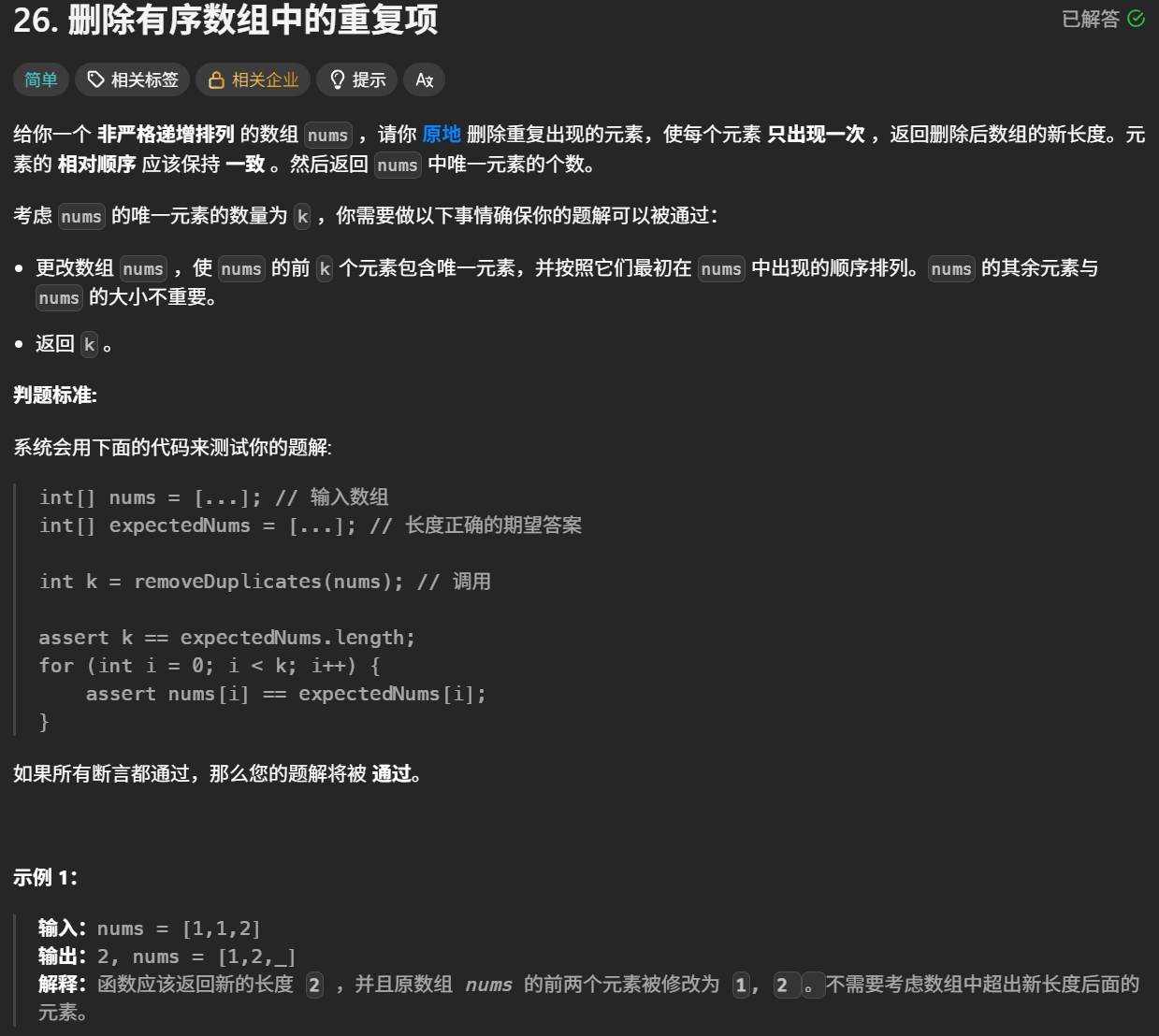
1 删除有序数组的重复项
方法一:双指针
思路:
这道题目的要求是:对给定的有序数组 nums 删除重复元素,在删除重复元素之后,每个元素只出现一次,并返回新的长度,上述操作必须通过原地修改数组的方法,使用 O(1) 的空间复杂度完成。
由于给定的数组 nums 是有序的,因此对于任意 i<j,如果 nums[i]=nums[j],则对任意 i≤k≤j,必有 nums[i]=nums[k]=nums[j],即相等的元素在数组中的下标一定是连续的。利用数组有序的特点,可以通过双指针的方法删除重复元素。
如果数组 nums 的长度为 0,则数组不包含任何元素,因此返回 0。
当数组 nums 的长度大于 0 时,数组中至少包含一个元素,在删除重复元素之后也至少剩下一个元素,因此 nums[0] 保持原状即可,从下标 1 开始删除重复元素。
定义两个指针 fast 和 slow 分别为快指针和慢指针,快指针表示遍历数组到达的下标位置,慢指针表示下一个不同元素要填入的下标位置,初始时两个指针都指向下标 1。
假设数组 nums 的长度为 n。将快指针 fast 依次遍历从 1 到 n−1 的每个位置,对于每个位置,如果 nums[fast]=nums[fast−1],说明 nums[fast] 和之前的元素都不同,因此将 nums[fast] 的值复制到 nums[slow],然后将 slow 的值加 1,即指向下一个位置。
遍历结束之后,从 nums[0] 到 nums[slow−1] 的每个元素都不相同且包含原数组中的每个不同的元素,因此新的长度即为 slow,返回 slow 即可。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
实现代码如下:
int removeDuplicates(int* nums,int numsSize)
{
if(numsSize==0)
return 0;
int fast=1,slow=1;
while(fast<numsSize)
{
if(nums[fast]!=nums[fast-1])
{
nums[slow]=nums[fast];
++slow;
}
fast++;
}
return slow;
}
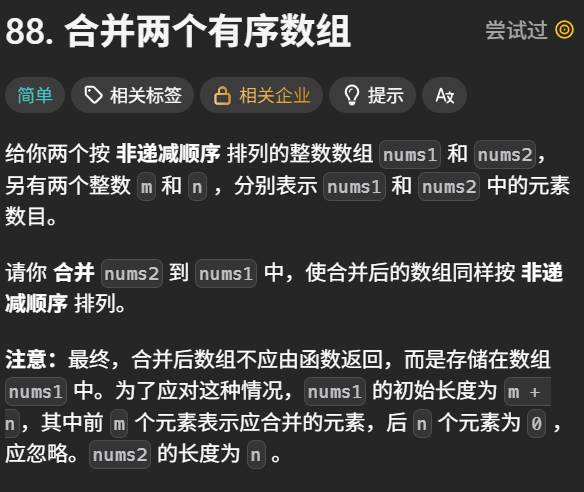
2 合并两个有序数组
方法一:直接合并后排序
最直观的方法是先将数组 nums2 放进数组 nums1 的尾部,然后直接对整个数组进行排序。、
int cmp(int* a, int* b) {
return *a - *b;//用于qsort的比较函数,返回负数表示*a < *b(升序排序)
}
//这是标准库排序函数 qsort 所需的比较函数,决定了排序的规则(这里是升序)
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i) {
nums1[m + i] = nums2[i];
}
qsort(nums1, nums1Size, sizeof(int), cmp);
}
方法二:双指针
方法一没有利用数组 nums 1 与 nums 2 已经被排序的性质。为了利用这一性质,我们可以使用双指针方法。这一方法将两个数组看作队列,每次从两个数组头部取出比较小的数字放到结果中
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
int sorted[m + n];
int cur;
while (p1 < m || p2 < n) {
if (p1 == m) {
cur = nums2[p2++];
} else if (p2 == n) {
cur = nums1[p1++];
} else if (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) {
cur = nums1[p1++];
} else {
cur = nums2[p2++];
}
sorted[p1 + p2 - 1] = cur;
}
for (int i = 0; i != m + n; ++i) {
nums1[i] = sorted[i];
}
}
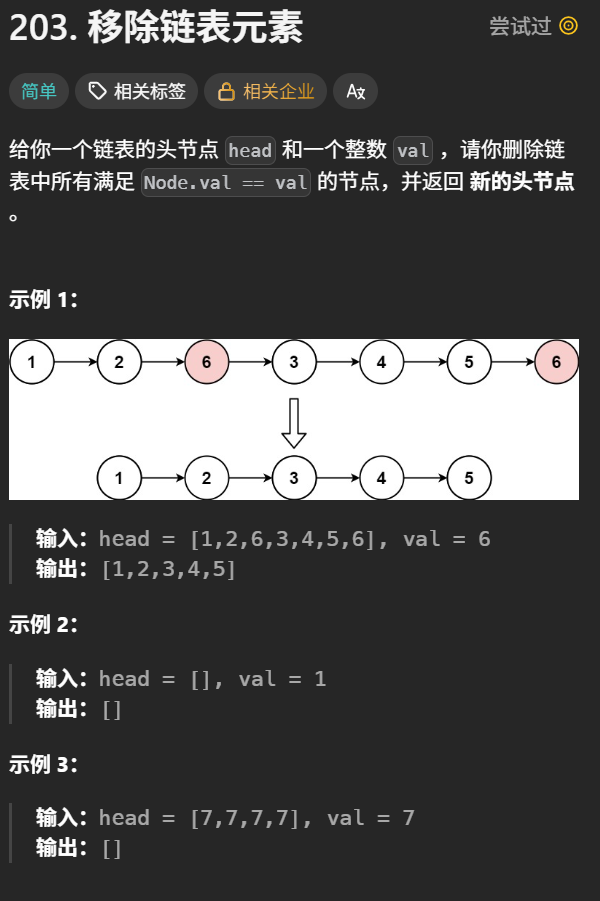
3 移除链表元素
方法一:创建新链表,将节点值不为val的节点尾插到新链表中,时间复杂度为O(N)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct LsitNode* removerElements(struct ListNode*head,int val)
{
//创建新链表
ListNode* newHead,*newTail;
newHead = NewTail = NULL:
ListNdoe* pcur = head;
while(pcur)
{
//判断pcur节点的值是否为val
if(pcur->val !=val)
{
//尾插
if(newHead == NULL)
{
//链表为空
newHead = newTail =pcur;
}
else
{
//链表非空
newTail->next = pcur;
newTail = newTail->next;
}
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
if(newTail)
newTail->next = NULL:
return newHead;
}
方法二:迭代
用 temp 表示当前节点。如果 temp 的下一个节点不为空且下一个节点的节点值等于给定的 val,则需要删除下一个节点。删除下一个节点可以通过以下做法实现:
temp.next=temp.next.next
如果 temp 的下一个节点的节点值不等于给定的 val,则保留下一个节点,将 temp 移动到下一个节点即可。
当 temp 的下一个节点为空时,链表遍历结束,此时所有节点值等于 val 的节点都被删除。
具体实现方面,由于链表的头节点 head 有可能需要被删除,因此创建哑节点 dummyHead,令 dummyHead.next=head,初始化 temp=dummyHead,然后遍历链表进行删除操作。最终返回 dummyHead.next 即为删除操作后的头节点。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* dummyHead = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummyHead->next = head;
struct ListNode* temp = dummyHead;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
if (temp->next->val == val) {
temp->next = temp->next->next;
} else {
temp = temp->next;
}
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
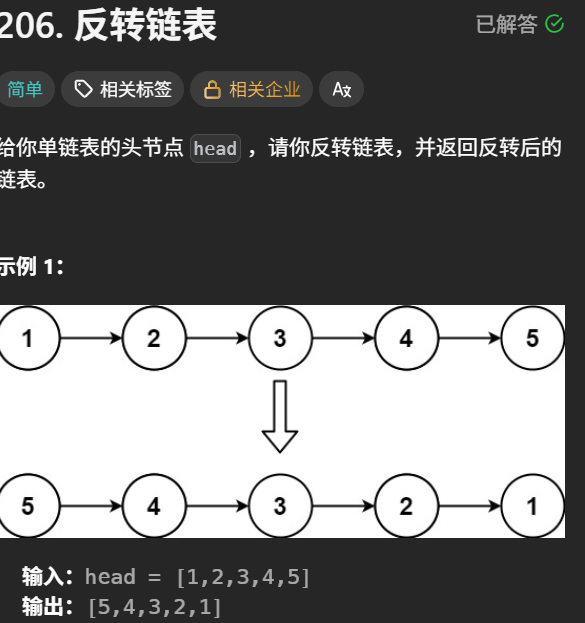
4 反转链表
思路一:创建新链表,遍历原链表将节点 头插 到新链表中 时间复杂度O(N)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
// 新链表的头节点,初始为 NULL
ListNode *newHead = NULL;
// 用于遍历原链表的指针
ListNode *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
// 保存原链表中当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode *nextNode = curr->next;
// 将当前节点头插到新链表中
curr->next = newHead;
newHead = curr;
// 继续遍历原链表的下一个节点
curr = nextNode;
}
// 返回反转后新链表的头节点
return newHead;
}
思路二:创建三个指针,改变指针的指向
Eg:三个指针分别是n1,n2.n3
最开始n1为NULL,n2为头节点,n3为头节点的下一个节点。让n2的next指针不指向n3,而是指向n1。之后n1指向n2,n2指向n3,n3指向n3->next.直到n3为空
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
return head;
}
ListNode*n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL,n2=head,n3=head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
if(n3)
{
n3=n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
5 链表的中间节点
思路一:求链表总长度,总长度/2取整就是链表中间节点的位置,遍历找中间节点 时间复杂度O(N)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
// 计算链表的总长度
int length = 0;
ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
length++;
curr = curr->next;
}
// 计算中间位置
int middlePos = length / 2;
// 再次遍历链表,找到中间位置的节点
curr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < middlePos; i++) {
curr = curr->next;
}
return curr;
}思路二:快慢指针,满指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步。当快指针遍历完链表,满指针走到的位置为中间节点。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fast,*slow;
fast=head;
slow=head;
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}6 合并两个有序链表
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
ListNode* newhead,*newTail;
newhead=newTail=NULL;
ListNode*l1=list1;
ListNode*l2=list2;
while(l1!=NULL&&l2!=NULL)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead=newTail=l1;
}
else
{
newTail->next=l1;
newTail=newTail->next;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead=newTail=l2;
}
else{
newTail->next=l2;
newTail=newTail->next;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
newTail->next=l1;
}
if(l2)
{
newTail->next=l2;
}
return newhead;
}7 链表的回文结构

思路一:创建数组(大小为900),遍历链表将·节点的值·存储在数组中,若数组为回文结构,则链表为回文结构·
思路一代码如下:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// write code here
int arr[900]={0};
ListNode*pcur = A;
int i=0;
while(pcur)
{
arr[i++]=pcur->val;
pcur=pcur->next;
}
int left=0,right=i-1;
while(left<right)
{
if(arr[left]!=arr[right])
{
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;注意:思路二只能用于已知数组大小的情况
思路二:找链表中间节点,将中间节点作为新链表的头节点,反转链表遍历原链表和反转之后的链表节点的值是否相同
// 找中间节点
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
// 创建快慢指针
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
// 反转链表
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL) {
return head;
}
// 创建三个指针
ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3;
n1 = NULL, n2 = head, n3 = n2->next;
while (n2) {
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1; // 链表的新的头结点
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// 1.找中间节点
ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);
// 2.反转以中间节点为头的链表
ListNode* right = reverseList(mid);
// 3.遍历原链表和反转后的链表,比较节点的值是否
ListNode* left = A;
while (right) {
if(left->val != right->val)
{
return false;
}
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
return true;
}