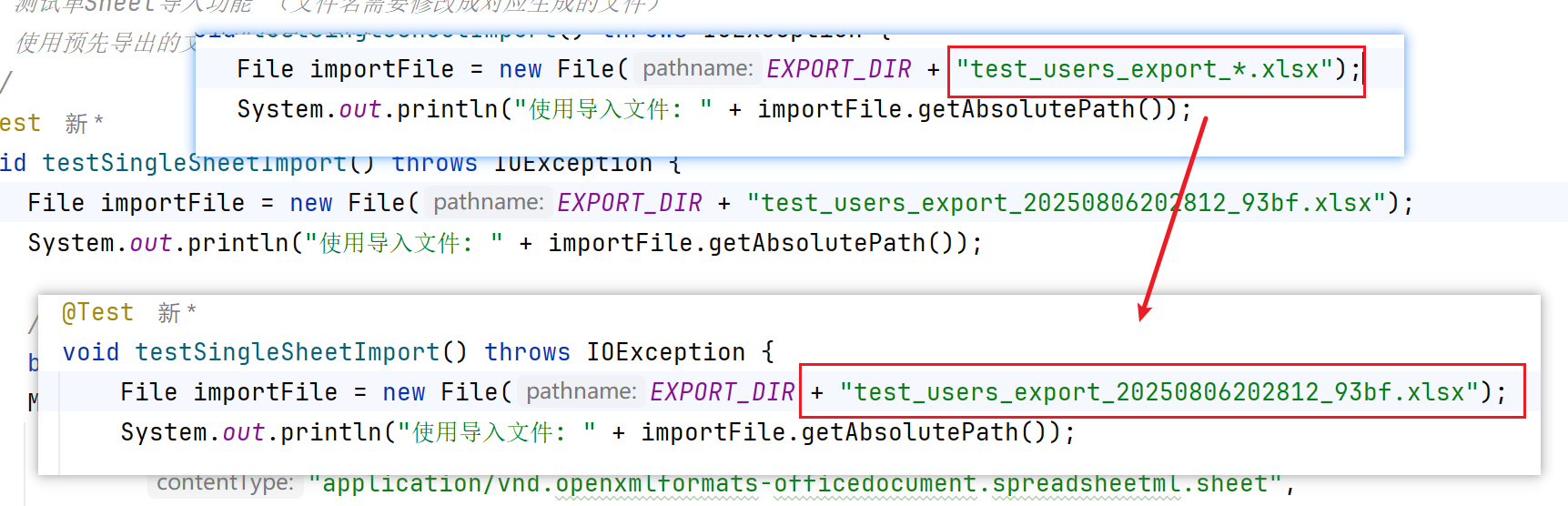
* 测试单Sheet导入功能 (文件名需要修改成对应生成的文件)
* 使用预先导出的文件进行导入测试
*/
@Test
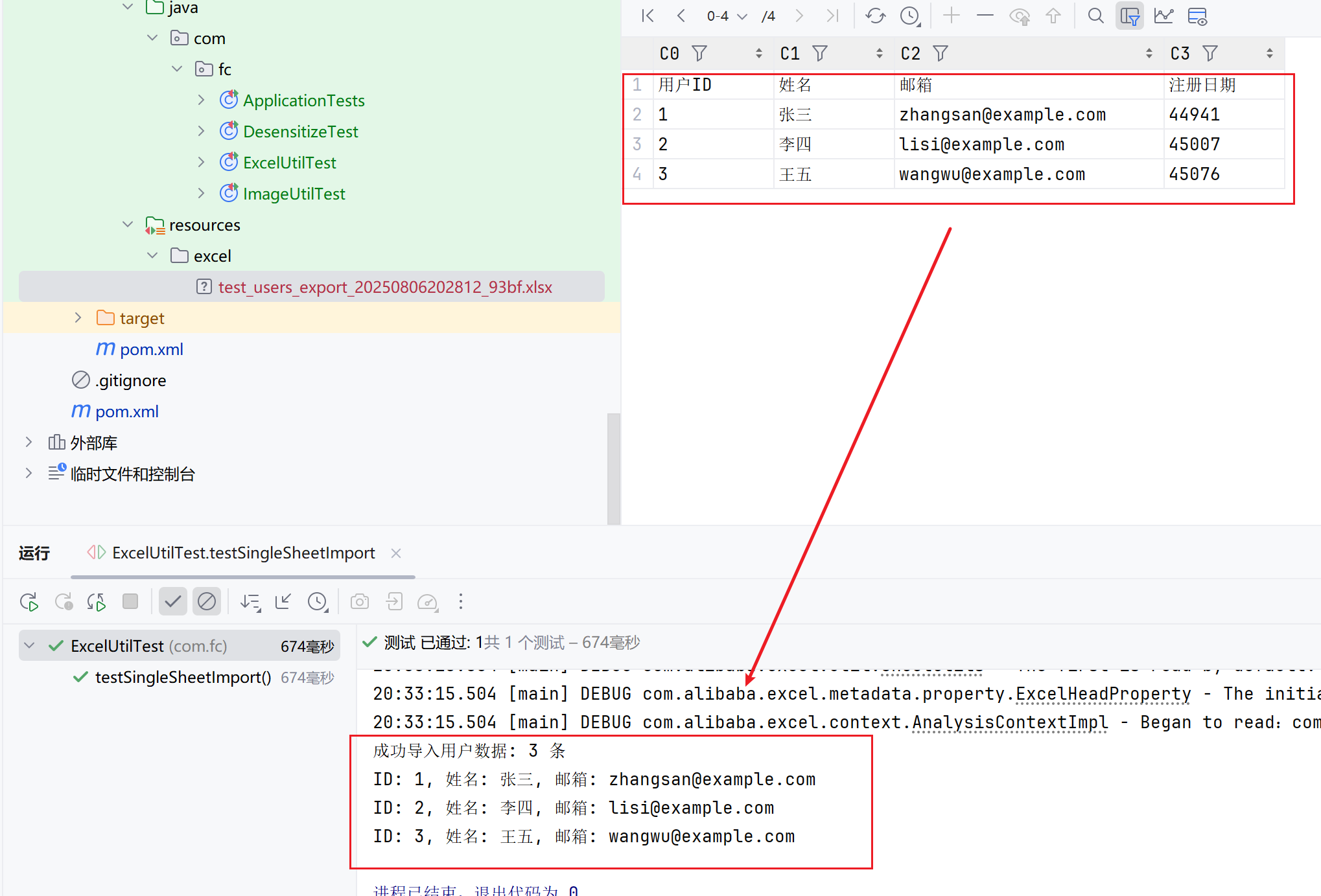
void testSingleSheetImport() throws IOException {
File importFile = new File(EXPORT_DIR + "test_users_export_20250806202812_93bf.xlsx");
System.out.println("使用导入文件: " + importFile.getAbsolutePath());
// 准备MultipartFile
byte[] fileContent = Files.readAllBytes(importFile.toPath());
MockMultipartFile mockFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"users.xlsx", "users.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
// 导入用户数据
List<User> importedUsers = excelUtil.importExcel(mockFile, User.class);
// 验证导入结果
assertEquals(testUsers.size(), importedUsers.size(), "导入的用户数量应匹配");
for (int i = 0; i < testUsers.size(); i++) {
User original = testUsers.get(i);
User imported = importedUsers.get(i);
assertEquals(original.getId(), imported.getId(), "用户ID应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getName(), imported.getName(), "用户名应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getEmail(), imported.getEmail(), "邮箱应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getRegisterDate(), imported.getRegisterDate(), "注册日期应匹配");
}
// 打印导入结果
System.out.println("成功导入用户数据: " + importedUsers.size() + " 条");
importedUsers.forEach(user ->
System.out.printf("ID: %d, 姓名: %s, 邮箱: %s%n",
user.getId(), user.getName(), user.getEmail()));
}
5.多Sheet导出
/**
* 测试多Sheet导出功能
* 文件将导出到 src/test/resources/excel 目录
*/
@Test
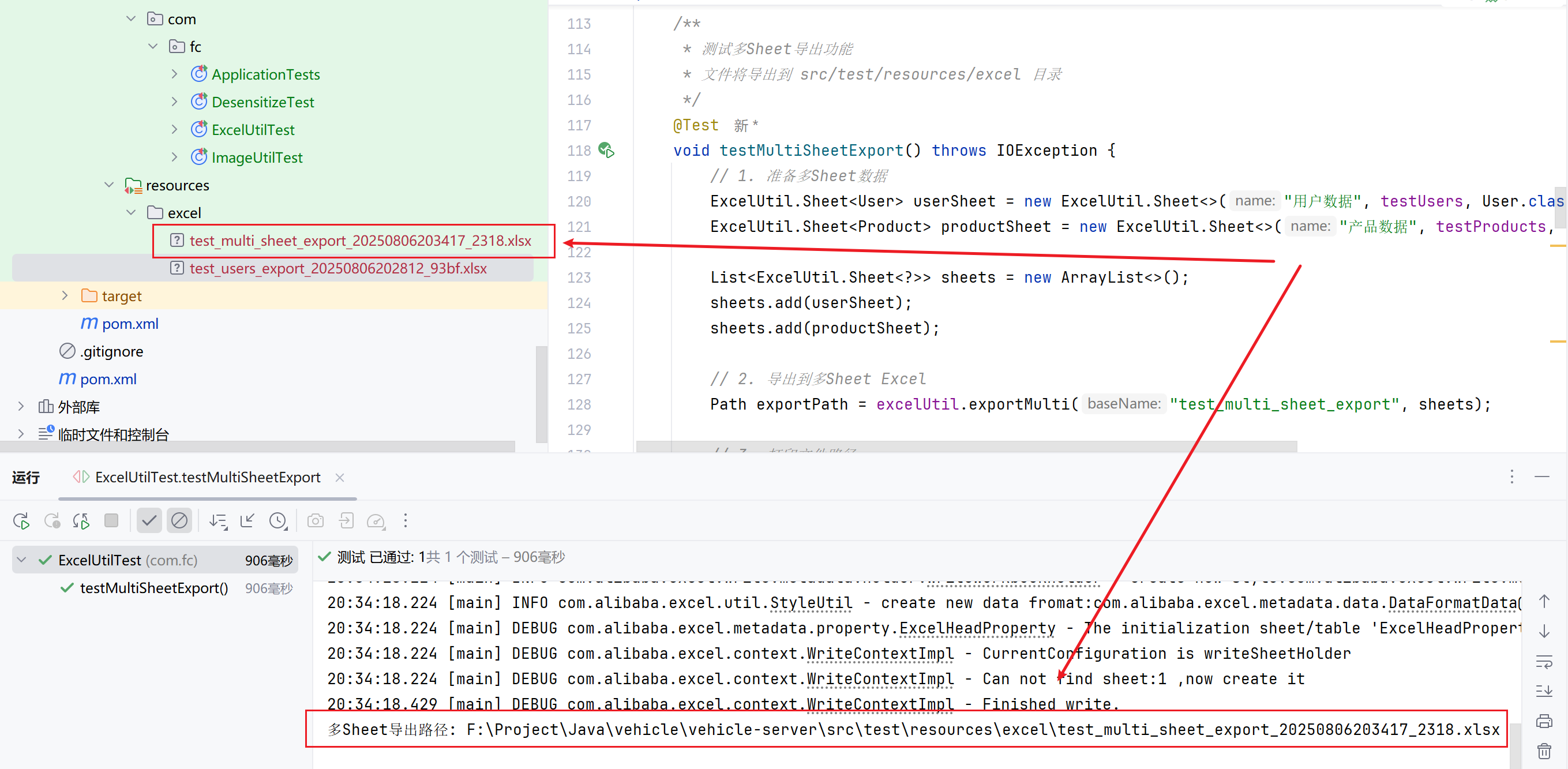
void testMultiSheetExport() throws IOException {
// 1. 准备多Sheet数据
ExcelUtil.Sheet<User> userSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("用户数据", testUsers, User.class);
ExcelUtil.Sheet<Product> productSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("产品数据", testProducts, Product.class);
List<ExcelUtil.Sheet<?>> sheets = new ArrayList<>();
sheets.add(userSheet);
sheets.add(productSheet);
// 2. 导出到多Sheet Excel
Path exportPath = excelUtil.exportMulti("test_multi_sheet_export", sheets);
// 3. 打印文件路径
System.out.println("多Sheet导出路径: " + exportPath.toAbsolutePath());
// 4. 验证文件已创建
assertTrue(Files.exists(exportPath), "导出的Excel文件应存在");
}
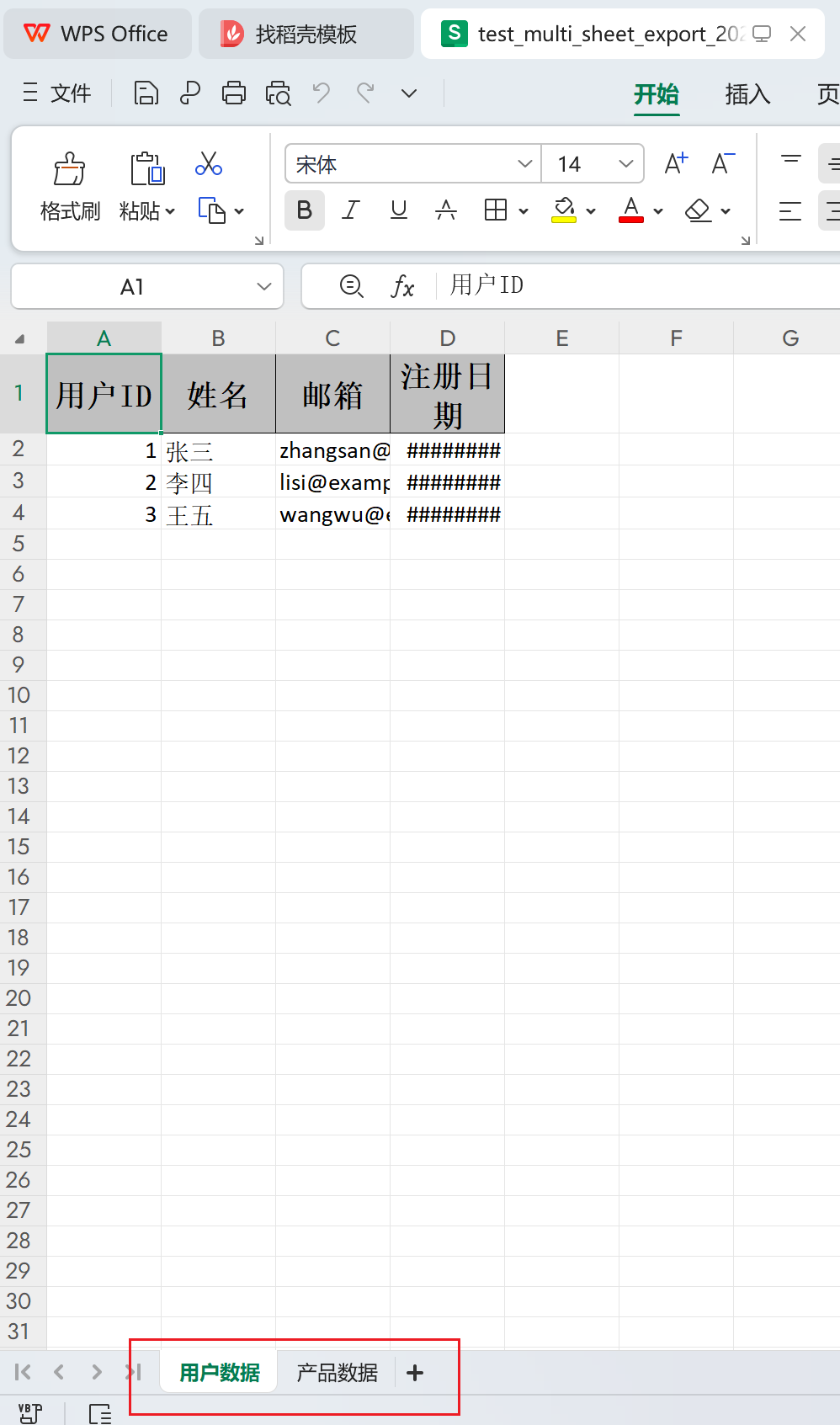
6.多Sheet导入
/**
* 测试多Sheet导入功能
* 使用预先导出的文件进行导入测试
*/
@Test
void testMultiSheetImport() throws IOException {
File importFile = new File(EXPORT_DIR + "test_multi_sheet_export_20250806203417_2318.xlsx");
System.out.println("使用导入文件: " + importFile.getAbsolutePath());
// 导入用户数据(第一个Sheet)
byte[] fileContent = Files.readAllBytes(importFile.toPath());
MockMultipartFile userFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"multi_sheet.xlsx", "multi_sheet.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
List<User> importedUsers = excelUtil.importExcel(userFile, User.class);
// 验证用户数据
assertEquals(testUsers.size(), importedUsers.size(), "导入的用户数量应匹配");
// 导入产品数据(第二个Sheet)
MockMultipartFile productFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"multi_sheet.xlsx", "multi_sheet.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
List<Product> importedProducts = EasyExcel.read(productFile.getInputStream())
.head(Product.class)
.sheet(1) // 第二个Sheet(索引从0开始)
.doReadSync();
// 验证产品数据
assertEquals(testProducts.size(), importedProducts.size(), "导入的产品数量应匹配");
for (int i = 0; i < testProducts.size(); i++) {
Product original = testProducts.get(i);
Product imported = importedProducts.get(i);
assertEquals(original.getProductId(), imported.getProductId(), "产品ID应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getName(), imported.getName(), "产品名称应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getPrice(), imported.getPrice(), 0.001, "产品价格应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getStock(), imported.getStock(), "库存数量应匹配");
}
// 打印导入结果
System.out.println("成功导入用户数据: " + importedUsers.size() + " 条");
System.out.println("成功导入产品数据: " + importedProducts.size() + " 条");
}
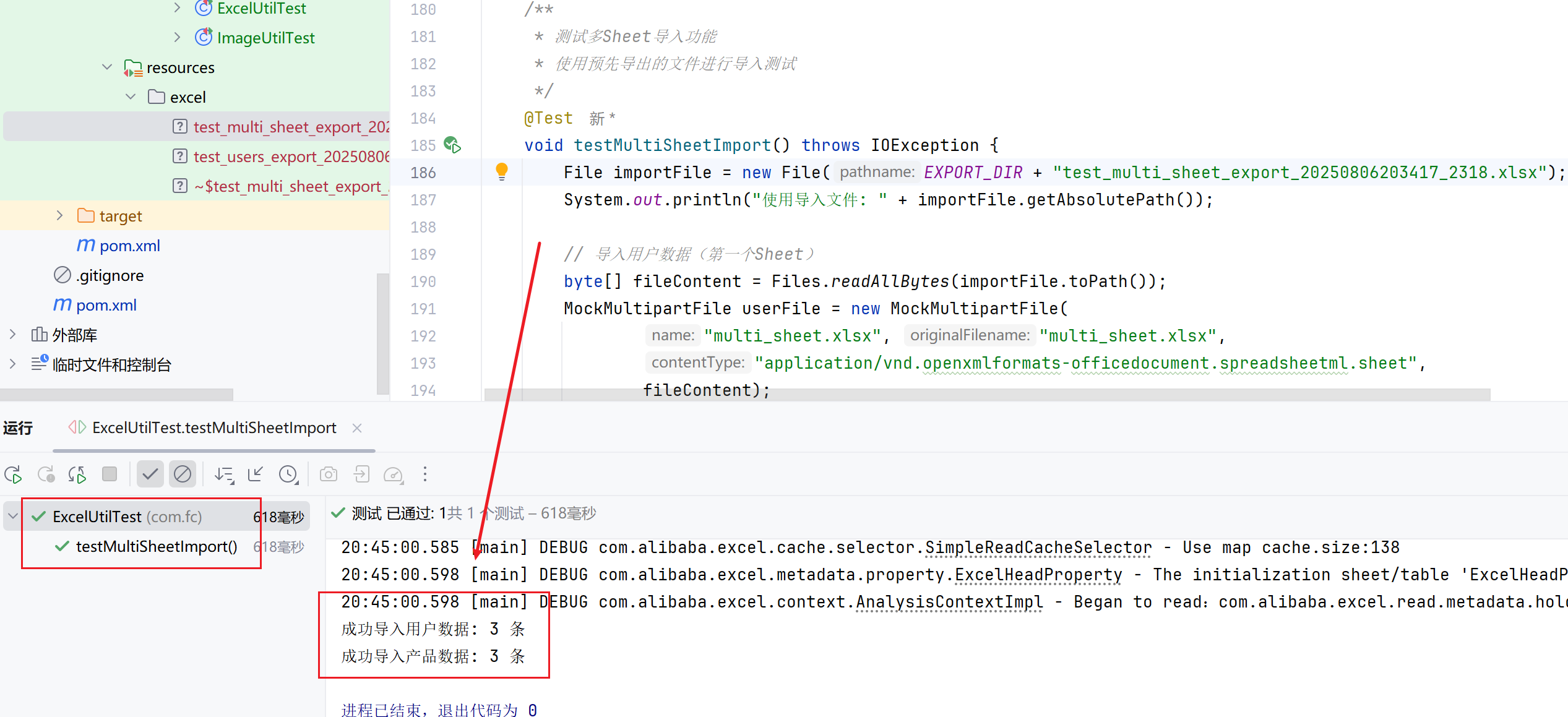
7.完整代码
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.fc.utils.ExcelUtil;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockMultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class ExcelUtilTest {
// 测试实体类 - 用户
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class User {
@ExcelProperty("用户ID")
private Long id;
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("邮箱")
private String email;
@ExcelProperty("注册日期")
private LocalDate registerDate;
}
// 测试实体类 - 产品
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class Product {
@ExcelProperty("产品ID")
private String productId;
@ExcelProperty("产品名称")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("价格")
private Double price;
@ExcelProperty("库存数量")
private Integer stock;
}
private ExcelUtil excelUtil;
private List<User> testUsers;
private List<Product> testProducts;
// 导出目录 - src/test/resources/excel
private static final String EXPORT_DIR = "src/test/resources/excel/";
@BeforeEach
void setUp() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
// 初始化ExcelUtil,设置导出目录
excelUtil = new ExcelUtil();
//反射获取数据
Field field = ExcelUtil.class.getDeclaredField("defaultExportDir");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(excelUtil, EXPORT_DIR);
// 准备测试用户数据
testUsers = new ArrayList<>();
testUsers.add(new User(1L, "张三", "zhangsan@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 15)));
testUsers.add(new User(2L, "李四", "lisi@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 3, 22)));
testUsers.add(new User(3L, "王五", "wangwu@example.com", LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 30)));
// 准备测试产品数据
testProducts = new ArrayList<>();
testProducts.add(new Product("P001", "笔记本电脑", 5999.0, 120));
testProducts.add(new Product("P002", "智能手机", 3999.0, 200));
testProducts.add(new Product("P003", "平板电脑", 2999.0, 150));
}
/**
* 测试单Sheet导出功能
* 文件将导出到 src/test/resources/excel 目录
*/
@Test
void testSingleSheetExport() throws IOException {
// 1. 创建用户数据Sheet
ExcelUtil.Sheet<User> userSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("用户列表", testUsers, User.class);
// 2. 导出用户数据到单Sheet Excel
Path exportPath = excelUtil.exportSingle("test_users_export", userSheet);
// 3. 打印文件路径
System.out.println("单Sheet导出路径: " + exportPath.toAbsolutePath());
// 4. 验证文件已创建
assertTrue(Files.exists(exportPath), "导出的Excel文件应存在");
assertTrue(exportPath.toString().endsWith(".xlsx"), "文件应为.xlsx格式");
assertTrue(Files.size(exportPath) > 0, "文件大小应大于0");
}
/**
* 测试多Sheet导出功能
* 文件将导出到 src/test/resources/excel 目录
*/
@Test
void testMultiSheetExport() throws IOException {
// 1. 准备多Sheet数据
ExcelUtil.Sheet<User> userSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("用户数据", testUsers, User.class);
ExcelUtil.Sheet<Product> productSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("产品数据", testProducts, Product.class);
List<ExcelUtil.Sheet<?>> sheets = new ArrayList<>();
sheets.add(userSheet);
sheets.add(productSheet);
// 2. 导出到多Sheet Excel
Path exportPath = excelUtil.exportMulti("test_multi_sheet_export", sheets);
// 3. 打印文件路径
System.out.println("多Sheet导出路径: " + exportPath.toAbsolutePath());
// 4. 验证文件已创建
assertTrue(Files.exists(exportPath), "导出的Excel文件应存在");
}
/**
* 测试单Sheet导入功能 (文件名需要修改成对应生成的文件)
* 使用预先导出的文件进行导入测试
*/
@Test
void testSingleSheetImport() throws IOException {
File importFile = new File(EXPORT_DIR + "test_users_export_*.xlsx");
System.out.println("使用导入文件: " + importFile.getAbsolutePath());
// 准备MultipartFile
byte[] fileContent = Files.readAllBytes(importFile.toPath());
MockMultipartFile mockFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"users.xlsx", "users.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
// 导入用户数据
List<User> importedUsers = excelUtil.importExcel(mockFile, User.class);
// 验证导入结果
assertEquals(testUsers.size(), importedUsers.size(), "导入的用户数量应匹配");
for (int i = 0; i < testUsers.size(); i++) {
User original = testUsers.get(i);
User imported = importedUsers.get(i);
assertEquals(original.getId(), imported.getId(), "用户ID应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getName(), imported.getName(), "用户名应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getEmail(), imported.getEmail(), "邮箱应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getRegisterDate(), imported.getRegisterDate(), "注册日期应匹配");
}
// 打印导入结果
System.out.println("成功导入用户数据: " + importedUsers.size() + " 条");
importedUsers.forEach(user ->
System.out.printf("ID: %d, 姓名: %s, 邮箱: %s%n",
user.getId(), user.getName(), user.getEmail()));
}
/**
* 测试多Sheet导入功能
* 使用预先导出的文件进行导入测试
*/
@Test
void testMultiSheetImport() throws IOException {
File importFile = new File(EXPORT_DIR + "test_multi_sheet_export_*.xlsx");
System.out.println("使用导入文件: " + importFile.getAbsolutePath());
// 导入用户数据(第一个Sheet)
byte[] fileContent = Files.readAllBytes(importFile.toPath());
MockMultipartFile userFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"multi_sheet.xlsx", "multi_sheet.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
List<User> importedUsers = excelUtil.importExcel(userFile, User.class);
// 验证用户数据
assertEquals(testUsers.size(), importedUsers.size(), "导入的用户数量应匹配");
// 导入产品数据(第二个Sheet)
MockMultipartFile productFile = new MockMultipartFile(
"multi_sheet.xlsx", "multi_sheet.xlsx",
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet",
fileContent);
List<Product> importedProducts = EasyExcel.read(productFile.getInputStream())
.head(Product.class)
.sheet(1) // 第二个Sheet(索引从0开始)
.doReadSync();
// 验证产品数据
assertEquals(testProducts.size(), importedProducts.size(), "导入的产品数量应匹配");
for (int i = 0; i < testProducts.size(); i++) {
Product original = testProducts.get(i);
Product imported = importedProducts.get(i);
assertEquals(original.getProductId(), imported.getProductId(), "产品ID应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getName(), imported.getName(), "产品名称应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getPrice(), imported.getPrice(), 0.001, "产品价格应匹配");
assertEquals(original.getStock(), imported.getStock(), "库存数量应匹配");
}
// 打印导入结果
System.out.println("成功导入用户数据: " + importedUsers.size() + " 条");
System.out.println("成功导入产品数据: " + importedProducts.size() + " 条");
}
}
四、扩展:自定义注解实现枚举类型转换
自定义注解实现枚举定义的
code->description的转化
1.枚举接口
public interface IEnum {
int getCode();
String getDescription();
}
2.枚举类
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
public enum TransportType implements IEnum{
SINGLE(1, "单边"),
BILATERAL(2, "往返");
private final int code;
private final String description;
TransportType(int code, String description) {
this.code = code;
this.description = description;
}
public static TransportType fromCode(int code) {
for (TransportType status : TransportType.values()) {
if (status.getCode() == code) {
return status;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("状态异常: " + code);
}
}
3.注解
import com.fc.enums.IEnum;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface EnumClass {
/**
* 指定枚举类,必须实现 IEnum 且有 fromCode(int) 静态方法
*/
Class<? extends IEnum> value();
}
4.转换类
import com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converter;
import com.alibaba.excel.enums.CellDataTypeEnum;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.GlobalConfiguration;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.ReadCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.property.ExcelContentProperty;
import com.fc.anno.EnumClass;
import com.fc.enums.IEnum;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class EnumConverter implements Converter<Object> {
/**
* key -> 枚举 Class
* value -> description -> code 的映射(导入用)
*/
private static final Map<Class<?>, Map<String, Integer>> DESC_TO_CODE_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* key -> 枚举 Class
* value -> code -> description 的映射(导出用)
*/
private static final Map<Class<?>, Map<Integer, String>> CODE_TO_DESC_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public Class<?> supportJavaTypeKey() {
return Object.class; // 支持任意枚举
}
@Override
public CellDataTypeEnum supportExcelTypeKey() {
return CellDataTypeEnum.STRING;
}
@Override
public Object convertToJavaData(ReadCellData<?> cellData,
ExcelContentProperty contentProperty,
GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
String cellValue = cellData.getStringValue();
if (cellValue == null || cellValue.trim().isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Class<? extends IEnum> enumClass = getEnumClass(contentProperty);
Map<String, Integer> descToCode = DESC_TO_CODE_CACHE
.computeIfAbsent(enumClass, this::buildDescToCodeMap);
Integer code = descToCode.get(cellValue.trim());
if (code == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("找不到对应枚举描述:" + cellValue);
}
Method fromCode = enumClass.getDeclaredMethod("fromCode", int.class);
return fromCode.invoke(null, code); // 返回 Integer 或枚举都行
}
@Override
public WriteCellData<?> convertToExcelData(Object value,
ExcelContentProperty contentProperty,
GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
if (value == null) {
return new WriteCellData<>("");
}
Class<? extends IEnum> enumClass = getEnumClass(contentProperty);
Map<Integer, String> codeToDesc = CODE_TO_DESC_CACHE
.computeIfAbsent(enumClass, this::buildCodeToDescMap);
int code;
if (value instanceof Number) {
code = ((Number) value).intValue();
} else if (value instanceof IEnum) {
code = ((IEnum) value).getCode();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("不支持的类型:" + value.getClass());
}
return new WriteCellData<>(codeToDesc.getOrDefault(code, ""));
}
private static Class<? extends IEnum> getEnumClass(ExcelContentProperty contentProperty) {
/* 重点:从注解里拿到枚举类 */
EnumClass enumClassAnno = contentProperty.getField().getAnnotation(EnumClass.class);
if (enumClassAnno == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("字段必须使用 @EnumClass 指定枚举");
}
return enumClassAnno.value();
}
private Map<Integer, String> buildCodeToDescMap(Class<?> enumClass) {
return Arrays.stream(enumClass.getEnumConstants())
.map(o -> (IEnum) o)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(IEnum::getCode, IEnum::getDescription));
}
private Map<String, Integer> buildDescToCodeMap(Class<?> enumClass) {
return Arrays.stream(enumClass.getEnumConstants())
.map(o -> (IEnum) o)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(IEnum::getDescription, IEnum::getCode));
}
}
5.使用示例

@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Product {
@ExcelProperty("产品ID")
private String productId;
@ExcelProperty("产品名称")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("价格")
private Double price;
@ExcelProperty(value = "运输类型",converter = EnumConverter.class)//使用自定义的转换类
@EnumClass(value = TransportType.class)//添加注解指定转换的枚举类,注意一定要实现接口IEnum
private Integer transportType;
}
6.测试
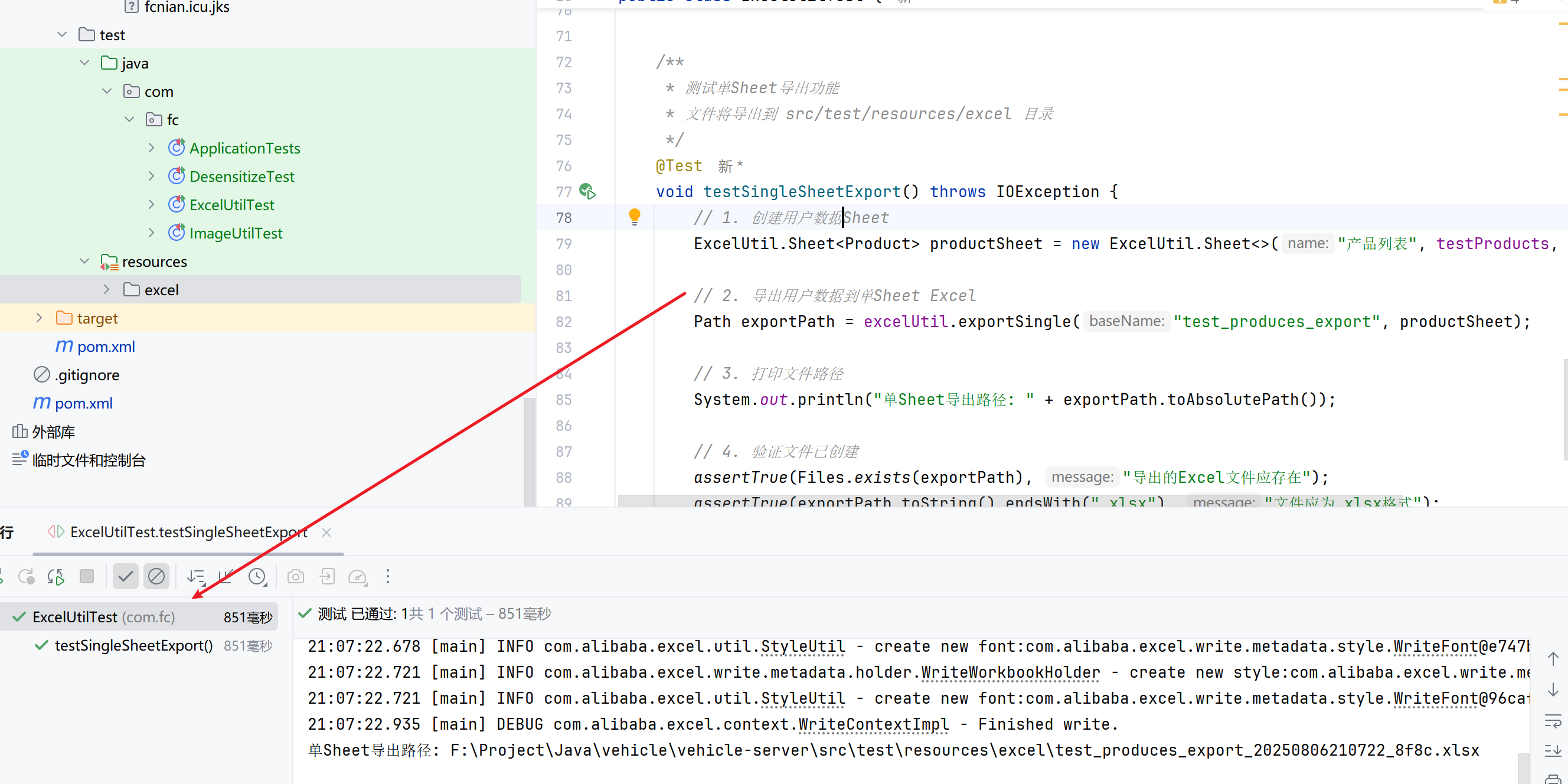
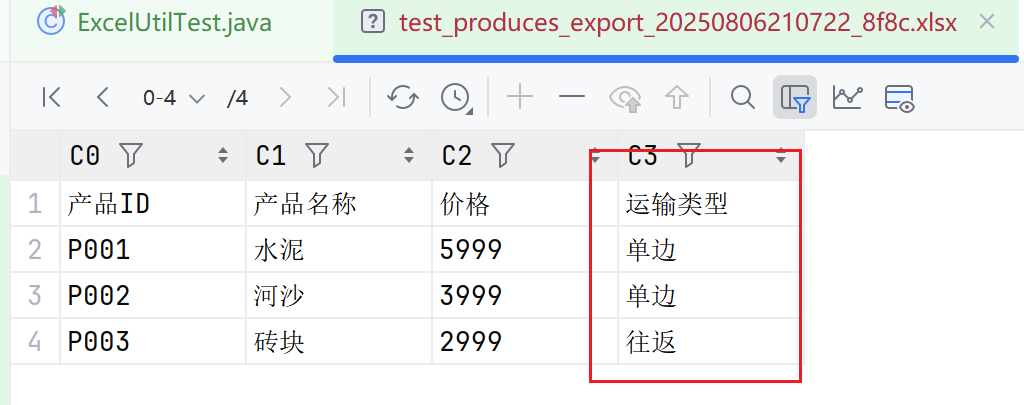
完整测试代码
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.fc.anno.EnumClass;
import com.fc.convert.EnumConverter;
import com.fc.enums.TransportType;
import com.fc.utils.ExcelUtil;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockMultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class ExcelUtilTest {
// 测试实体类 - 产品
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class Product {
@ExcelProperty("产品ID")
private String productId;
@ExcelProperty("产品名称")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("价格")
private Double price;
@ExcelProperty(value = "运输类型",converter = EnumConverter.class)
@EnumClass(value = TransportType.class)
private Integer transportType;
}
private ExcelUtil excelUtil;
private List<Product> testProducts;
// 导出目录 - src/test/resources/excel
private static final String EXPORT_DIR = "src/test/resources/excel/";
@BeforeEach
void setUp() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
// 初始化ExcelUtil,设置导出目录
excelUtil = new ExcelUtil();
//反射获取数据
Field field = ExcelUtil.class.getDeclaredField("defaultExportDir");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(excelUtil, EXPORT_DIR);
// 准备测试产品数据
testProducts = new ArrayList<>();
testProducts.add(new Product("P001", "水泥", 5999.0, 1));
testProducts.add(new Product("P002", "河沙", 3999.0, 1));
testProducts.add(new Product("P003", "砖块", 2999.0, 2));
}
/**
* 测试单Sheet导出功能
* 文件将导出到 src/test/resources/excel 目录
*/
@Test
void testSingleSheetExport() throws IOException {
// 1. 创建用户数据Sheet
ExcelUtil.Sheet<Product> productSheet = new ExcelUtil.Sheet<>("产品列表", testProducts, Product.class);
// 2. 导出用户数据到单Sheet Excel
Path exportPath = excelUtil.exportSingle("test_produces_export", productSheet);
// 3. 打印文件路径
System.out.println("单Sheet导出路径: " + exportPath.toAbsolutePath());
// 4. 验证文件已创建
assertTrue(Files.exists(exportPath), "导出的Excel文件应存在");
assertTrue(exportPath.toString().endsWith(".xlsx"), "文件应为.xlsx格式");
assertTrue(Files.size(exportPath) > 0, "文件大小应大于0");
}
}
总结
本Excel处理工具类旨在为开发者提供一套简洁高效的Excel操作解决方案。基于成熟的EasyExcel技术栈,覆盖了从基础数据导入导出、多Sheet复杂报表生成到枚举类型自动转换的完整场景。通过合理的API设计、严谨的资源管理和智能的类型转换机制,显著降低了Excel处理的开发门槛。