贪心算法
贪心的本质是:选择每一阶段的局部最优,从而达到全局最优
做题的时候,只要想清楚 局部最优 是什么,如果推导出全局最优,其实就够了。
相减问题(怎么相减利润最大化)
买卖股票的最佳实际
思路:如果第i天卖出股票,则最大利润为(该天的股价-前面天数中最小的股价),然后与已知的最大利润比较,如果大于则更新当前最大利润的值
只要找到一个最低买入价
minPrice,然后在后面找到最大差价。遍历价格数组,同时维护:
当前最小价格
minPrice当前最大利润
maxProfit = max(maxProfit, prices[i] - minPrice)

class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
// 初始化最大利润为0,最低价格为第一个价格
int maxProfit = 0;
int minPrice = 100000;
// 遍历价格数组
for (int price : prices) {
// 更新最低价格
minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, price);
// 更新最大利润
maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, price - minPrice);
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
买卖股票的最佳实际Ⅱ
遍历整个股票交易日价格列表 price,并执行贪心策略:所有上涨交易日都买卖(赚到所有利润),所有下降交易日都不买卖(永不亏钱)。
- 设 tmp 为第 i-1 日买入与第 i 日卖出赚取的利润,即 tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1] ;
- 当该天利润为正 tmp > 0,则将利润加入总利润 profit;当利润为 0 或为负,则直接跳过;
- 遍历完成后,返回总利润 profit。
等价于每天都与前一天做交易,赚才去买
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
if (tmp > 0) profit += tmp;
}
return profit;
}
}
抵达问题(抵达范围内是否出现更大的抵达范围)
跳跃游戏
此处i比较“原本范围内出现的最大抵达值”,由原本起始点字母出现的最大抵达范围一直在更新
思路:就是从起点出发,能够达到的最大点位,如果小于抵达不了则错误
- 如果某一个作为 起跳点 的格子可以跳跃的距离是 3,那么表示后面 3 个格子都可以作为 起跳点
- 可以对每一个能作为 起跳点 的格子都尝试跳一次,把 能跳到最远的距离 不断更新
- 如果可以一直跳到最后,就成功了

class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int maxReach = 0; // 记录能到达的最远索引
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前位置 i 已经超出最大可达范围,则说明无法继续前进
if (i > maxReach) {
return false;
}
// 更新最大可达范围
maxReach = Math.max(maxReach, i + nums[i]);
// 如果最大可达范围已经超过或等于最后一个索引,则返回 true
if (maxReach >= n - 1) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
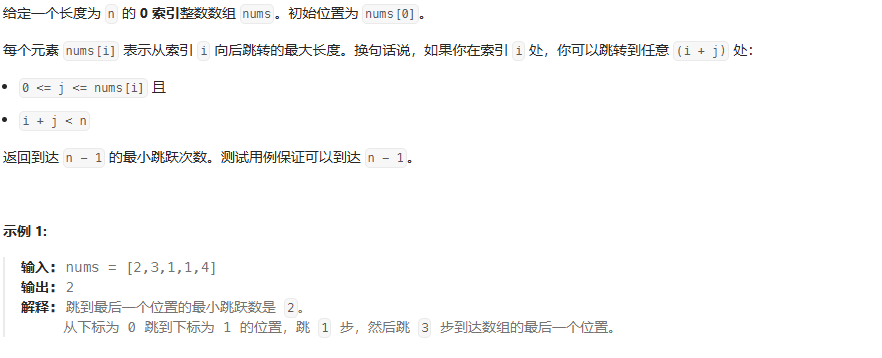
跳跃游戏Ⅱ(判断跳不跳)
此处i比较“原本出现范围的最大值”
思路:注意这个肯定是可以抵达到的 所以不需要判断 i > maxReach 无法抵达情况
可以这样想:判断当前节点能够抵达最大范围,在这范围内都要可以跳跃的,只有抵达范围边界,才会jumps加1, // 并选取当前节点抵达范围内的范围节点最大抵达范围,如果最大抵达范围大于nums.length长度,返回jumps
维护两个变量:
curEnd:当前跳跃可达的最远边界。curFarthest:在当前跳跃范围内能到达的最远位置。
从左到右遍历数组(不包含最后一个元素,因为到达最后一个元素就结束):
- 不断更新
curFarthest = max(curFarthest, i + nums[i])。 - 当
i到达curEnd时,说明当前跳跃范围已经用完,需要增加一次跳跃次数jumps++,并更新curEnd = curFarthest。
如果 curEnd 已经到达或超过末尾,返回 jumps。
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int jumps = 0;
int curEnd = 0;
int curFarthest = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
curFarthest = Math.max(curFarthest, i + nums[i]);
if (i == curEnd) {
jumps++;
curEnd = curFarthest;
if (curEnd >= nums.length - 1) {
break;
}
}
}
return jumps;
}
划分字母区间
此处i比较“原本范围内出现的最大抵达值”,由原本起始点字母出现的最大抵达范围一直在更新
思路: 重复的字母只能出现在同一区间,那么建立字母表,记录字母出现的最大下表。就可以将问题转为抵达问题 // 即使在抵达范围内的元素出现了更大的抵达值,就直到指针到达该最大抵达值位置

public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String s){
char[] sChar = s.toCharArray();
int n = s.length();
int[] last = new int[26];
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
last[sChar[i] - 'a'] = i;// 每个字母出现的最后下标
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
right = Math.max(right,last[sChar[i]-'a']); // 当前字母可以抵达最大范围
if(i == right){
ans.add(right-left+1);
left = right+1;
}
}
return ans;
}
矩阵
堆
数组中第K个最大元素

public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
// 转换为找第n-k小的元素(从0开始)
return quickselect(nums, 0, n - 1, n - k);
}
// 使用Hoare分区方案的快速选择算法
private int quickselect(int[] nums, int left, int right, int k) {
if (left == right) return nums[k]; // 基线条件
// 随机选择pivot避免最坏情况
int pivotIndex = left + new Random().nextInt(right - left + 1);
int pivotValue = nums[pivotIndex];
// 分区 每次循环只交换一次
// 初始化左右指针
int i = left - 1, j = right + 1;
while (i < j) {
// 从左找到第一个不小于pivot的元素
do i++; while (nums[i] < pivotValue); // 先执行循环体,再检查条件
// 从右找到第一个不大于pivot的元素
do j--; while (nums[j] > pivotValue);
// 交换这两个元素
if (i < j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
// 根据k的位置决定处理哪一部分
// j停止的位置就是小于midValue范围
if (k <= j) {
return quickselect(nums, left, j, k);
} else {
return quickselect(nums, j + 1, right, k);
}
}快排解法(随机选元素)
private Random rand = new Random();
public int findKthLargest (int[] nums,int k){
int n = nums.length;
return quickSelect(nums,0,n-1,n-k);
}
private int quickSelect(int[] nums,int left,int right,int targetIndex){
int pivotIndex = partiton(nums,left,right);
if(pivotIndex == targetIndex){
return nums[pivotIndex];
}else if(pivotIndex > targetIndex){
return quickSelect(nums,left,pivotIndex-1,targetIndex);
}else {
return quickSelect(nums, pivotIndex+1, right, targetIndex);
}
}
private int partiton(int[] nums,int left,int right){
int pivotIndex = left + rand.nextInt(right-left+1); // 随机选取节点
int pivotValue = nums[pivotIndex]; // 该节点值
swap(nums,pivotIndex,right); // 将该值放到末尾
int storeIndex = left;
for(int i = left;i<right;i++){ // 单指针划分小于/大于pivotValue区间
if(nums[i]<pivotValue){
swap(nums,storeIndex,i);
storeIndex++;
}
}
swap(nums,storeIndex,right); // 再把中位值互换回来
return storeIndex;
}
private void swap(int[] nums,int i,int j){
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
这个不太行,标准应该是快速排序
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
// 1. 定义桶数组,大小 20001,表示存储 [-10000, 10000] 范围内的整数频率
int[] buckets = new int[20001];
int n = nums.length;
// 2. 统计每个数字出现的次数
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// nums[i] + 10000 是为了将负数映射到 0~20000 的索引范围
buckets[nums[i] + 10000]++;
}
// 3. 从大到小遍历桶(即从最大值到最小值)
for (int i = 20000; i >= 0; i--) {
// 每访问一个桶,就相当于从最大值开始往下数 k 个
k -= buckets[i];
if (k <= 0) {
// 桶索引还原为原值:i - 10000
return i - 10000;
}
}
return 0; // 理论上不会走到这里
}
快速排序
递归+分区+互换值
// 分治快排
class QuickSort {
public void quickSort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return; // 递归结束条件 索引
int pivotIndex = partition(nums, left, right); // 找到 pivot 位置
quickSort(nums, left, pivotIndex - 1); // 排序左半部分
quickSort(nums, pivotIndex + 1, right); // 排序右半部分
}
// 分区函数
private int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
int pivot = nums[right]; // 选取最后一个元素作为 pivot
int i = left; // i 指向比 pivot 小的区域的末尾
for (int j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (nums[j] < pivot) { // 如果当前元素比 pivot 小
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
}
}
swap(nums, i, right); // pivot 放到中间
return i; // 返回 pivot 位置
}
// 交换值函数
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 6, 8, 10, 1, 2, 1};
QuickSort qs = new QuickSort();
qs.quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
栈
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();有效括号

class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
//特殊情况
if(s.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
//创建栈,字符类型
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(c == '('){
stack.push(')');
}
else if(c == '{'){
stack.push('}');
}
else if(c=='['){
stack.push(']');
}
// 要先判断是否为空,再判断出栈
else if(stack.empty() || c!=stack.pop()){
return false;
}
}
if(stack.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}每日温度
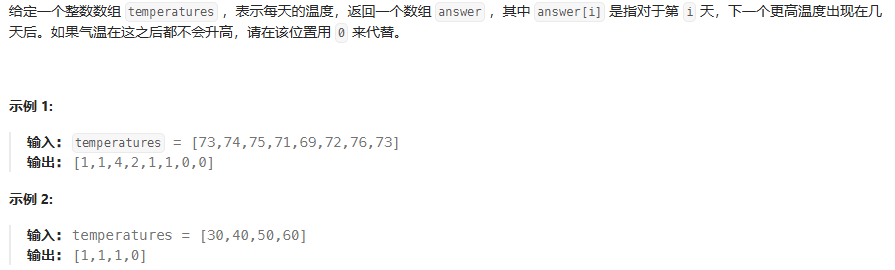
stack.peek() 返回栈顶元素,但不弹出(空栈会抛出异常)
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.length;
int[] result = new int[n];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // 单调递减栈,存索引
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前温度比栈顶索引的温度高,则计算等待天数
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
int prevIndex = stack.pop();
result[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex;
}
// 当前索引入栈
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}
