个人主页:chian-ocean
文章专栏-Linux
前言:
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人类阅读和编写,也易于机器解析和生成。它常用于客户端和服务器之间的数据传输,尤其是在 Web 开发中非常常见。

JSON库的安装
yum安装
sudo yum install jsoncpp-devel
- 这里面是已经安装好的
Nothing to do
JSON介绍
JSON(JavaScript 对象表示法)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,设计上简洁易读。它是基于文本的,易于人类理解和编写,也易于机器解析和生成。JSON 经常用于 Web 应用中,尤其是前端与后端之间的数据交换。
JSON的基本结构
SON 主要有两种数据结构:
- 对象(Object):由一组由键(键值对)组成的无序集合。对象在 JSON 中由大括号
{}包围。
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 25,
"isStudent": true
}
- 数组(Array):由多个按顺序排列的值组成。数组在 JSON 中由方括号
[]包围。
["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
- 嵌套对象和数组:JSON 允许对象和数组嵌套,即一个 JSON 对象的值可以是另一个对象或数组。
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"isStudent": false,
"courses": ["Math", "Physics", "Chemistry"],
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "New York",
"zip": "10001"
},
"spouse": null
}
JSON的数据类型
- 字符串(String):必须用双引号
"括起来,支持 Unicode 字符。 - 数字(Number):可以是整数或浮动数,且没有引号。
- 布尔值(Boolean):可以是
true或false。 - 数组(Array):由零个或多个数据项组成,数据项之间用逗号分隔。
- 对象(Object):由一对一对的键值对组成,键和值之间用冒号
:分隔,多个键值对之间用逗号,分隔。 - null:表示一个空值
Jsoncpp使用
JSON对象的创建
[[include]] <iostream>
[[include]] <string>
[[include]] <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个 JSON 对象
Json::Value root;
// 向 JSON 对象中添加键值对
root["name"] = "Alice"; // 字符串
root["age"] = 25; // 数字
root["isStudent"] = true; // 布尔值
cout << root.toStyledString() <<endl; //打印
return 0;
}
输出
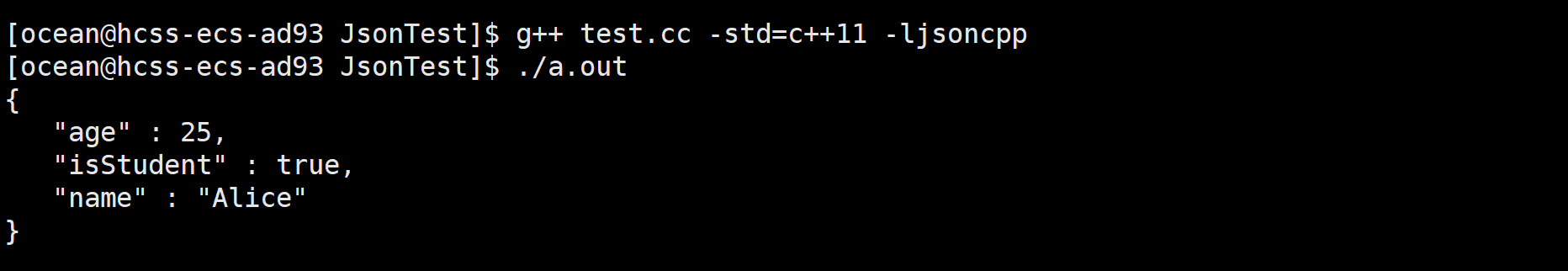
FastWriter转换成字符串风格
FastWriter是jsoncpp中的一个类,它用于将Json::Value对象转换为 JSON 字符串,且具有高效的序列化速度FastWriter会生成一个紧凑的 JSON 字符串(没有缩进和换行),非常适合于数据传输和存储。FastWriter与StreamWriter类相比,速度较快,但它不支持格式化输出(即不支持缩进和换行),所以适用于需要高效、简洁的输出场景。
[[include]] <iostream>
[[include]] <string>
[[include]] <jsoncpp/json/json.h> // 引入 jsoncpp 库头文件
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个 JSON 对象
Json::Value root;
// 向 JSON 对象中添加键值对
root["name"] = "Alice"; // 添加字符串键值对,"name" 键对应 "Alice"
root["age"] = 25; // 添加数字键值对,"age" 键对应 25
root["isStudent"] = true; // 添加布尔值键值对,"isStudent" 键对应 true
// 输出格式化的 JSON 字符串,带有缩进和换行
cout << "Formatted JSON Output:" << endl;
cout << root.toStyledString() << endl;
// 使用 FastWriter 生成紧凑的 JSON 字符串(没有缩进和换行)
Json::FastWriter w; // 创建 FastWriter 对象
string jsonstr = w.write(root); // 将 JSON 对象转换为紧凑的 JSON 字符串
// 输出紧凑格式的 JSON 字符串
cout << "Compact JSON Output (FastWriter):" << endl;
cout << "jsonstr: " << jsonstr << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
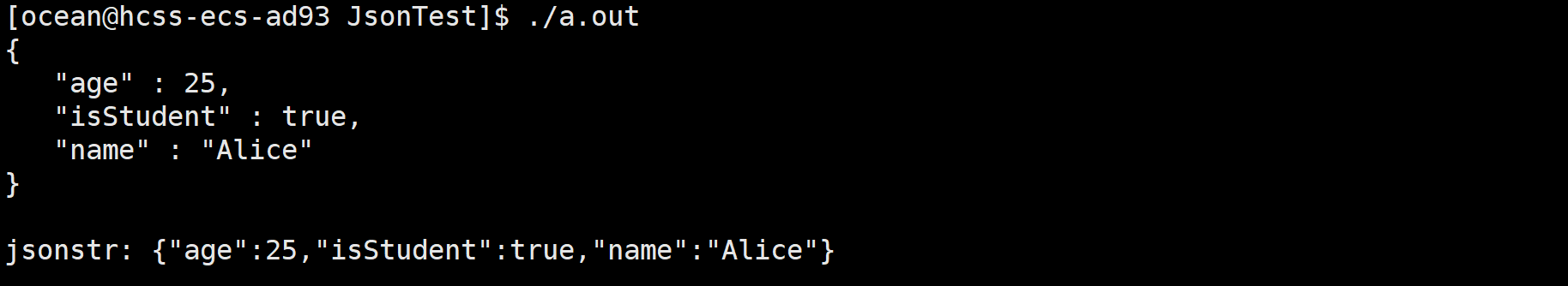
Reader转换成value
在 jsoncpp 中,如果你想将 JSON 字符串(std==string 类型)转换为 Json==Value 对象,可以使用 Json==Reader 或 Json==CharReader 来进行解析。Json==Value 是 jsoncpp 中用来表示 JSON 数据的核心类,Json==Reader 用于将 JSON 字符串解析为 Json::Value 对象。
[[include]] <iostream>
[[include]] <string>
[[include]] <jsoncpp/json/json.h> // 引入 jsoncpp 库头文件
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个空的 JSON 对象
Json::Value root;
// 向 JSON 对象中添加键值对
root["name"] = "Alice"; // 字符串:向 root 中添加键为 "name" 的字符串 "Alice"
root["age"] = 25; // 数字:向 root 中添加键为 "age" 的整数 25
root["isStudent"] = true; // 布尔值:向 root 中添加键为 "isStudent" 的布尔值 true
// 输出格式化的 JSON 对象(带缩进和换行)
cout <<"root: \n" << root.toStyledString() << endl;
// toStyledString() 会输出格式化的 JSON 字符串(带缩进和换行,易于阅读)
// 使用 FastWriter 生成紧凑格式的 JSON 字符串(没有缩进和换行)
Json::FastWriter w; // 创建 FastWriter 对象 w
string jsonstr = w.write(root); // 将 root 转换为紧凑格式的 JSON 字符串,并存储在 jsonstr 中
// 输出紧凑格式的 JSON 字符串
cout << "jsonstr: " << jsonstr << endl;
// 由于 FastWriter 会去掉换行和空格,这里的输出不会有任何格式化
// 创建 Json::Reader 对象,用于解析 JSON 字符串
Json::Reader r;
// 创建一个 Json::Value 对象 res 用于存储解析后的 JSON 数据
Json::Value res;
// 使用 Json::Reader 对象解析 JSON 字符串 jsonstr
if (r.parse(jsonstr, res)) {
// 如果解析成功,输出格式化后的 JSON 对象
cout <<"res: \n" << res.toStyledString() << endl;
} else {
// 如果解析失败,输出错误信息
cout << "Failed to parse the JSON string!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
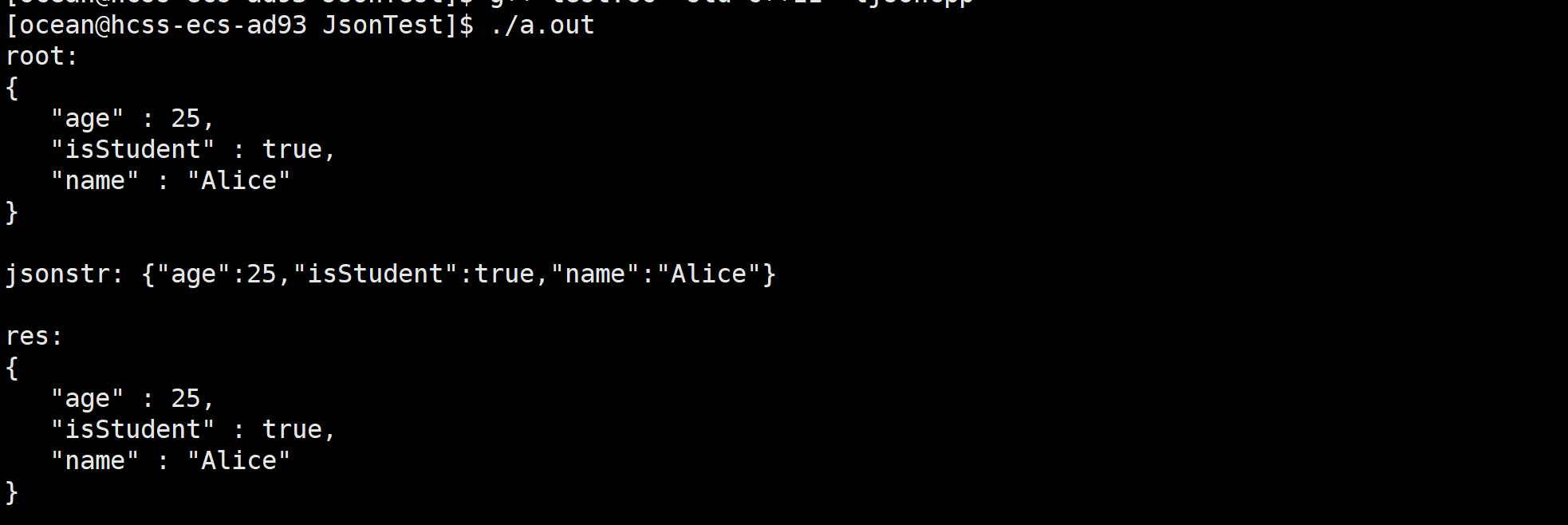
将序列化与反序列化用JSON改写
Requset
序列化
bool Serialize(std::string *out)
{
[[ifdef]] Myself
// 构建有效载荷
// 将x_转换为字符串并加入空格分隔符
std==string s = std==to_string(x_);
s += space_sep; // 添加空格分隔符
s += op_; // 添加操作符
s += space_sep; // 添加空格分隔符
s += std::to_string(y_); // 将y_转换为字符串并添加
*out = s; // 将构建的字符串赋值给输出参数
return true;
[[else]]
// 如果不是在Myself模式下,使用JSON格式序列化
Json::Value root;
root["x"] = x_; // 将x_值放入JSON根节点
root["y"] = y_; // 将y_值放入JSON根节点
root["op"] = op_; // 将操作符op_放入JSON根节点
Json::FastWriter w; // 创建一个JSON序列化工具
*out = w.write(root); // 使用JSON工具将根节点序列化为字符串并赋值给输出参数
return true;
[[endif]]
}
在Myself宏定义的情况下,序列化数据为一个简单的字符串格式,通过空格分隔x_、op_和y_。
如果Myself宏没有定义,则使用Json::Value将数据序列化为JSON格式。
反序列化
// 反序列化 x + y
bool Deserialize(const std::string &in)
{
[[ifdef]] Myself
// 解析有效载荷
// 查找第一个空格分隔符的位置
auto pos1 = in.find(space_sep);
if (pos1 == std==string==npos) // 如果没有找到空格分隔符,返回失败
return false;
// 提取x的部分
std::string part_x = in.substr(0, pos1);
// 查找最后一个空格分隔符的位置
auto pos2 = in.rfind(space_sep);
// 提取操作符部分
std::string oper = in.substr(pos1 + 1, pos2);
// 提取y的部分
std::string part_y = in.substr(pos2 + 1);
// 如果空格分隔符之间的距离不为2,说明格式不正确
if (pos2 != pos1 + 2)
return false;
// 解析操作符(目前假设是单字符)
op_ = in[pos1 + 1];
// 将x和y从字符串转换为整数
x_ = std::stoi(part_x);
y_ = std::stoi(part_y);
return true;
[[else]]
// 如果不是在Myself模式下,使用JSON格式反序列化
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader r;
// 解析输入字符串为JSON格式
r.parse(in, root);
// 提取x、y和op的值
x_ = root["x"].asInt(); // 提取x的整数值
y_ = root["y"].asInt(); // 提取y的整数值
op_ = root["op"].asString(); // 提取操作符的字符串值
return true;
[[endif]]
}
Response
序列化
// 序列化 r code
bool Serialize(std::string *out)
{
[[ifdef]] Myself
// 构建有效载荷
// 将result_转换为字符串
std==string s = std==to_string(result_);
// 添加空格分隔符
s += space_sep;
// 将code_转换为字符串并添加
s += std::to_string(code_);
// 将构建的字符串赋值给输出参数
*out = s;
return true;
[[else]]
// 如果不是在Myself模式下,使用JSON格式序列化
Json::Value root;
// 将result_和code_添加到JSON对象中
root["result"] = result_;
root["code"] = code_;
Json::FastWriter w; // 创建一个JSON序列化工具
// 使用JSON工具将数据序列化为字符串并赋值给输出参数
*out = w.write(root);
return true;
[[endif]]
}
反序列化
bool Deserialize(const std::string &in)
{
[[ifdef]] Myself
// 查找空格分隔符的位置
auto pos = in.find(space_sep);
// 提取result_的部分(空格之前的部分)
std::string res = in.substr(0, pos);
// 提取code_的部分(空格之后的部分)
std::string code = in.substr(pos + 1);
// 如果空格分隔符的位置不唯一,说明格式不正确
if (pos != in.rfind(space_sep))
return false;
// 将提取的result_和code_从字符串转换为整数
result_ = std::stoi(res);
code_ = std::stoi(code);
return true;
[[else]]
// 如果不是在Myself模式下,使用JSON格式反序列化
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader r;
// 解析输入的字符串为JSON格式
r.parse(in, root);
// 提取JSON中的result和code值,未赋值到result_和code_,需要修正为赋值操作
result_ = root["result"].asInt(); // 提取result并赋值给result_
code_ = root["code"].asInt(); // 提取code并赋值给code_
return true;
[[endif]]
}