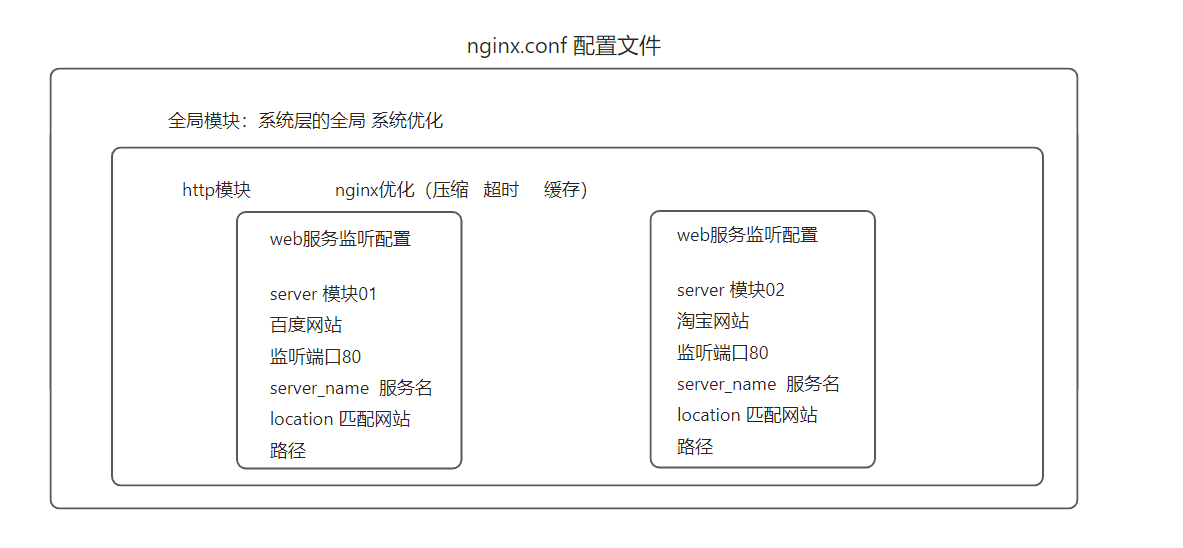
1、Nginx 配置
1.1 全局配置
## 运行用户,若编译时未指定则默认为 nobody
## user nobody; user nginx
## 工作进程数量,可配置成服务器内核数 * 2,如果网站访问量不大,一般设为1就够用了
worker_processes 4;
## 错误日志文件的位置
## error_log logs/error.log;
## PID 文件的位置
pid logs/nginx.pid;
1.2 I/O事件配置
events {
## 使用epoll模型,2.6及以上版本的系统内核,建议使用epoll模型以提高性能
use epoll;
## 每个进程处理 4096 个连接
worker_connections 4096;
}
## 如提高每个进程的连接数还需执行“ulimit -n 65535”命令临时修改本地每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数。
## 在Linux平台上,在进行高并发TCP连接处理时,最高的并发数量都要受到系统对用户单一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制(这是因为系统为每个TCP连接都要创建一个socket句柄,每个socket句柄同时也是一个文件句柄)。
## 可使用ulimit -a命令查看系统允许当前用户进程打开的文件数限制。
/etc/security/limits.conf
## epoll是Linux内核为处理大批句柄而作改进的poll,是Linux下多路复用IO接口select/poll的增强版本,它能显著的减少程序在大量并发连接中只有少量活跃的情况下的系统CPU利用率。
## 若工作进程数为 8,每个进程处理 4096 个连接,则允许 Nginx 正常提供服务的连接数已超过 3 万个(4 096×8=32768),当然具体还要看服务器硬件、网络带宽等物理条件的性能表现。
1.3 HTTP 配置
http {
## 文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include mime.types;
## 默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
## 日志格式设定
## log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
## '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
## '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
## 访问日志位置
## access_log logs/access.log main; 访问网站的日志
## 支持文件发送(下载)
sendfile on;
## 此选项允许或禁止使用socket的TCP_CORK的选项(发送数据包前先缓存数据),此选项仅在使用sendfile的时候使用
## tcp_nopush on;
## 连接保持超时时间,单位是秒
## keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
## gzip模块设置,设置是否开启gzip压缩输出
## gzip on;
1.4 Web服务监听配置
##Web 服务的监听配置
server {
##监听地址及端口
listen 80;
##站点域名,可以有多个,用空格隔开
server_name www.fyl.com;
##网页的默认字符集
charset utf-8;
##根目录配置
location / {
##网站根目录的位置/usr/local/nginx/html
root html;
##默认首页文件名
index index.html index.php;
}
location /zjl {
##网站根目录的位置/usr/local/nginx/html
root /usr/local/nginx/html/zjl;
##默认首页文件名
index index.html index.php;
}
##内部错误的反馈页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
##错误页面配置
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
1.5 其他配置
日志格式设定
$remote_addr与$http_x_forwarded_for用以记录客户端的ip地址;
$remote_user:用来记录客户端用户名称;
$time_local: 用来记录访问时间与时区;
$request: 用来记录请求的url与http协议;
$status: 用来记录请求状态;成功是200,
$body_bytes_sent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;
$http_referer:用来记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的;
$http_user_agent:记录客户浏览器的相关信息;
通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过$remote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址。
====================================================================================
location常见配置指令,root、alias、proxy_pass
root(根路径配置):root /var/www/html
请求www.benet.com/test/1.html,会返回文件/var/www/html/test/1.html
alias(别名配置):alias /var/www/html
请求www.benet.com/test/1.html,会返回文件/var/www/html/1.html
proxy_pass(反向代理配置)
2、访问状态统计配置
2.1 查看已安装的模块
查看已安装的 Nginx 是否包含 HTTP_STUB_STATUS 模块
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
可查看 nginx 已安装的所有模块
cat /opt/nginx-1.20.2/auto/options | grep YES
2.2 修改 nginx.conf 配置文件
修改 nginx.conf 配置文件,指定访问位置并添加 stub_status 配置
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
cp nginx.conf nginx.conf.bak
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
http {
......
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.php;
}
##添加 stub_status 配置##
location /status { #访问位置为/status www.benet.com/status
stub_status on; #打开状态统计功能
access_log off; #关闭此位置的日志记录
}
}
}
2.3 重启服务-访问测试
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.21/status
Active connections :表示当前的活动连接数;
server accepts handled requests :表示已经处理的连接信息,三个数字依次表示已处理的连接数、成功的TCP握手次数、 已处理的请求数。
可 curl -s http://192.168.10.21/status 结合 awk与if 语句进行性能监控。
3、基于授权的访问控制
3.1 生成用户密码认证文件
yum install -y httpd-tools
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db zhangsan
chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
chmod 400 /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
3.2 修改主配置文件相对应目录,添加认证配置项
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
server {
location / {
......
##添加认证配置##
auth_basic "secret"; #设置密码提示框文字信息
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db;
}
}
3.3 重启服务-访问测试
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.21
4、基于客户端的访问控制
访问控制规则如下:
deny IP/IP 段:拒绝某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问。
allow IP/IP 段:允许某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问。
规则从上往下执行,如匹配则停止,不再往下匹配。
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
server {
location / {
......
##添加控制规则##
allow 192.168.10.20; #允许访问的客户端 IP
deny all; #拒绝其它IP客户端访问
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
5、基于域名
5.1 为虚拟主机提供域名解析
echo "192.168.10.21 www.yjs.com www.benet.com" >> /etc/hosts
5.2 为虚拟主机准备网页文档
mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/html/benet
mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/html/yjs
echo "<h1>www.yjs.com</h1>" > /usr/local/nginx/html/yjs/index.html
echo "<h1>www.benet.com</h1>" > /usr/local/nginx/html/benet/index.html
5.3 修改nginx配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
http {
......
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.yjs.com; #设置域名www.yjs.com
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.yjs.access.log; #设置日志名
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/yjs; #设置www.yjs.com 的工作目录
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.benet.com; #设置域名www.benet.com
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.log;
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/benet;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
}
5.4 重启服务-访问测试
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问
http://www.yjs.com
http://www.benet.com
6、基于IP
6.1 配置server1
ifconfig ens33:0 192.168.10.40 netmask 255.255.255.0
创建 一个ens36 或者37的网卡 192.168.10.40
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
http {
......
server {
listen 192.168.10.22:80; #设置监听地址192.168.10.22
server_name www.yjs.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.yjs.access.log;
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/yjs;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}1
}
6.2 配置server 2
server {
listen 192.168.10.40:80; #设置监听地址192.168.10.40
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.log;
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/benet;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问
http://192.168.10.22
http://192.168.10.40
7、基于端口
7.1 配置端口1
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
http {
......
server {
listen 192.168.10.22:8080; #设置监听 8080 端口
server_name www.yjs.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.yjs.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/yjs;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
7.2 配置端口2
server {
listen 192.168.10.22:8888; #设置监听 8888 端口
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/benet;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
7.3 重启服务-测试访问
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问
http://192.168.10.21:8080
http://192.168.10.21:8888
总结