1. 技巧及注意事项
1. 引入虚拟头结点。
2. 多利用指针保存节点,此时不用纠结连接顺序会使链表断开的问题。
3. 头插常用于使链表逆序。所谓的头插,也要在虚拟头结点之后插入。因此更准确地说,是每次都在虚拟头结点后尾插,以达到逆序链表的效果。
4. 尝试使用快慢指针。
5. 加深理解引用传递:对于 Node cur = head; 这行代码,意为使得 cur 和 head 指向同一个内存地址。因此,只有修改 cur 或 head 的内部结构而非其本身时,影响会传递给对方。这表示,当执行 cur.next = null 时,此时修改的是引用的内部结构,因此 head.next 也会变为 null。当执行 cur = cur.next 或 cur = null 时,这时改变的是 cur 指向的目标,而 head 指向的目标从未改变,因此 head 不受任何影响。反过来改变 head 也是遵循上述逻辑,双方逻辑完全对称。
6. 尽量不要调用自定义的方法,涉及到引用的传递问题。
2. 基础链表问题
本题使用头插法(虚拟头结点之后)。

如图所示,我们需要保存这几个节点来辅助完成插入。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
ListNode retNext = ret.next;
ret.next = cur;
cur.next = retNext;
cur = curNext;
}
return ret.next;
}
}使用快慢指针。注意 while 条件不能改变。尽量不要在使用快慢指针时杂糅其他逻辑,因为此时 fast 和 slow 都会因 head 内部结构的变化而发生变化。
对于偶数个节点的链表,slow 最终指向靠后的位置,也就是后半段的起点。
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
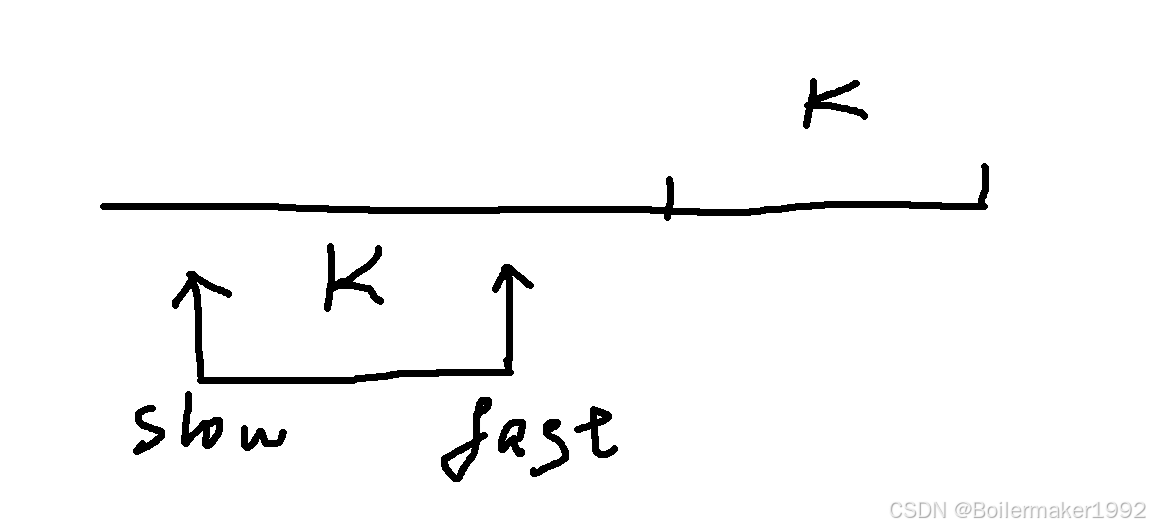
使得 fast 比 slow 先走 k 步,再一起走即可。
class Solution {
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
int count = k - 1;
while (count != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
count--;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
}双指针,谁小尾插谁到新链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = ret;
ListNode cur1 = list1;
ListNode cur2 = list2;
// 谁小尾插谁
while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
if (cur1.val < cur2.val) {
ListNode next1 = cur1.next;
cur.next = cur1;
cur = cur.next;
cur1 = next1;
} else {
ListNode next2 = cur2.next;
cur.next = cur2;
cur = cur.next;
cur2 = next2;
}
}
// 还有剩余的,全部添加到末尾
if (cur1 != null) {
cur.next = cur1;
}
if (cur2 != null) {
cur.next = cur2;
}
return ret.next;
}
}如果两个链表节点数量相同,是否相交就很容易判断了,只需让两个指针一起动,每次判断引用是否相同即可。
进一步想,如果节点数量不同,并且还相交了,那么肯定是相交前的部分有节点数量差。
其实类似于 “返回倒数第 k 个节点” 这道题的思路,就是想办法让节点数量多的链表的指针提前移动一定的步数,使得二者可以并行。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while (curA != null && curB != null) {
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
ListNode cur1 = headA;
ListNode cur2 = headB;
if (curA == null) {
while (curB != null) {
cur2 = cur2.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
}
if (curB == null) {
while (curA != null) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
curA = curA.next;
}
}
while (cur1 != null) {
if (cur1 == cur2) {
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return null;
}
}public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}这道题要找入环点。两个指针在环中相遇的时刻,fast 比 slow 多走了 a 个整圈。
设环长 m,起点离入环点 n,相遇点离入环点 x,方程为:2 (n + x) = n + a*m + x
可以得出 n + x = a*m ---> n = a*m - x,根据这个等式就可以很容易找到 n 了,因为只需让一个指针从起点出发,另一个指针从相遇点出发,它们一定能在入环点相遇。
3. 综合链表问题
综合链表问题其实就是一道题融合几种基础链表问题,首先要将其拆分为小问题。
链表部分的题目都没有过多难的算法,都是题目怎么说就怎么写,也就是模拟。
面试题 02.04. 分割链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode smallerList = new ListNode(0);
ListNode largerList = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur1 = smallerList;
ListNode cur2 = largerList;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
cur1.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
} else {
cur2.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
/* 这一步很关键,因为 largerList 的最后一个节点
可能仍然指向原链表中的某个节点(这些节点可能已经
被分配到smallerList中),从而导致环。*/
cur2.next = null;
cur1.next = largerList.next;
return smallerList.next;
}
}先使用快慢指针,找到中点,再将后半段逆序,再依次比较。
注意,将后半段逆序是比较简单的做法,如果要将前半段逆序,那么要考虑修改 head 引起 fast 错误移动的问题。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
if (fast != null && fast.next == null) { // 奇数
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode list = new ListNode(0);
while (slow != null) {
ListNode slowNext = slow.next;
ListNode listNext = list.next;
list.next = slow;
slow.next = listNext;
slow = slowNext;
}
list = list.next;
while (list != null) {
if (list.val != head.val) {
return false;
}
list = list.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
}class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
// 使用快慢指针找中点,并分割前后半段
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode half = slow.next;
slow.next = null; // 分割
// 将后半段逆序
ListNode reverseList = null;
ListNode cur = half;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
if (reverseList == null) {
cur.next = null;
reverseList = cur;
} else {
cur.next = reverseList;
reverseList = cur;
}
cur = next;
}
// 合并两个链表
ListNode cur1 = head;
ListNode cur2 = reverseList;
while (cur2 != null) { // 前半段长度 >= 后半段长度
ListNode next1 = cur1.next;
ListNode next2 = cur2.next;
// 在 cur1 和 next1 之间插入 cur2
cur1.next = cur2;
cur2.next = next1;
cur1 = next1;
cur2 = next2;
}
}
}class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
int carryBit = 0;
// 任一个链表没遍历完,或有进位没处理,则继续
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carryBit != 0) {
// 若某一链表已遍历完,用 0 代替其值
int val1 = (l1 != null) ? l1.val : 0;
int val2 = (l2 != null) ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = val1 + val2 + carryBit;
int currentVal = sum % 10; // 取模得个位
carryBit = sum / 10; // 进位:0 或 1
cur.next = new ListNode(currentVal);
cur = cur.next;
if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
return head.next;
}
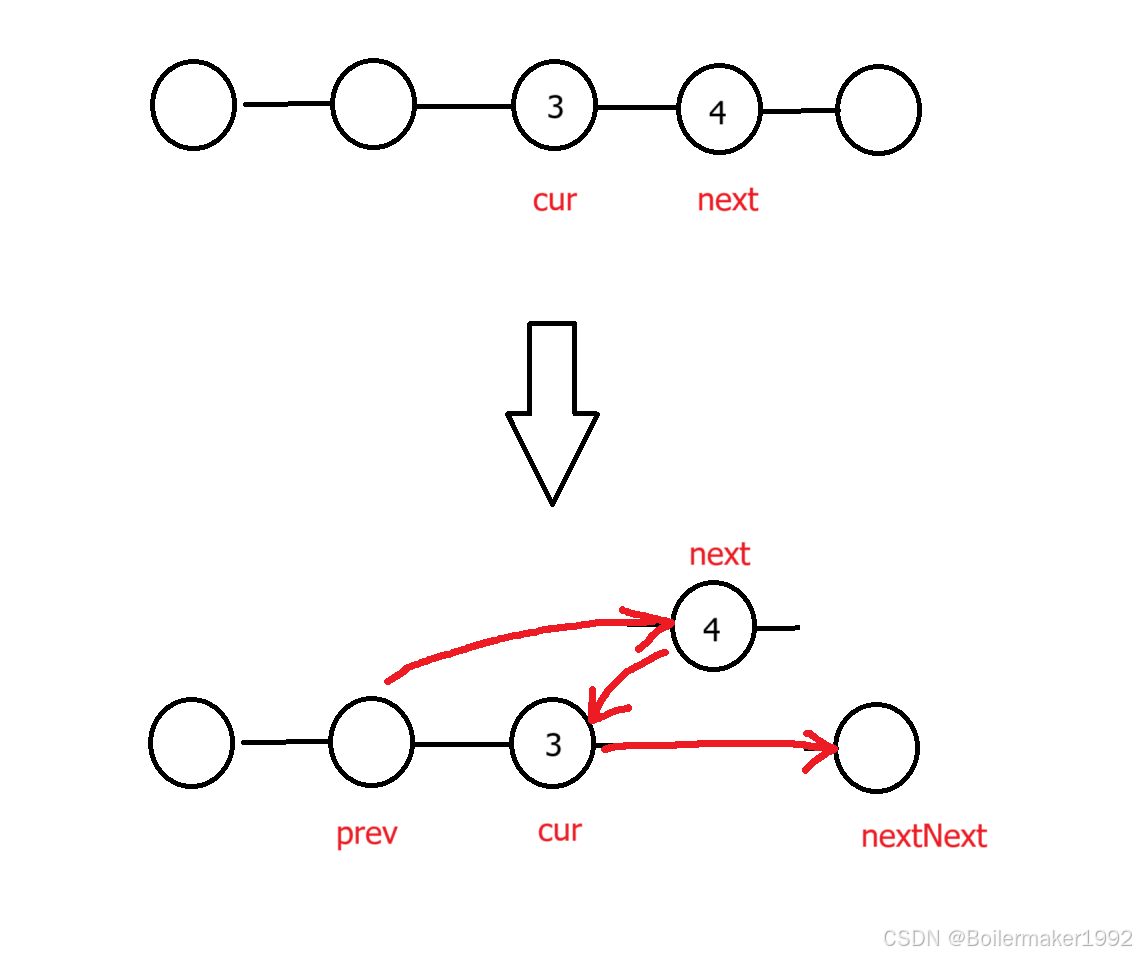
}如图,两两交换节点至少需要影响四个节点。
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
ret.next = head;
ListNode prev = ret;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
ListNode nextNext = next.next;
prev.next = next;
next.next = cur;
cur.next = nextNext;
prev = cur;
cur = nextNext;
}
return ret.next;
}
}class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 先计算一下需要几次逆序操作
ListNode temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
count = count / k;
// 核心逻辑
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = ret;
while (head != null && count != 0) {
ListNode rest = split(head, k); // 截断 head
cur.next = reverse(head); // 逆序
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) { // 使 cur 指向尾节点,为下次拼接准备
cur = cur.next;
}
head = rest; // head 依然能找到未处理部分
count--;
}
cur.next = head; // 根据题意,不足 k 的部分不应改变顺序,直接拼接
return ret.next;
}
// 截断链表
// 这个方法返回 head 的剩余部分
// 由于这个方法会改变 head 的内部结构,因此必须返回未处理的部分,否则找不到
private ListNode split(ListNode head, int k) {
int count = k - 1;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null && count > 0) {
cur = cur.next;
count--;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = null; // 此时修改 head 内部
return temp;
}
// 逆序链表
// 该方法将传入的 cur 整个逆序
private ListNode reverse(ListNode cur) {
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
ListNode retNext = ret.next;
ret.next = cur;
cur.next = retNext;
cur = curNext;
}
return ret.next;
}
}将这些 list 都放入小根堆中,比较的元素就是头结点的值。
由此,每次 poll 出的一定是持有最小头结点的 list。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(
(v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val);
// 先放头结点
for (ListNode head : lists) {
if (head != null) {
heap.offer(head);
}
}
ListNode ret = new ListNode(0);
ListNode prev = ret;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
ListNode temp = heap.poll();
prev.next = temp;
prev = prev.next;
temp = temp.next;
if (temp == null) {
continue;
}
heap.offer(temp);
}
return ret.next;
}
}