引言:微服务通信的演进之路
在微服务架构中,服务间的通信是系统设计的核心挑战之一。从最初的HttpClient到RestTemplate,再到如今的声明式HTTP客户端,微服务通信方式经历了显著的演进。Spring Cloud OpenFeign作为声明式REST客户端的优秀实现,正在重新定义微服务间的通信方式。
传统的HTTP客户端使用方式存在诸多痛点:需要手动构建URL、处理序列化/反序列化、处理异常、管理连接池等。这些重复性工作不仅降低了开发效率,还容易引入错误。OpenFeign的出现彻底改变了这一现状,让开发者能够专注于业务逻辑,而不是通信细节。
什么是OpenFeign?
OpenFeign是一个基于Java的声明式HTTP客户端,最初由Netflix开发并开源,后来成为Spring Cloud生态系统的重要组成部分。它通过简单的接口和注解,将HTTP请求转化为Java方法调用,极大地简化了微服务间的通信。
核心特性概览
- 声明式API:通过接口和注解定义HTTP请求
- 服务发现集成:无缝集成Eureka、Consul、Nacos等服务注册中心
- 负载均衡:内置客户端负载均衡功能
- 熔断降级:支持Hystrix和Resilience4j熔断机制
- 灵活配置:支持全局和客户端级别的细粒度配置
快速开始:搭建OpenFeign环境
环境准备与依赖配置
首先在Spring Boot项目中添加OpenFeign依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 可选:增强的HTTP客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-okhttp</artifactId>
<version>11.0</version>
</dependency>
启用OpenFeign功能
在主应用类上添加@EnableFeignClients注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
基础用法:从简单示例开始
定义第一个Feign客户端
@FeignClient(name = "user-service", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface UserFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable Long id);
@PostMapping("/users")
ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user);
@GetMapping("/users")
ResponseEntity<List<User>> getAllUsers();
}
在服务中调用Feign客户端
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderService {
private final UserFeignClient userFeignClient;
public Order createOrder(Long userId, OrderRequest request) {
// 调用用户服务验证用户信息
ResponseEntity<User> response = userFeignClient.getUserById(userId);
User user = response.getBody();
if (user != null && user.isActive()) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(userId);
order.setAmount(request.getAmount());
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
throw new BusinessException("用户不存在或未激活");
}
}
进阶配置:深度定制OpenFeign
自定义配置类
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
/**
* 配置日志级别
* NONE: 不记录任何日志
* BASIC: 仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码和执行时间
* HEADERS: 记录BASIC级别信息+请求和响应头信息
* FULL: 记录所有请求和响应明细
*/
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
/**
* 配置连接超时和读取超时
*/
@Bean
public Request.Options options() {
return new Request.Options(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, true);
}
/**
* 配置重试机制
*/
@Bean
public Retryer retryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(100, 1000, 3);
}
}
应用配置示例
feign:
client:
config:
default: # 全局默认配置
connectTimeout: 5000
readTimeout: 10000
loggerLevel: basic
user-service: # 特定服务配置
connectTimeout: 3000
readTimeout: 5000
loggerLevel: full
logging:
level:
com.example.clients.UserFeignClient: DEBUG
高级特性:提升系统可靠性
熔断降级机制
// 1. 定义Fallback类
@Component
@Slf4j
public class UserFeignFallback implements UserFeignClient {
@Override
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(Long id) {
log.warn("用户服务不可用,返回默认用户信息");
return ResponseEntity.ok(User.createDefaultUser(id));
}
@Override
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(User user) {
throw new ServiceUnavailableException("用户服务暂时不可用");
}
}
// 2. 配置Fallback
@FeignClient(
name = "user-service",
url = "${feign.client.user-service.url}",
fallback = UserFeignFallback.class
)
public interface UserFeignClient {
// 接口方法
}
请求拦截器
@Component
public class AuthRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
// 添加认证令牌
String token = getAuthToken();
template.header("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
// 添加追踪ID
template.header("X-Request-ID", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
private String getAuthToken() {
// 从安全上下文中获取令牌
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null && authentication.getCredentials() instanceof String) {
return (String) authentication.getCredentials();
}
return "";
}
}
性能优化:提升通信效率
连接池配置
# 使用OKHttp连接池
feign:
okhttp:
enabled: true
httpclient:
enabled: false
# 连接池配置
okhttp:
max-idle-connections: 200
keep-alive-duration: 300
connect-timeout: 3000
read-timeout: 10000
GZIP压缩配置
feign:
compression:
request:
enabled: true
mime-types: text/xml,application/xml,application/json
min-request-size: 2048
response:
enabled: true
实战案例:电商系统中的应用
服务间调用示例
// 商品服务客户端
@FeignClient(name = "product-service", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface ProductFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
Product getProductById(@PathVariable Long id);
@PostMapping("/products/{id}/stock/decrease")
ResponseEntity<Void> decreaseStock(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam Integer quantity);
}
// 订单服务客户端
@FeignClient(name = "order-service", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface OrderFeignClient {
@PostMapping("/orders")
Order createOrder(@RequestBody OrderCreateRequest request);
@GetMapping("/orders/users/{userId}")
List<Order> getUserOrders(@PathVariable Long userId);
}
// 在购物车服务中协调多个服务
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CartService {
private final ProductFeignClient productFeignClient;
private final OrderFeignClient orderFeignClient;
@Transactional
public Order checkout(Long userId, List<CartItem> cartItems) {
// 验证商品信息并减少库存
for (CartItem item : cartItems) {
productFeignClient.decreaseStock(item.getProductId(), item.getQuantity());
}
// 创建订单
OrderCreateRequest request = new OrderCreateRequest(userId, cartItems);
return orderFeignClient.createOrder(request);
}
}
常见问题与解决方案
1. 序列化问题
问题描述:Date类型序列化格式不一致
解决方案:统一配置Jackson日期格式
spring:
jackson:
date-format: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
time-zone: GMT+8
serialization:
write-dates-as-timestamps: false
2. 复杂参数传递
问题描述:GET请求传递对象参数
解决方案:使用@SpringQueryMap注解
@FeignClient(name = "search-service")
public interface SearchFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/search")
SearchResult search(@SpringQueryMap SearchCriteria criteria);
}
3. 文件上传支持
解决方案:配置form encoder
@Configuration
public class FeignFormConfig {
@Bean
public Encoder feignFormEncoder() {
return new SpringFormEncoder(new JacksonEncoder());
}
}
// 文件上传客户端
@FeignClient(name = "file-service", configuration = FeignFormConfig.class)
public interface FileUploadFeignClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/upload", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
UploadResult uploadFile(@RequestPart("file") MultipartFile file);
}
监控与诊断
日志配置
logging:
level:
com.example.clients: DEBUG
feign:
client:
config:
default:
loggerLevel: FULL
分布式追踪集成
@Configuration
public class TraceFeignConfig {
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor tracingRequestInterceptor() {
return template -> {
// 传递追踪头信息
template.header("X-B3-TraceId", MDC.get("X-B3-TraceId"));
template.header("X-B3-SpanId", MDC.get("X-B3-SpanId"));
template.header("X-B3-ParentSpanId", MDC.get("X-B3-ParentSpanId"));
};
}
}
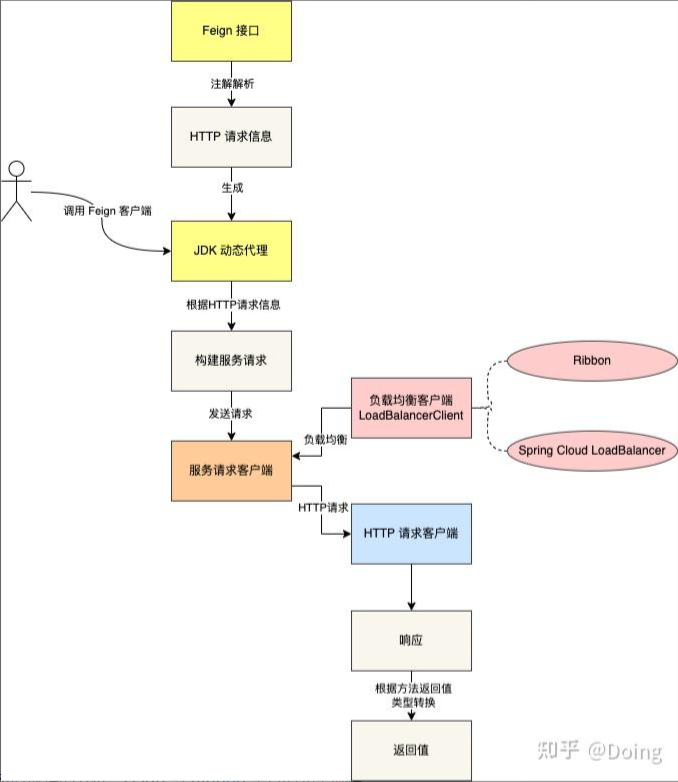
核心原理
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 的核心实现是 声明式 REST 客户端 和 动态代理机制 。
核心组件
- @EnableFeignClients:这个注解用于启动 Feign 客户端的支持。在 Spring Boot 应用中,当你添加了这个注解后,Spring 会扫描指定包下的所有带有 @FeignClient 注解的接口,并为它们创建代理对象。
- @FeignClient:通过该注解定义一个 Feign 客户端,可以指定服务名(用于服务发现)、URL、编码器、解码器等属性。每个被标记的接口都会被增强生成 JDK 动态代理对象,实际请求会通过这些动态代理对象发送出去。
- Feign.Builder:Feign 的核心构建者类,它负责根据配置创建具体的 Feign 客户端实例。Spring Cloud 对默认的 Builder 进行了扩展,加入了负载均衡( Ribbon / LoadBalancer )、熔断器( Hystrix )等功能。
- LoadBalancerFeignClient:当与 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 集成时,OpenFeign 使用的是一种特殊的服务请求客户端 —— LoadBalancerClient,它能够利用 Ribbon / Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 提供的负载均衡策略来选择服务实例进行调用。
- Decoder, Encoder, Logger, ErrorDecoder 等:这些是Feign的内部组件,分别用于处理响应的反序列化、请求的序列化、日志记录以及错误处理等功能。Spring Cloud 允许开发者自定义这些组件的行为。
工作流程
1、初始化: 在 Spring 容器启动期间,Spring Cloud 会扫描所有标注有@FeignClient的接口,为它们生成 JDK 动态代理对象,然后注入到 Spring 容器中。
2、创建Feign客户端: 利用 Feign.builder() 方法结合各种配置(如编码器、解码器、拦截器、接口注解配置等),构造出 Feign 动态代理客户端。如果整合了负载均衡器,则会使用 LoadBalancerClient 作为最终的客户端实现。
以 spring-cloud-starter-openfeign 包的 4.2.1 版本源码为例:
public class FeignClientFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<Object>, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryAware {
/**
* FeignClientFactoryBean 的 getObject() 方法是 Spring 容器用来获取由该工厂 Bean 创建的 Feign 客户端实例的方法。
* getObject() 方法最终返回的是一个动态代理对象,这个对象实现了 @FeignClient 定义的接口,并能够将接口方法调用转换为 HTTP 请求
*/
@Override
public Object getObject() {
return getTarget();
}
/**
* 创建并返回一个 Feign 客户端实例
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
<T> T getTarget() {
// 获取 FeignClientFactory 实例
FeignClientFactory feignClientFactory = beanFactory != null ? beanFactory.getBean(FeignClientFactory.class)
: applicationContext.getBean(FeignClientFactory.class);
// 使用 FeignClientFactory 构建 Feign.Builder 实例 (代码见后)
Feign.Builder builder = feign(feignClientFactory);
// 如果 URL 未提供且不在配置中可用,则尝试通过负载均衡选择实例
if (!StringUtils.hasText(url) && !isUrlAvailableInConfig(contextId)) {
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("For '" + name + "' URL not provided. Will try picking an instance via load-balancing.");
}
if (!name.startsWith("http://") && !name.startsWith("https://")) {
url = "http://" + name;
} else {
url = name;
}
url += cleanPath();
// 通过负载均衡创建客户端动态代理实例 (代码见后)
return (T) loadBalance(builder, feignClientFactory, new HardCodedTarget<>(type, name, url));
}
// 否则使用固定 URL 创建客户端
if (StringUtils.hasText(url) && !url.startsWith("http://") && !url.startsWith("https://")) {
url = "http://" + url;
}
// 获取服务请求客户端:
// 1、如果没有额外引入任何 HTTP 客户端库(如 Apache HttpClient 或 OkHttp),
// 并且也没有启用负载均衡组件(Ribbon 或 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer),
// 那么默认使用的 Client 是 Feign 自带的基于 HttpURLConnection 的实现。
// 2、如果启用了负载均衡组件,则使用的 Client 默认是 FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient(未开启失败重试时)
Client client = getOptional(feignClientFactory, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
// 如果启用负载均衡组件(Spring Cloud LoadBalancer),但由于这里不需要负载均衡,
// 所以通过 getDelegate() 获取到具体的 HTTP 请求客户端(比如 HttpURLConnection)即可
if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
if (client instanceof RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
// 应用自定义构建器定制化
applyBuildCustomizers(feignClientFactory, builder);
// 获取 Targeter 实例,并使用它来创建目标客户端动态代理实例
Targeter targeter = get(feignClientFactory, Targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, feignClientFactory, resolveTarget(feignClientFactory, contextId, url));
}
/**
* 创建并返回一个已配置好的 Feign.Builder 实例
*/
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignClientFactory context) {
FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class);
Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(type);
// @formatter:off
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
// 设置日志记录器,用于输出请求/响应详情
.logger(logger)
// 将 Java 对象编码为 HTTP 请求体(如 JSON、XML)。默认实现是 SpringEncoder,使用 Spring MVC 的 HttpMessageConverter。
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
// Decoder:将 HTTP 响应体解码为 Java 对象。默认实现是 SpringDecoder,同样基于 HttpMessageConverter。
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
// Contract:负责解析接口上的注解(如 @RequestMapping, @GetMapping 等)。默认是 SpringMvcContract,支持 Spring MVC 注解风格。
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// @formatter:on
// 设置重试策略(Retryer)、错误处理器(ErrorDecoder)、请求拦截器(RequestInterceptor)、连接超时等配置项
// 所有这些配置都支持用户自定义覆盖,默认值来自 Spring Boot 自动配置
configureFeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
/**
* 通过负载均衡创建客户端动态代理实例
* @param builder 已配置好的 Feign.Builder 实例
* @param context FeignClientFactory,用于从 Spring 容器中获取 Bean
* @param target 一个封装了目标服务名称和 URL 的对象(通常是服务名,例如 http://service-name)
*/
protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignClientFactory context, HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
// 获取服务请求客户端:
// 如果启用了负载均衡组件,则使用的 Client 默认是 FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient(未开启失败重试时)
// FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient 内会通过负载均衡获取一个服务实例,把服务名替换为真实IP和端口号,再发起 HTTP 请求。
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
// 设置 HTTP 请求客户端
builder.client(client);
// 应用额外定制化配置
applyBuildCustomizers(context, builder);
// 获取 Targeter
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
// 创建动态代理实例
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer?");
}
}
public class ReflectiveFeign<C> extends Feign {
// FeignClientFactoryBean 中的 targeter.target(...) 最终都会调用到 ReflectiveFeign.newInstance(...) 方法创建动态代理对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target, C requestContext) {
TargetSpecificationVerifier.verify(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler =
targetToHandlersByName.apply(target, requestContext);
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
// 最终返回的是一个 JDK 动态代理对象
T proxy =
(T)
Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
for (MethodHandler methodHandler : methodToHandler.values()) {
if (methodHandler instanceof DefaultMethodHandler) {
((DefaultMethodHandler) methodHandler).bindTo(proxy);
}
}
return proxy;
}
}
public class FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient implements Client {
/**
* 真正执行 HTTP 请求的底层客户端(如 Apache HttpClient、OkHttp、JDK HttpURLConnection 等)
* FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient 是一个装饰器模式的应用,它将实际请求委托给这个 delegate 执行
*/
private final Client delegate;
/**
* 用于服务发现和实例选择的负载均衡客户端
* Spring Cloud 2020 之前的旧版本是 RibbonLoadBalancerClient
* Spring Cloud 2020 之后的新版本是 BlockingLoadBalancerClient
*/
private final LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
// (省略其他)...
// 执行 HTTP 请求
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
// 将请求的 URL 解析为 URI
final URI originalUri = URI.create(request.url());
// 提取主机名作为 serviceId(即服务名称),比如 "order-service"
String serviceId = originalUri.getHost();
Assert.state(serviceId != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
// 获取负载均衡策略使用的“hint”,通常是从请求头中提取的路由提示信息,比如可以基于请求头指定调用某个区域的服务实例
String hint = getHint(serviceId);
// 构建负载均衡请求上下文,request 里会包含请求体、头、方法等信息。
DefaultRequest<RequestDataContext> lbRequest = new DefaultRequest<>(
new RequestDataContext(buildRequestData(request), hint));
// 生命周期方法回调
Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> supportedLifecycleProcessors = LoadBalancerLifecycleValidator
.getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(
loadBalancerClientFactory.getInstances(serviceId, LoadBalancerLifecycle.class),
RequestDataContext.class, ResponseData.class, ServiceInstance.class);
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onStart(lbRequest));
// 根据服务名称,选取服务实例
// choose() 方法背后调用了 Ribbon 或 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 的负载均衡策略算法(如轮询、随机、权重等)
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose(serviceId, lbRequest);
org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.Response<ServiceInstance> lbResponse = new DefaultResponse(
instance);
// 如果没有找到可用服务实例,构造一个 503 响应返回,同时通知生命周期处理器请求失败
if (instance == null) {
String message = "Load balancer does not contain an instance for the service " + serviceId;
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle
.onComplete(new CompletionContext<ResponseData, ServiceInstance, RequestDataContext>(
CompletionContext.Status.DISCARD, lbRequest, lbResponse)));
return Response.builder()
.request(request)
.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE.value())
.body(message, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
.build();
}
// 重构 URL:使用选中的 ServiceInstance 替换原始 URL 中的 host 部分。
// 例如把 http://order-service/api/order/1 变成 http://192.168.1.10:8080/api/order/1
String reconstructedUrl = loadBalancerClient.reconstructURI(instance, originalUri).toString();
Request newRequest = buildRequest(request, reconstructedUrl, instance);
// 通过底层的 HTTP 客户端(delegate)发送请求,并通知生命周期处理器执行回调方法
return executeWithLoadBalancerLifecycleProcessing(delegate, options, newRequest, lbRequest, lbResponse,
supportedLifecycleProcessors);
}
}
3、发起HTTP请求: 应用代码从 Spring 容器中获取到的 Feign 客户端,实际上是上面步骤 2 构造出来的 JDK 动态代理。当程序中调用 Feign 客户端的方法时,实际上是在调用由 JDK 动态生成的代理对象的方法,这个代理对象会将方法调用转换为 HTTP 请求,然后通过 HTTP 客户端发送出去。
4、响应处理: 收到响应后,相应的解码器会被用来解析响应内容,并将其转换为目标方法的返回值类型。
工作流程总结