一、进程
1. 概念:进程(Process)是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础
2. 进程之间可以相互独立运行、互不干扰,也可以相互访问、操作
二、线程
1. 概念:操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位
2. 一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程
三、多线程的语法
1. 类:Thread
2. 引用命名空间:using System.Threading;
3. 声明一个新线程:Thread 线程名 = new Thread();
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
Console.WriteLine("线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
4. 启动线程:线程名.Start();
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
5. 设置为后台线程:线程名.IsBackground = true;
(1)当所有前台线程结束的时候,整个程序就结束了。无论是否还有后台线程在运行。
(2)后台线程会随着应用程序进程的终止而终止
(3)如果不设置为后台线程,可能导致进程无法正常关闭
(4)若线程1无限循环:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
}运行结果如下:(无限循环执行)
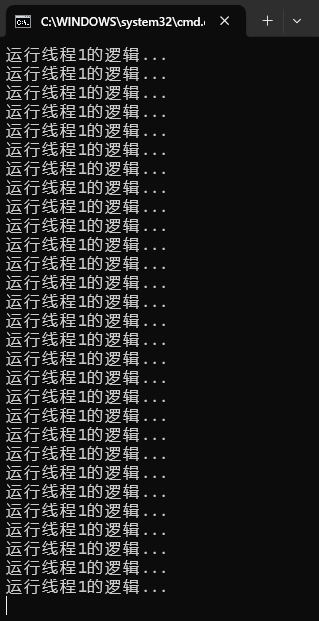
(5)设置线程1为后台线程:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
// 设置为后台线程
t1.IsBackground = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
Console.WriteLine("运行主线程的逻辑...");
}
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
}运行结果如下:(主线程结束后线程1也结束)
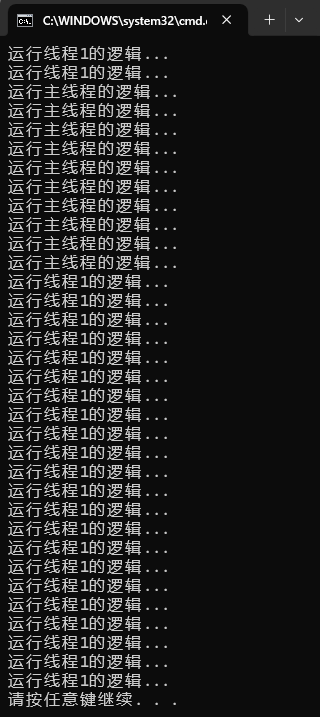
6. 释放线程:
(1)如果开启的线程不是死循环,不需要刻意去关闭
(2)如果开启的线程是死循环,有两种关闭方式:
①设置bool标识
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
static bool isRuning = true;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
// 设置为后台线程
t1.IsBackground = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
Console.WriteLine("运行主线程的逻辑...");
}
// 释放线程
// 1.设置bool标识
isRuning = false;
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
while (isRuning) {
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
}运行结果如下:
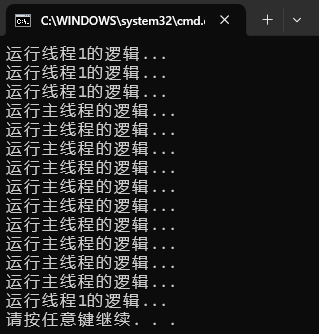
②调用线程提供的Abort方法
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
// static bool isRuning = true;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
// 设置为后台线程
t1.IsBackground = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
Console.WriteLine("运行主线程的逻辑...");
}
// 释放线程
// 1.设置bool标识
// isRuning = false;
// 2.使用线程的Abort方法
t1.Abort();
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
}运行结果同上。
注意:在.Net core版本中无法中止,会发生报错
7. 休眠线程:Thread.Sleep();
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Multithreading
{
class Program
{
// static bool isRuning = true;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个新线程
// 注意:线程执行的代码需要封装到一个新函数中
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadMethod1);
// 启动线程
t1.Start();
// 设置为后台线程
t1.IsBackground = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
Console.WriteLine("运行主线程的逻辑...");
}
// 释放线程
// 1.设置bool标识
// isRuning = false;
// 2.使用线程的Abort方法
t1.Abort();
// 休眠线程
// 在哪个函数中调用,就使哪个线程休眠
Thread.Sleep(1000); // 使线程休眠1000毫秒 1秒=1000毫秒
}
static void threadMethod1()
{
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("运行线程1的逻辑...");
}
}
}
}四、线程之间共享数据
1. 多个线程之间使用的内存使共享的,都属于应用程序(进程)
2. 要注意:当多线程同时操作同一片内存区域时可能会出问题,但是可以通过加锁的形式避免