Markdown转Word完整教程:从原理到实现
前言
在技术文档编写和学术论文创作中,Markdown因其简洁的语法和良好的可读性而广受欢迎。然而,在实际工作中,我们经常需要将Markdown文档转换为Word格式,以便与同事协作、提交正式文档或满足特定的格式要求。
本文将详细介绍Markdown转Word的各种方法、技术原理和代码实现,帮助读者掌握这一实用技能。
目录
Markdown转Word的常见需求
1.1 业务场景
- 技术文档发布:将GitHub上的README文档转换为Word格式供客户查看
- 学术论文写作:在Markdown中快速编写,最终转换为符合期刊要求的Word格式
- 企业文档管理:将技术文档转换为企业标准的Word模板格式
- 多格式发布:同一份内容需要同时发布到网站和生成PDF/Word版本
1.2 转换要求
- 格式保真度:标题、列表、表格、代码块等格式需要准确转换
- 图片处理:本地图片和网络图片的正确嵌入
- 特殊元素:数学公式、流程图、图表等复杂元素的处理
- 中文支持:良好的中文字体和编码支持
转换方法对比
2.1 在线转换工具
优点:
- 操作简单,无需安装软件
- 支持多种格式转换
- 界面友好
缺点:
- 文件大小限制
- 隐私安全问题
- 功能有限,无法自定义
2.2 桌面软件
优点:
- 功能相对完整
- 支持批量转换
- 离线使用
缺点:
- 需要安装额外软件
- 更新维护成本高
- 扩展性差
2.3 编程实现
优点:
- 高度可定制
- 支持批量处理
- 可集成到工作流中
- 支持复杂逻辑处理
缺点:
- 需要编程知识
- 开发成本较高
技术原理深度解析
3.1 Markdown解析原理
Markdown是一种轻量级标记语言,其解析过程包括:
# Markdown解析的基本流程
def parse_markdown(content):
# 1. 词法分析 - 识别各种标记符号
tokens = tokenize(content)
# 2. 语法分析 - 构建抽象语法树
ast = build_ast(tokens)
# 3. 渲染 - 转换为目标格式
output = render(ast, target_format)
return output
3.2 Word文档结构
Word文档(.docx)实际上是一个ZIP压缩包,包含:
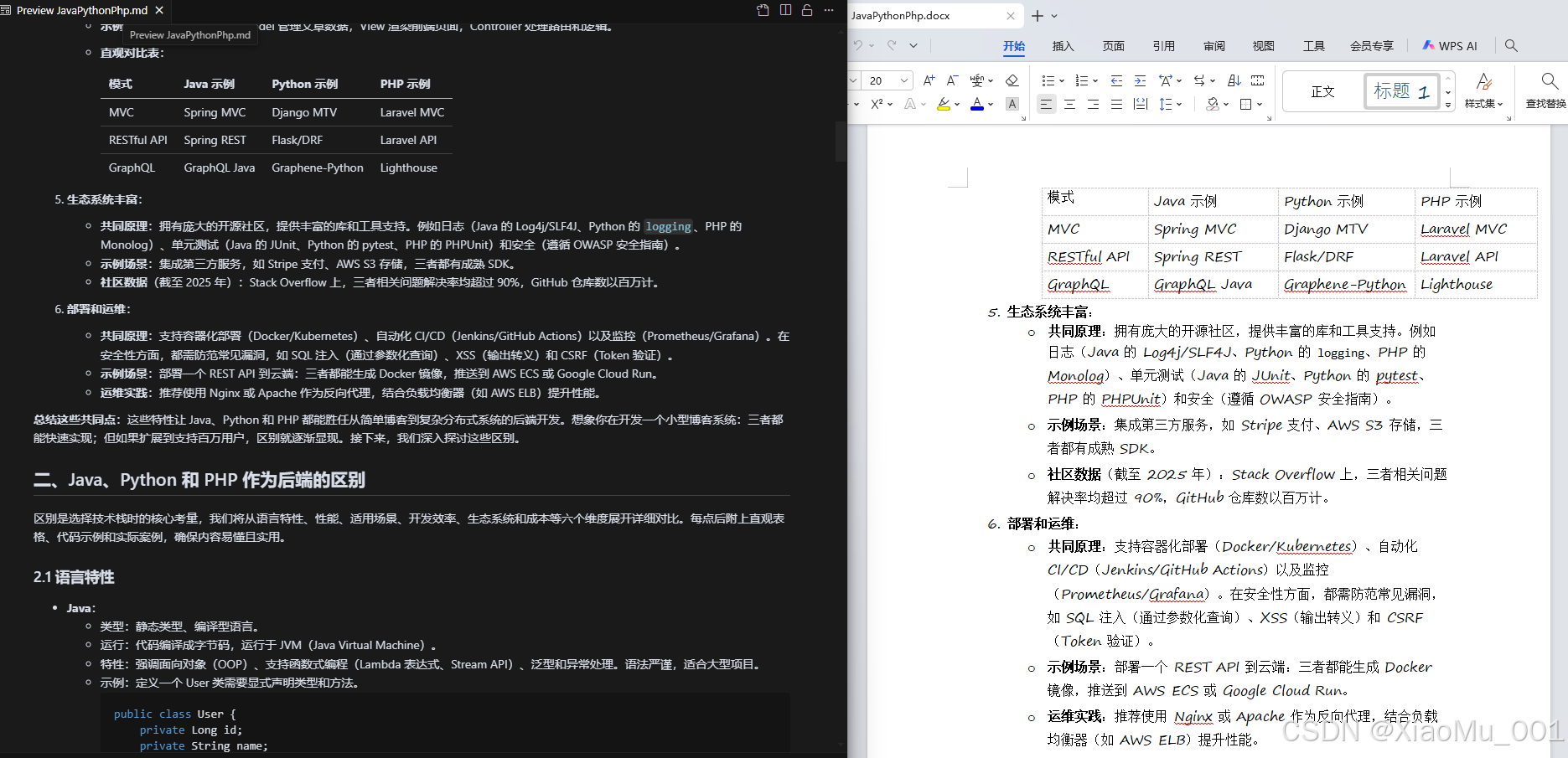
3.3 转换映射关系
| Markdown元素 | Word对应元素 | 转换方式 |
|---|---|---|
| # 标题 | Heading 1 | 样式映射 |
| 粗体 | Bold | 字符格式 |
| 斜体 | Italic | 字符格式 |
代码块 |
代码样式段落 | 段落样式 |
| 图片 | 内嵌图片 | 媒体嵌入 |
| 链接 | 超链接 | 超链接对象 |
| 表格 | Word表格 | 表格对象 |
代码实现详解
4.1 环境准备
# 安装必要的Python包
pip install pypandoc playwright pillow
# 安装Pandoc
# Windows: 下载安装包
# Linux: sudo apt-get install pandoc
# macOS: brew install pandoc
# 安装Playwright浏览器
playwright install
4.2 核心转换类
import re
import os
import tempfile
import sys
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
import pypandoc
class MarkdownToWordConverter:
"""Markdown到Word转换器"""
def __init__(self):
self.temp_dir = None
self.image_counter = 0
def convert(self, input_path, output_path):
"""主转换方法"""
try:
# 1. 读取Markdown文件
md_content = self._read_markdown(input_path)
# 2. 预处理特殊内容
processed_content = self._preprocess_content(md_content, input_path)
# 3. 使用Pandoc转换
self._convert_with_pandoc(processed_content, output_path)
print(f"转换完成: {output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换失败: {e}")
raise
4.3 Mermaid图表处理
def render_mermaid(self, code):
"""使用Playwright渲染Mermaid图表为PNG"""
try:
with sync_playwright() as p:
browser = p.chromium.launch(headless=True)
page = browser.new_page()
# 构建包含Mermaid的HTML页面
html = f"""
<html>
<body>
<pre class="mermaid">{code}</pre>
<script type="module">
import mermaid from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@10/dist/mermaid.esm.min.mjs';
mermaid.initialize({{
startOnLoad: true,
theme: 'default',
fontFamily: 'Arial, sans-serif'
}});
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
page.set_content(html)
page.wait_for_selector('.mermaid svg', timeout=15000)
# 获取SVG边界框并截图
bbox = page.evaluate('document.querySelector(".mermaid svg").getBBox()')
clip = {
'x': bbox['x'] - 10,
'y': bbox['y'] - 10,
'width': bbox['width'] + 20,
'height': bbox['height'] + 20
}
screenshot = page.screenshot(type='png', clip=clip, omit_background=True)
browser.close()
return screenshot
except Exception as e:
print(f"渲染Mermaid图表时出错: {e}")
return None
4.4 图片处理优化
def process_images(self, md_content, temp_dir, md_dir):
"""处理Markdown中的图片引用"""
def replace_image(match):
alt_text = match.group(1)
img_path = match.group(2)
# 处理本地图片
if not img_path.startswith(('http://', 'https://')):
try:
abs_img_path = os.path.normpath(os.path.join(md_dir, img_path))
if os.path.exists(abs_img_path):
# 生成ASCII文件名避免编码问题
img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_path)[1] or '.png'
temp_img_name = f"img_{self.image_counter}{img_ext}"
self.image_counter += 1
temp_img_path = os.path.join(temp_dir, temp_img_name)
# 复制图片文件
with open(abs_img_path, 'rb') as src, open(temp_img_path, 'wb') as dst:
dst.write(src.read())
print(f"图片已处理: {temp_img_name}")
return f''
else:
print(f"警告: 图片未找到: {abs_img_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理图片 {img_path} 时出错: {e}")
return match.group(0)
return re.sub(r'!\[(.*?)\]\((.*?)\)', replace_image, md_content)
4.5 Pandoc转换配置
def _convert_with_pandoc(self, content, output_path):
"""使用Pandoc进行最终转换"""
# 创建临时Markdown文件
temp_md_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, 'temp.md')
with open(temp_md_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(content)
# Pandoc转换参数
pandoc_args = [
'--from=markdown+pipe_tables+grid_tables+multiline_tables',
'--to=docx',
'--standalone',
'--wrap=preserve',
'--markdown-headings=atx',
'--reference-doc=template.docx', # 可选:使用自定义模板
]
# 切换到临时目录执行转换
original_cwd = os.getcwd()
try:
os.chdir(self.temp_dir)
pypandoc.convert_file(
'temp.md',
'docx',
outputfile=output_path,
extra_args=pandoc_args
)
finally:
os.chdir(original_cwd)
高级功能实现
5.1 自定义样式模板
def create_custom_template(self, template_path):
"""创建自定义Word模板"""
# 可以通过修改reference-doc参数使用自定义模板
# 模板文件需要包含预定义的样式
pass
5.2 批量转换
def batch_convert(self, input_dir, output_dir, pattern="*.md"):
"""批量转换Markdown文件"""
import glob
md_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_dir, pattern))
for md_file in md_files:
filename = os.path.basename(md_file)
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, filename.replace('.md', '.docx'))
self.convert(md_file, output_file)
5.3 元数据提取
def extract_metadata(self, content):
"""提取Markdown文档元数据"""
metadata = {}
# 提取YAML前置元数据
yaml_match = re.match(r'^---\n(.*?)\n---\n', content, re.DOTALL)
if yaml_match:
yaml_content = yaml_match.group(1)
# 解析YAML内容
import yaml
metadata = yaml.safe_load(yaml_content)
# 提取标题
title_match = re.search(r'^#\s+(.+)$', content, re.MULTILINE)
if title_match:
metadata['title'] = title_match.group(1).strip()
return metadata
常见问题与解决方案
6.1 中文编码问题
问题:转换后的Word文档中文显示乱码
解决方案:
# 确保文件读写使用UTF-8编码
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# Pandoc参数中添加编码支持
pandoc_args.extend([
'--from=markdown+pipe_tables+grid_tables+multiline_tables',
'--to=docx',
'--standalone',
'--wrap=preserve',
'--markdown-headings=atx',
])
6.2 图片路径问题
问题:图片无法正确显示
解决方案:
def normalize_image_paths(self, content, base_dir):
"""标准化图片路径"""
def fix_path(match):
alt_text = match.group(1)
img_path = match.group(2)
# 转换为绝对路径
if not os.path.isabs(img_path):
abs_path = os.path.join(base_dir, img_path)
if os.path.exists(abs_path):
return f''
return match.group(0)
return re.sub(r'!\[(.*?)\]\((.*?)\)', fix_path, content)
6.3 表格格式问题
问题:复杂表格格式丢失
解决方案:
# 使用Pandoc的表格扩展
pandoc_args = [
'--from=markdown+pipe_tables+grid_tables+multiline_tables+table_captions',
'--to=docx',
'--standalone',
]
6.4 数学公式支持
问题:LaTeX数学公式无法正确渲染
解决方案:
# 添加数学公式支持
pandoc_args.extend([
'--from=markdown+tex_math_dollars',
'--mathjax', # 或使用 --katex
])
性能优化建议
7.1 内存优化
def process_large_file(self, input_path, output_path, chunk_size=1024*1024):
"""处理大文件的内存优化方案"""
# 分块读取大文件
with open(input_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
while True:
chunk = f.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
# 处理每个块
self._process_chunk(chunk)
7.2 并发处理
import concurrent.futures
import threading
def parallel_convert(self, file_list, max_workers=4):
"""并行转换多个文件"""
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor:
futures = []
for input_file, output_file in file_list:
future = executor.submit(self.convert, input_file, output_file)
futures.append(future)
# 等待所有任务完成
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
try:
result = future.result()
print(f"转换完成: {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换失败: {e}")
7.3 缓存机制
import hashlib
import pickle
class CachedConverter:
def __init__(self, cache_dir=".cache"):
self.cache_dir = cache_dir
os.makedirs(cache_dir, exist_ok=True)
def get_file_hash(self, file_path):
"""计算文件哈希值"""
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
return hashlib.md5(f.read()).hexdigest()
def is_cached(self, input_path, output_path):
"""检查是否已缓存"""
input_hash = self.get_file_hash(input_path)
cache_file = os.path.join(self.cache_dir, f"{input_hash}.cache")
if os.path.exists(cache_file) and os.path.exists(output_path):
# 检查输出文件是否比缓存文件新
if os.path.getmtime(output_path) > os.path.getmtime(cache_file):
return True
return False
总结与展望
8.1 技术总结
本文详细介绍了Markdown转Word的完整解决方案,包括:
- 多种转换方法对比:在线工具、桌面软件、编程实现各有优劣
- 技术原理深度解析:从Markdown解析到Word文档结构的完整流程
- 完整代码实现:包含Mermaid图表、图片处理、中文支持等高级功能
- 问题解决方案:针对常见问题的具体解决方法
- 性能优化策略:内存优化、并发处理、缓存机制等
8.2 应用价值
- 提高工作效率:自动化文档转换流程
- 保证格式一致性:统一的转换标准
- 支持复杂内容:图表、公式、多媒体等
- 易于集成:可集成到CI/CD流程中
8.3 未来发展方向
- AI辅助转换:利用机器学习优化转换质量
- 实时协作:支持多人实时编辑和转换
- 云端服务:提供SaaS转换服务
- 更多格式支持:支持更多输入输出格式
8.4 学习建议
对于想要深入学习文档转换技术的读者,建议:
- 掌握基础:熟悉Markdown语法和Word文档结构
- 实践项目:从简单转换开始,逐步增加复杂度
- 关注更新:跟踪Pandoc等工具的最新版本
- 社区参与:参与开源项目,分享经验
附录
A. 完整代码示例
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Markdown到Word转换器完整实现
支持Mermaid图表、图片处理、中文支持等功能
"""
import re
import os
import tempfile
import sys
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
import pypandoc
class MarkdownToWordConverter:
def __init__(self):
self.temp_dir = None
self.image_counter = 0
def convert(self, input_path, output_path):
"""主转换方法"""
try:
# 创建临时目录
self.temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
print(f"临时目录: {self.temp_dir}")
# 读取Markdown文件
md_content = self._read_markdown(input_path)
# 预处理内容
processed_content = self._preprocess_content(md_content, input_path)
# 使用Pandoc转换
self._convert_with_pandoc(processed_content, output_path)
print(f"转换完成: {output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换失败: {e}")
raise
finally:
# 清理临时文件
if self.temp_dir and os.path.exists(self.temp_dir):
import shutil
shutil.rmtree(self.temp_dir)
def _read_markdown(self, input_path):
"""读取Markdown文件"""
try:
with open(input_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取Markdown文件失败: {e}")
raise
def _preprocess_content(self, content, input_path):
"""预处理Markdown内容"""
md_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(input_path))
# 处理Mermaid图表
content = self._process_mermaid(content)
# 处理图片
content = self._process_images(content, md_dir)
return content
def _process_mermaid(self, content):
"""处理Mermaid图表"""
def replace_mermaid(match):
code = match.group(1).strip()
png_bytes = self._render_mermaid(code)
if png_bytes:
try:
fd, path = tempfile.mkstemp(suffix='.png', dir=self.temp_dir)
os.write(fd, png_bytes)
os.close(fd)
rel_path = os.path.basename(path)
print(f"Mermaid图表已保存: {path}")
return f''
except Exception as e:
print(f"保存Mermaid图表时出错: {e}")
return match.group(0)
return re.sub(r'```mermaid\s*\n(.*?)\n```', replace_mermaid, content, flags=re.DOTALL | re.IGNORECASE)
def _render_mermaid(self, code):
"""渲染Mermaid图表为PNG"""
try:
with sync_playwright() as p:
browser = p.chromium.launch(headless=True)
page = browser.new_page()
html = f"""
<html>
<body>
<pre class="mermaid">{code}</pre>
<script type="module">
import mermaid from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@10/dist/mermaid.esm.min.mjs';
mermaid.initialize({{ startOnLoad: true, theme: 'default' }});
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
page.set_content(html)
page.wait_for_selector('.mermaid svg', timeout=15000)
bbox = page.evaluate('document.querySelector(".mermaid svg").getBBox()')
clip = {
'x': bbox['x'] - 10,
'y': bbox['y'] - 10,
'width': bbox['width'] + 20,
'height': bbox['height'] + 20
}
screenshot = page.screenshot(type='png', clip=clip, omit_background=True)
browser.close()
return screenshot
except Exception as e:
print(f"渲染Mermaid图表时出错: {e}")
return None
def _process_images(self, content, md_dir):
"""处理图片"""
def replace_image(match):
alt_text = match.group(1)
img_path = match.group(2)
if not img_path.startswith(('http://', 'https://')):
try:
abs_img_path = os.path.normpath(os.path.join(md_dir, img_path))
print(f"处理图片: {abs_img_path}")
if os.path.exists(abs_img_path):
img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_path)[1] or '.png'
temp_img_name = f"img_{self.image_counter}{img_ext}"
self.image_counter += 1
temp_img_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, temp_img_name)
with open(abs_img_path, 'rb') as src, open(temp_img_path, 'wb') as dst:
dst.write(src.read())
print(f"图片已复制到: {temp_img_path}")
return f''
else:
print(f"警告: 图片未找到: {abs_img_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理图片 {img_path} 时出错: {e}")
return match.group(0)
return re.sub(r'!\[(.*?)\]\((.*?)\)', replace_image, content)
def _convert_with_pandoc(self, content, output_path):
"""使用Pandoc进行转换"""
temp_md_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, 'temp.md')
try:
with open(temp_md_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(content)
print(f"临时Markdown文件已生成: {temp_md_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"写入临时Markdown文件失败: {e}")
raise
output_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(output_path))
if not os.access(output_dir, os.W_OK):
print(f"错误: 输出目录 {output_dir} 无写入权限")
raise PermissionError(f"输出目录 {output_dir} 无写入权限")
pandoc_args = [
'--from=markdown+pipe_tables+grid_tables+multiline_tables',
'--to=docx',
'--standalone',
'--wrap=preserve',
'--markdown-headings=atx',
]
original_cwd = os.getcwd()
try:
os.chdir(self.temp_dir)
print(f"Pandoc工作目录: {self.temp_dir}")
pypandoc.convert_file(
'temp.md',
'docx',
outputfile=output_path,
extra_args=pandoc_args
)
finally:
os.chdir(original_cwd)
def main():
"""主函数"""
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("用法: python md_to_docx.py input.md output.docx")
sys.exit(1)
input_path = sys.argv[1]
output_path = sys.argv[2]
if not os.path.exists(input_path):
print(f"错误: 输入文件 {input_path} 不存在")
sys.exit(1)
converter = MarkdownToWordConverter()
converter.convert(input_path, output_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
B. 使用说明
安装依赖:
pip install pypandoc playwright pillow playwright install安装Pandoc:
- Windows: 下载安装包
- Linux:
sudo apt-get install pandoc - macOS:
brew install pandoc
使用方法:
python md_to_docx.py input.md output.docx
C. 注意事项
- 确保所有依赖包正确安装
- 图片路径使用相对路径
- 大文件转换时注意内存使用
- 定期更新Pandoc版本以获得最新功能
本文档提供了Markdown转Word的完整解决方案,希望对读者有所帮助。如有问题,欢迎交流讨论。