4. 基础查询
进入编写 ES 语句的地方:Kibanna 中编写 ES 查询语句
4.1. 分词器
官方提供的分词器有这么几种: Standard、Letter、Lowercase、Whitespace、UAX URL Email、Classic、Thai等,中文分词器可以使用第三方的比如IK分词器。
我们一般使用IK分词效果比较好。
ik_smart # 只对句子分一次
ik_max_word # 最大限度的分,对分过的词还分
# 官方的
standard # 分词过于简单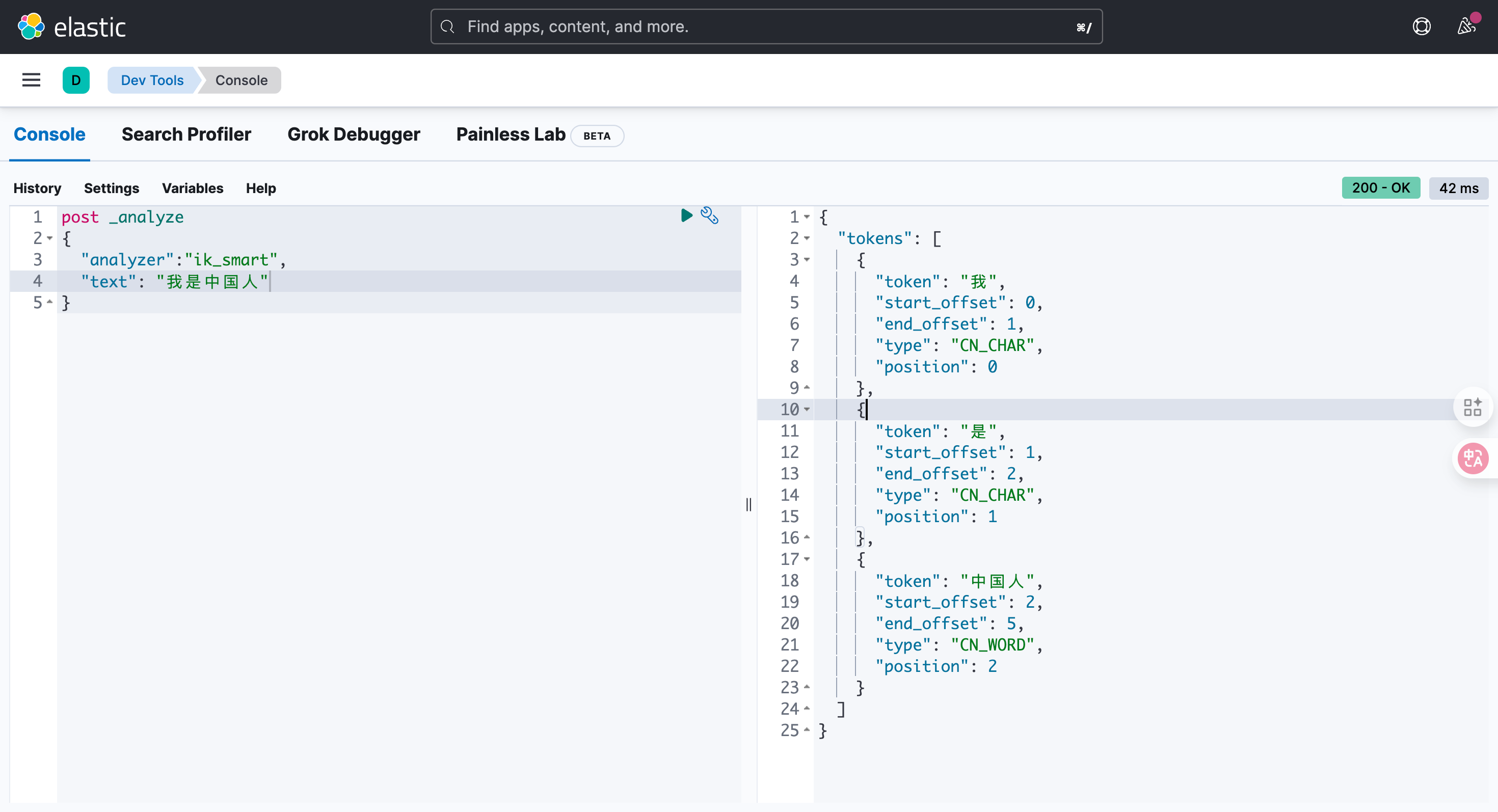
可以试试 ik_max_word
post _analyze
{
"analyzer":"ik_smart",
"text": "我是中国人"
}
结果:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "我",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 1,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "是",
"start_offset": 1,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "中国人",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 2
}
]
}4.2. 索引库操作
ES 软件的索引可以类比为 MySQL 中库的概念,创建一个索引,类似于创建一个库、
4.2.1. 创建索引
PUT /{索引名称}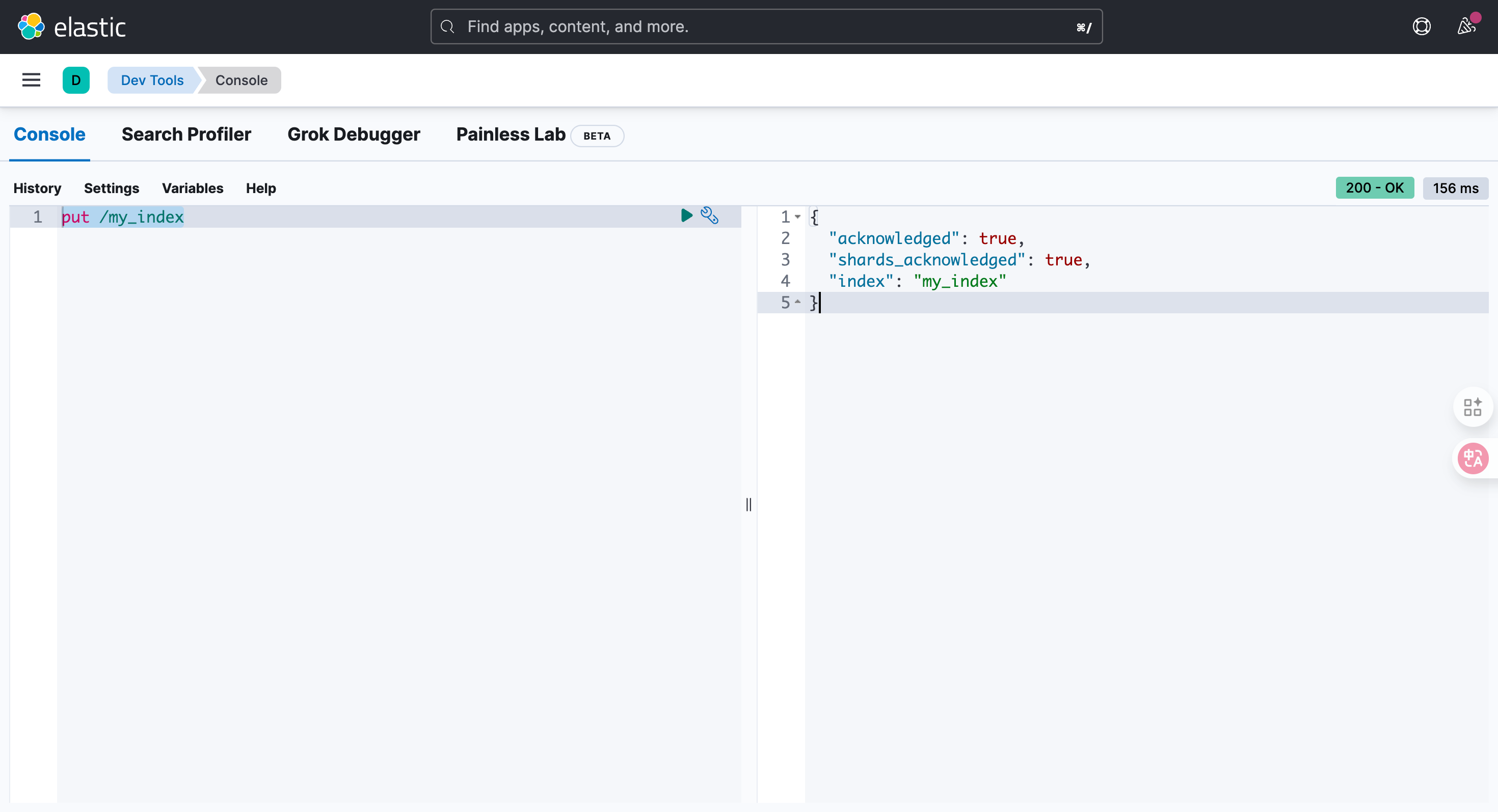
put /my_index
结果:
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "my_index"
}4.2.2. 查看所有索引
GET /_cat/indices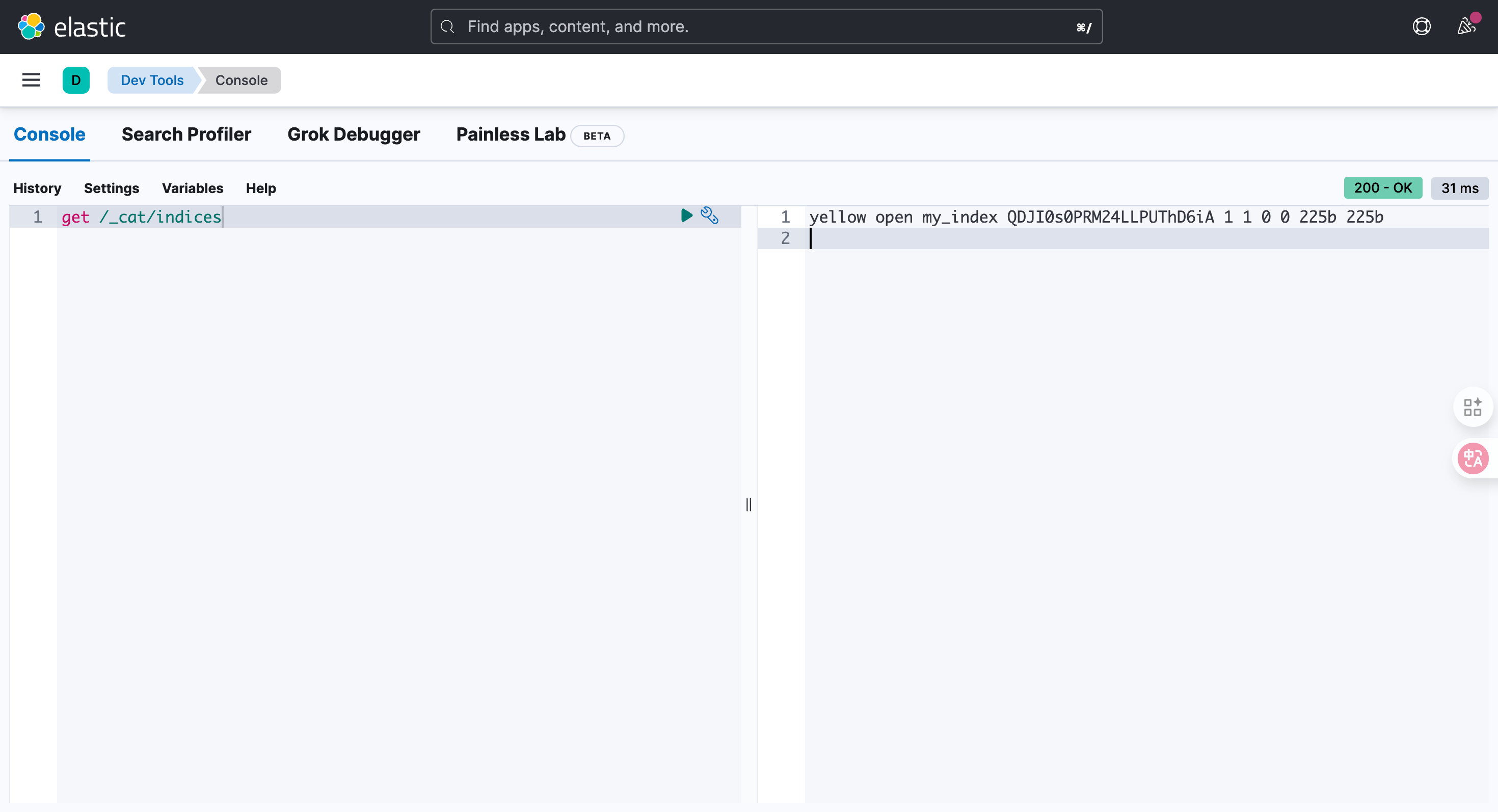
get /_cat/indices
yellow open my_index QDJI0s0PRM24LLPUThD6iA 1 1 0 0 225b 225b4.2.3. 查看单个索引
GET /my_index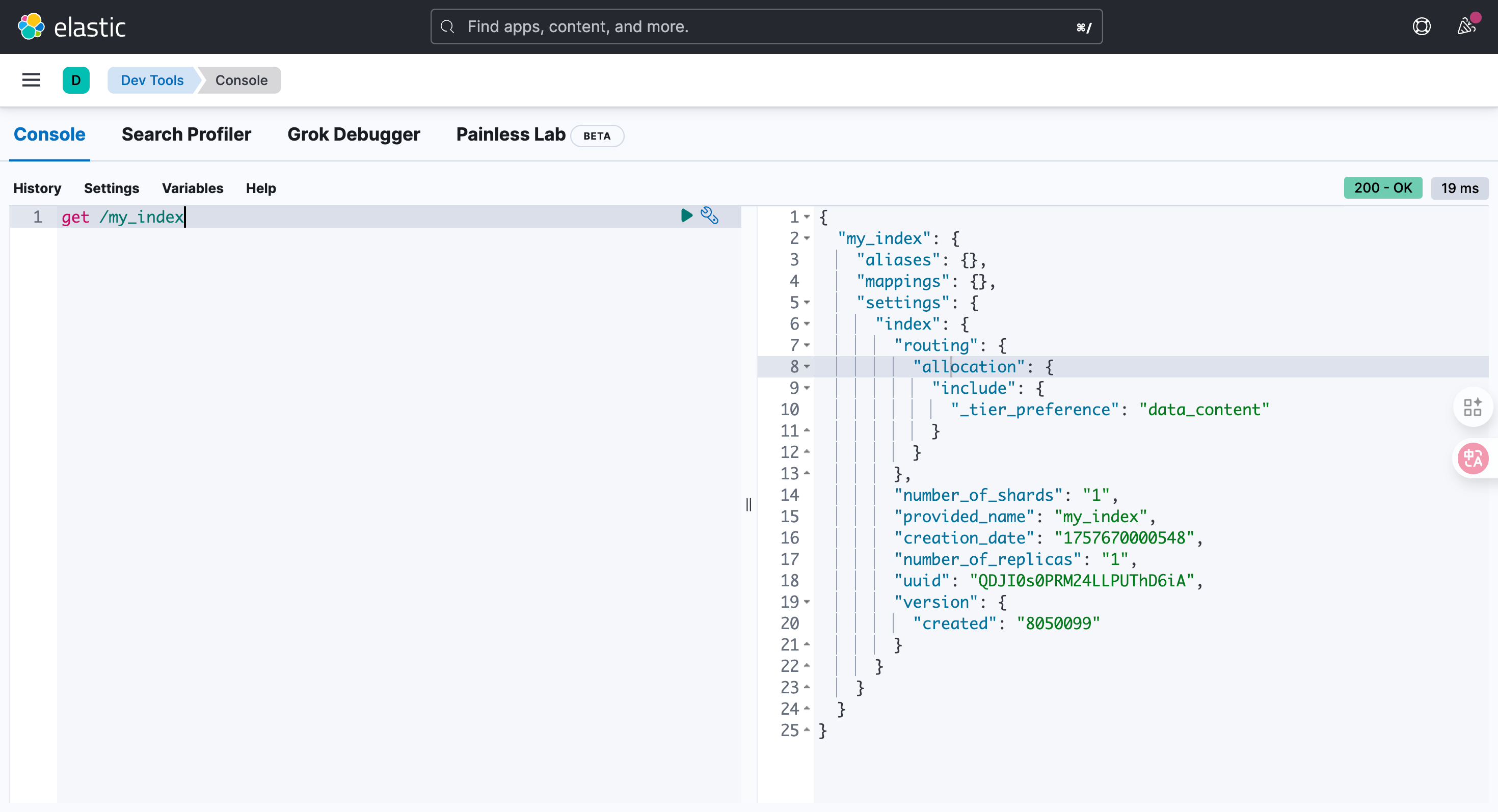
get /my_index
{
"my_index": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "my_index",
"creation_date": "1757670000548",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "QDJI0s0PRM24LLPUThD6iA",
"version": {
"created": "8050099"
}
}
}
}
}4.2.4. 删除索引
DELETE /{索引名称}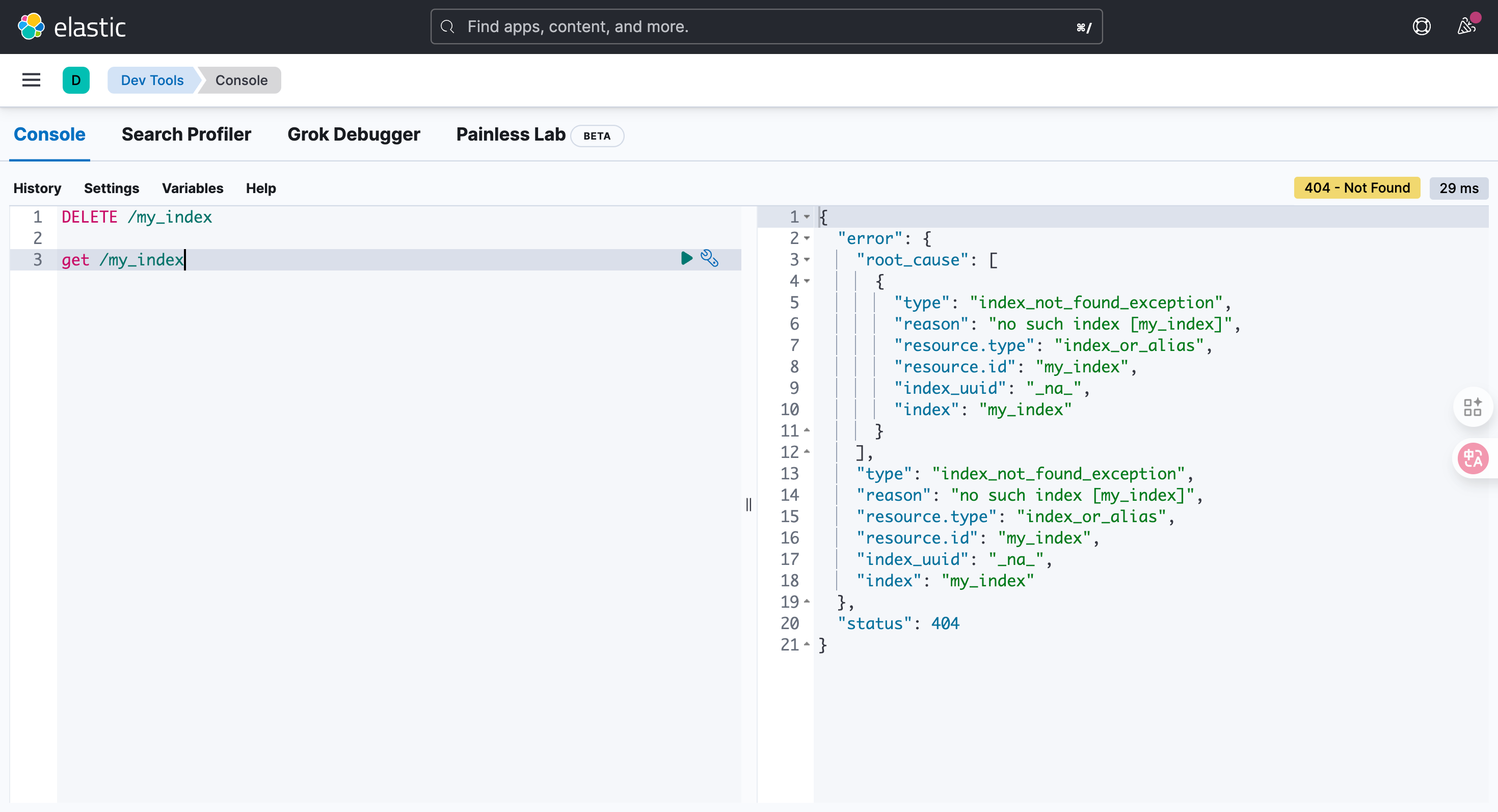
DELETE /my_index
get /my_index
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [my_index]",
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "my_index",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "my_index"
}
],
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [my_index]",
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "my_index",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "my_index"
},
"status": 404
}4.3. 文档操作
文档 = 数据行。是动态地创建字段的,不一定文档提前创建,没有就当前创建。
文档是 ES 软件搜索数据的最小单位, 不依赖预先定义字段,所以可以将文档类比为表的一行JSON类型的数据。
我们知道关系型数据库中,要提前定义字段才能使用,在Elasticsearch中,对于字段是非常灵活的,有时候我们可以忽略该字段,或者动态的添加一个新的字段。
4.3.1. 创建文档
在创建数据时,需要指定唯一性标识,那么请求范式 POST,PUT 都可以。
POST 不带也可以,帮你指定一个。
所以这里的_doc是创建文档必须指定的吗?是的 7.x 就是了,固定的类型名。不支持自定义了。
这里看到 post 的自定生成了一个_id
post /my_index/_doc
{
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "XHJVPZkB5uVO7EK7pY3P",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1
}put 不指定 id 就会直接进行报错
put /my_index/_doc/2
{
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1
}4.3.2. 查看文档
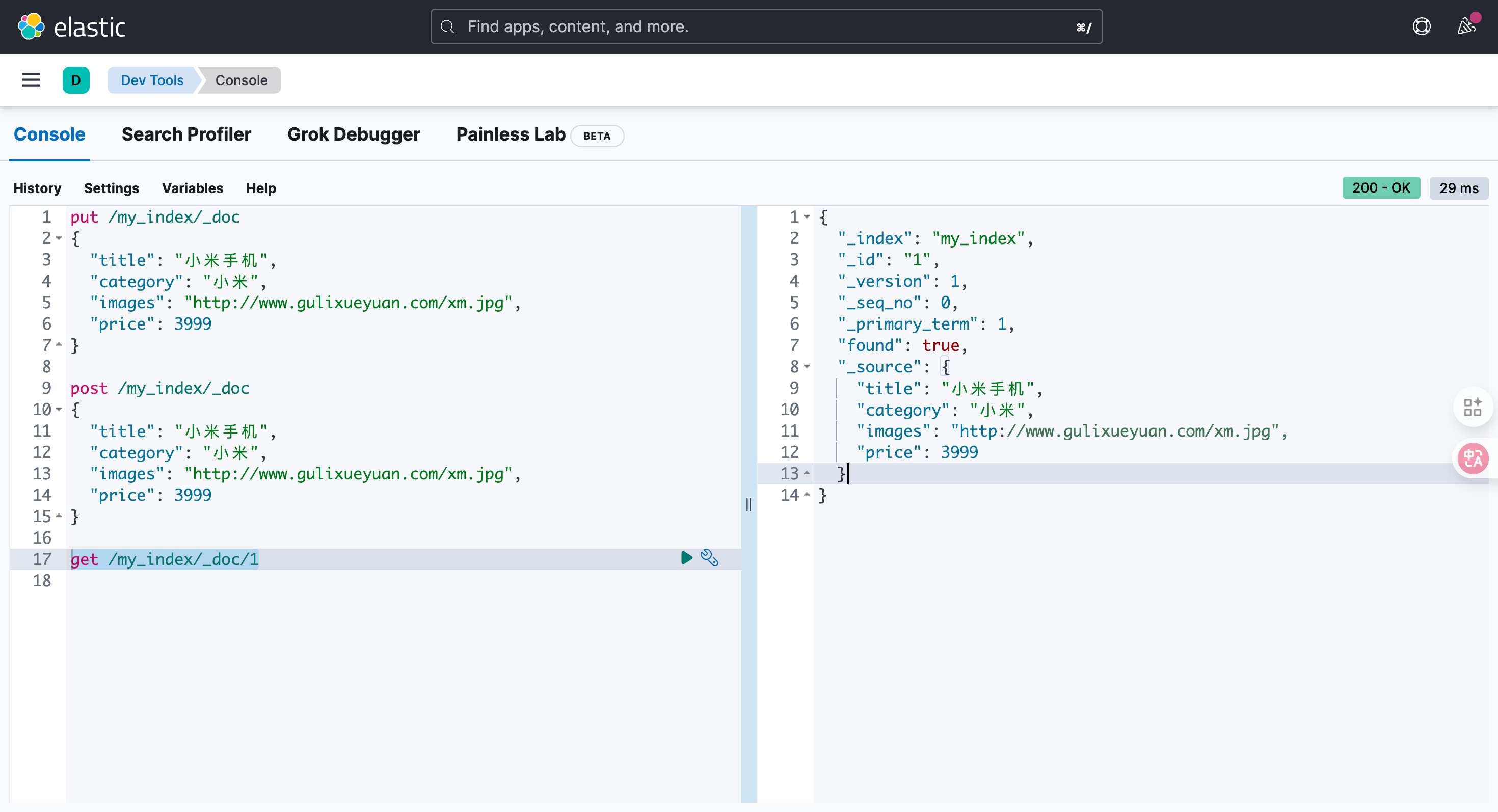
get /my_index/_doc/1
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
}_version不用管,你改一次,他自己就会变,就和 git 版本一样
4.3.3. 查看所有文档
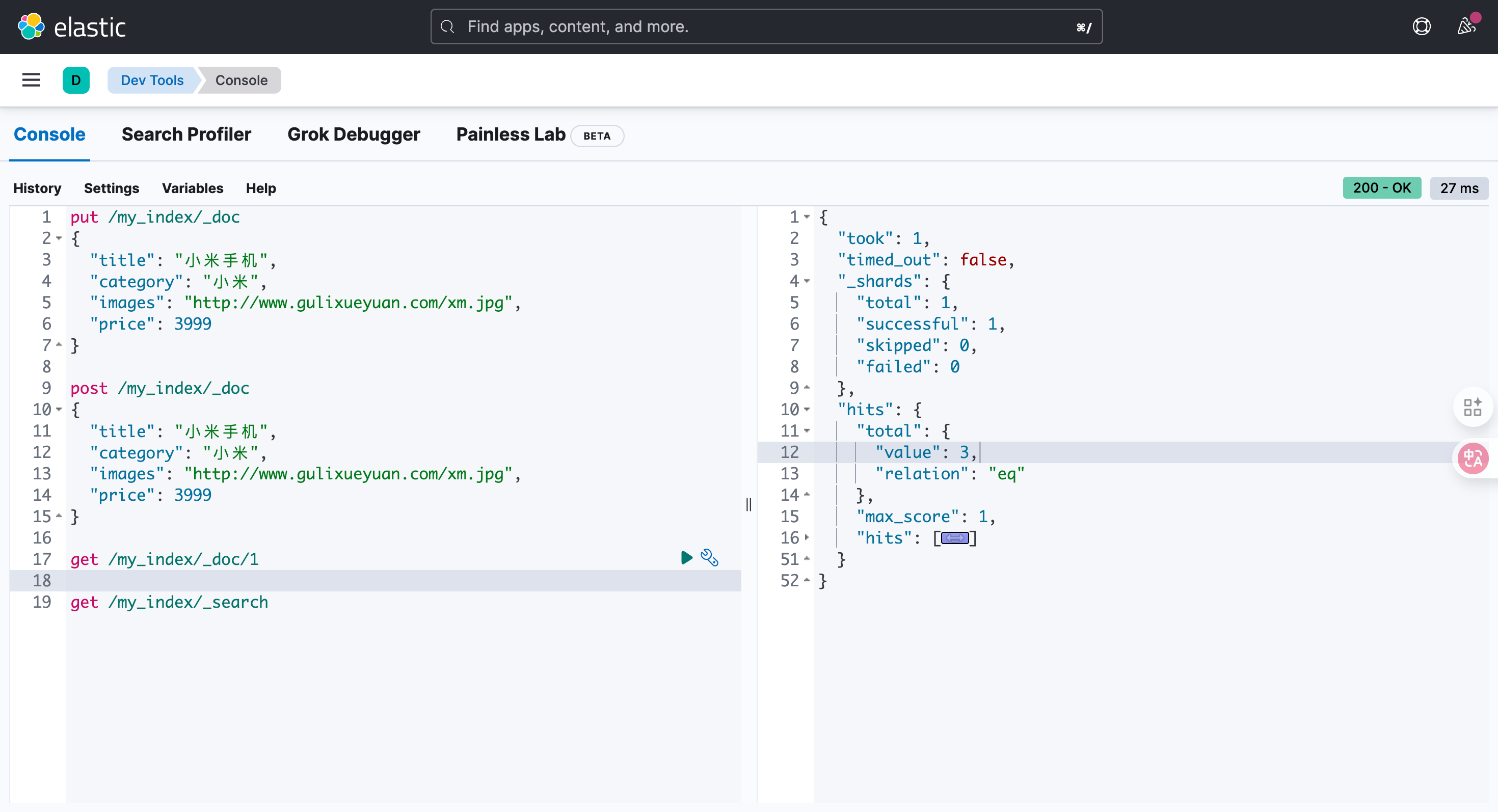
结果去看hits就能看到了
get /my_index/_search
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
},
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "XHJVPZkB5uVO7EK7pY3P",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
},
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
}
]
}
}4.3.4. 修改文档
post 和 put 都可以修改:全部属性
如果一不小心,只剩下了一个字段,那么该文档直接改变了,有的字段直接消失了
put /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 4500
}
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 4,
"_seq_no": 5,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 4500
}
}4.3.5. 修改局部属性
只能用 POST 进行局部更新
如果没有该字段,那么也就是创建一个新字段!
POST /my_index/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"price": 4500
}
}
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 12,
"_seq_no": 13,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"category": "小米",
"images": "http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price": 4500
}
}4.3.6. 删除文档
DELETE /my_index/_doc/XHJVPZkB5uVO7EK7pY3P
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_id": "XHJVPZkB5uVO7EK7pY3P",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 18,
"_primary_term": 1
}4.4. 映射 mapping
索引-字段-约束,这叫做映射。
创建数据库表需要设置字段名称,类型,长度,约束等;索引库也一样,需要知道这个类型下有哪些字段,每个字段有哪些约束信息,这就叫做映射(mapping)。
4.4.1. 查看映射
get /my_index/_mapping
{
"my_index": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"category": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"images": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"pri": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"price": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}4.4.2. 动态映射
我们没有指定字段的类型关系,叫做自动映射,系统自动给的。
在关系数据库中,需要事先创建数据库,然后在该数据库下创建数据表,并创建 表字段、类型、长度、主键等,最后才能基于表插入数据。
而Elasticsearch中不 需要定义 Mapping 映射(即关系型数据库的表、字段等),在文档写入 Elasticsearch时,会根据文档字段自动识别类型,这种机制称之为动态映射。
数据 |
对应的类型 |
null |
字段不添加 |
true|flase |
boolean |
字符串 |
text(默认)/keyword |
数值 |
long |
小数 |
float |
日期 |
date |
- text类型一旦可以分词,就不能进行聚合(分组)
- keyworld类型不能分词,可以进行聚合(分组)
如果你在es中把这个字段指定类型为keyword:那么就代表这个字段的值不会进行分词,也即不会进行全文检索。(精准查询)
不能全文检索,是因为不能再分词了,不代表不能查询,精确查询就可以了。
分词会有两次,第一次建立索引分词,第二次是搜索时还继续分词。
index:true 代表要不要建立倒排索引,要注意:倒排索引和分词没有必然联系,不分词也可以简历倒排索引
分词就是能不能拆开:所以看属性能不能分词,比如分类为红米,比如标题为红米手机
可以理解为模糊查询为分词,不分词就是精准查询
4.4.3. 静态映射
建立索引库的时候,同时去建立映射关系等
静态映射是在Elasticsearch中也可以事先定义好映射,即手动映射,包含文档的各字段类型、分词器、分词等,这称为静态映射。
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"index": true,
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": true
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": true
},
"price": {
"type": "integer",
"index": true
}
}
}
}
GET /my_index/_mapping
{
"my_index": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"category": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"price": {
"type": "integer"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}自定义 马平平 映射类型
type分类如下:
- 字符串:text(支持分词)和 keyword(不支持分词)。
- text:该类型被用来索引长文本,在创建索引前会将这些文本进行分词,转化为词的组合,建立索引;允许es来检索这些词,text类型不能用来排序和聚合。
- keyword:该类型不能分词,可以被用来检索排序和聚合、
- 数值型:short、byte、integer、long、double、float
- 日期型:date
- 布尔型:boolean
- 特殊数据类型:nested【对象类型】
4.4.4. nested 介绍
nested:类型是一种特殊的对象object数据类型(specialised version of the object datatype ),允许对象数组彼此独立地进行索引和查询。
demo: 建立一个普通的my_comment_index索引
如上所示,所以我们有一个文档描述了一个帖子和一个包含帖子上所有评论的内部对象评论。但是Elasticsearch搜索中的内部对象并不像我们期望的那样工作。
PUT my_comment_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "狂人日记",
"body": "《狂人日记》是一篇象征性和寓意很强的小说,当时,鲁迅对中国国民精神的麻木愚昧颇感痛切。",
"comments": [
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 34,
"rating": 8,
"comment": "非常棒的文章",
"commented_on": "30 Nov 2023"
},
{
"name": "李四",
"age": 38,
"rating": 9,
"comment": "文章非常好",
"commented_on": "25 Nov 2022"
},
{
"name": "王五",
"age": 33,
"rating": 7,
"comment": "手动点赞",
"commented_on": "20 Nov 2021"
}
]
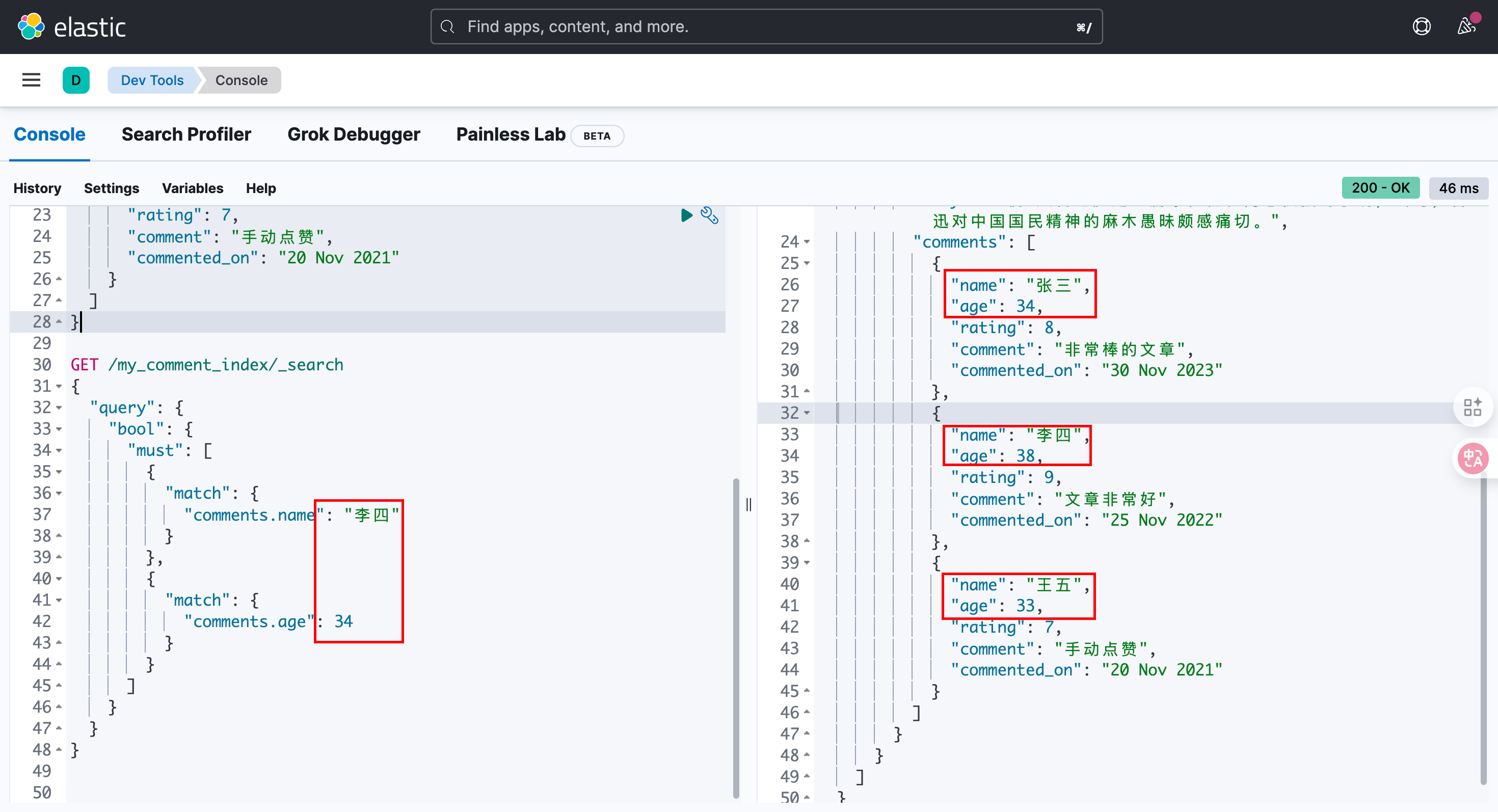
}2)步骤2 : 执行查询
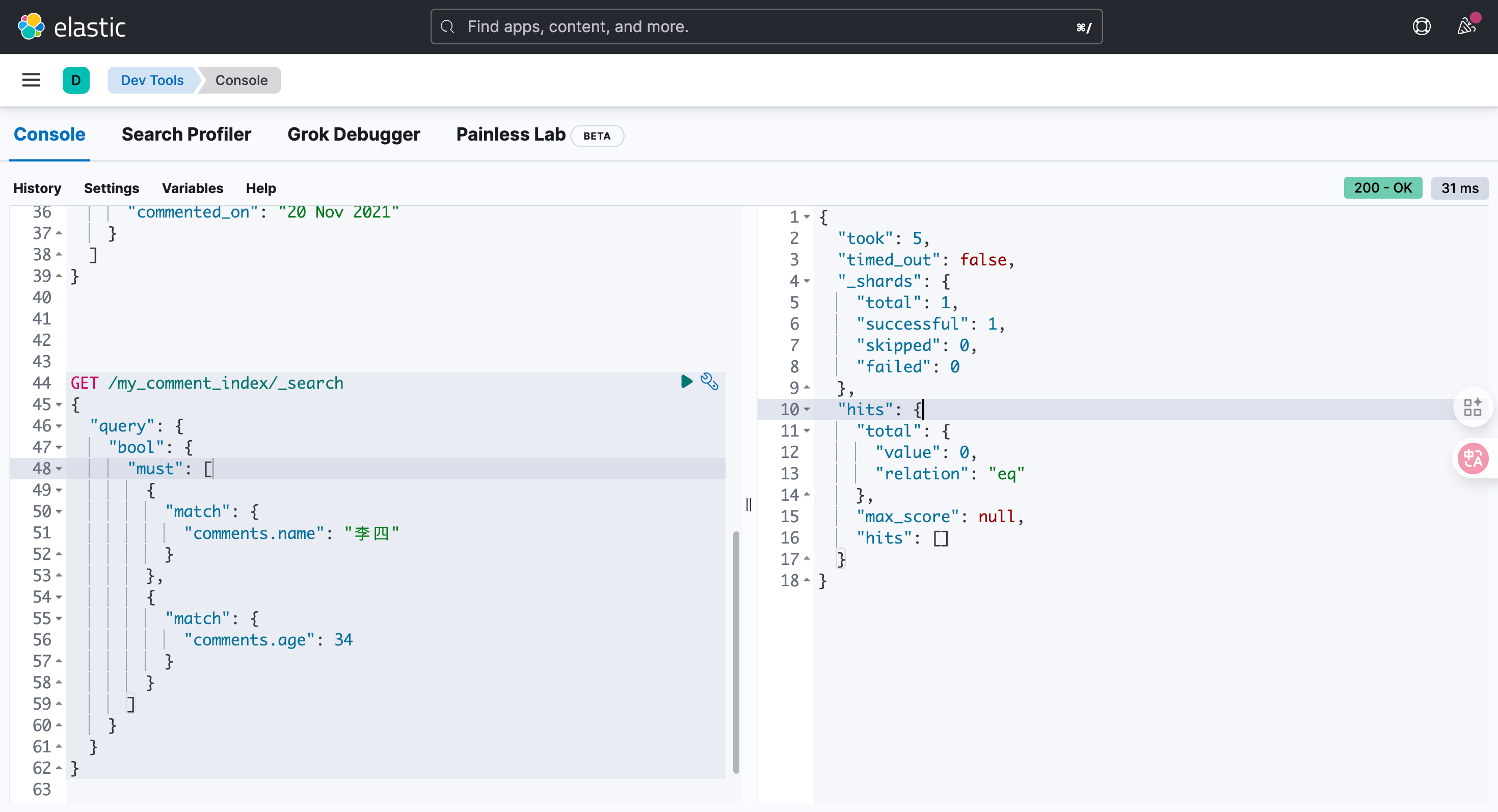
GET /my_comment_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"comments.name": "李四"
}
},
{
"match": {
"comments.age": 34
}
}
]
}
}
}这里去分析查询结果,它不像是按照我们预期的方式进行运行的!根本就不存在这样的评论,但是确能查出结果!
对象数组底层的存储方式,对象数组中对象会打散。
某个属性单独拎出来,然后组合在一起,这样 名字与age 没有非常强的对应关系了。
没有了对象与对象间的独立隔离关系,这叫扁平化存储。
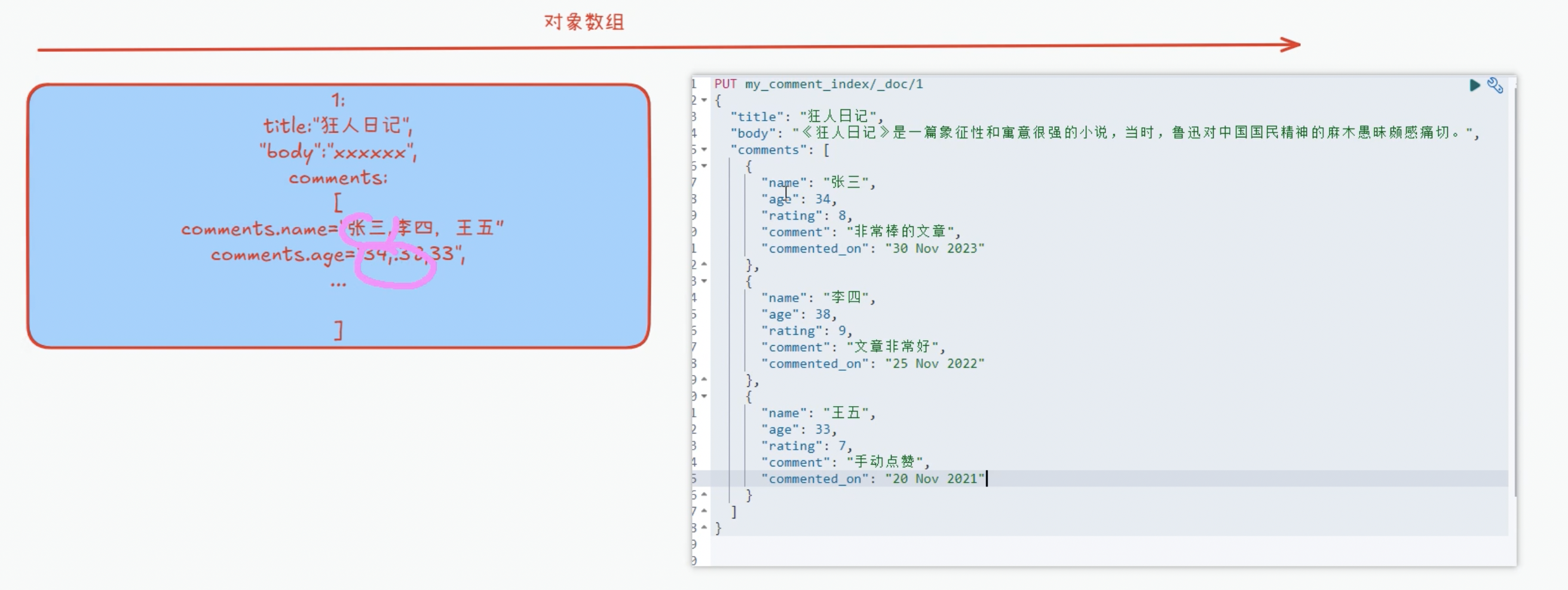
- 能不能不这样存储呢?需要设置类型:nested!
3)步骤3:删除当前索引
DELETE /my_comment_index步骤4:建立一个nested 类型的(comments字段映射为nested类型,而不是默认的object类型)
PUT my_comment_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"comments": {
"type": "nested"
}
}
}
}
PUT my_comment_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "狂人日记",
"body": "《狂人日记》是一篇象征性和寓意很强的小说,当时,鲁迅对中国国民精神的麻木愚昧颇感痛切。",
"comments": [
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 34,
"rating": 8,
"comment": "非常棒的文章",
"commented_on": "30 Nov 2023"
},
{
"name": "李四",
"age": 38,
"rating": 9,
"comment": "文章非常好",
"commented_on": "25 Nov 2022"
},
{
"name": "王五",
"age": 33,
"rating": 7,
"comment": "手动点赞",
"commented_on": "20 Nov 2021"
}
]
}重新进行查询
GET /my_comment_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"comments.name": "李四"
}
},
{
"match": {
"comments.age": 34
}
}
]
}
}
}结果发现没有返回任何的文档,这是何故?
不再打散,组合!
当将字段设置为nested 嵌套对象将数组中的每个对象索引为单独的文档,这意味着可以独立于其他对象查询每个嵌套对象。文档的内部表示:
每个内部对象都在内部存储为单独的文档。 这保持了他们的领域之间的关系。
{
{
"comments.name": "张三",
"comments.comment": " 非常棒的文章 ",
"comments.age": 34 ,
"comments.rating": 9
},
{
"comments.name": "李四",
"comments.comment": " 文章非常好",
"comments.age": 38,
"comments.rating": 8
},
{
"comments.name": " 王五",
"comments.comment": "手动点赞",
"comments.age": 33 ,
"comments.rating": 7
},
{
"title": " 狂人日记 ",
"body": "《狂人日记》是一篇象征性和寓意很强的小说,当时,鲁迅对中国... "
}
}