🌈欢迎来到C++专栏 ~~ 类和对象(中)
- (꒪ꇴ꒪(꒪ꇴ꒪ )🐣,我是Scort🎓
- 🌍博客主页:张小姐的猫~江湖背景
- 快上车🚘,握好方向盘跟我有一起打天下嘞!
- 送给自己的一句鸡汤🤔:
- 🔥真正的大师永远怀着一颗学徒的心
- 作者水平很有限,如果发现错误,可在评论区指正,感谢🙏
- 🎉🎉欢迎持续关注!

类和对象(中)—— 日期类的实现
一. show time 少年
继类和对象上篇中篇后,我们把这些学到的知识都用起来,来写一个日期类。下面我贴出头文件,能独立写完,算是真正弄懂了。所有要注意的小点我都写出来了,文章尽量呈现知其然知其所以然,let’s go
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
//构造函数
Date::Date(int year = 0, int month = 1, int day = 1);
//析构函数、拷贝构造、赋值重载都不用写
//Date(const Date& d)
//{
// cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;
//}
void Print();
int getMonthDay(int year, int month);
//运算符重载系列
bool operator>(const Date& d);
bool operator>=(const Date& d);
bool operator<(const Date& d);
bool operator<=(const Date& d);
bool operator==(const Date& d);
bool operator!= (const Date& d);
// d1 += 100;
Date& operator+=(int day);
// d1 + 100;
Date operator+(int day);
// d1 -= 100;
Date& operator-=(int day);
// d1 - 100;
Date operator-(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
//后置 --
Date operator--(int);
// 日期 - 日期
int operator-(const Date& d);
// 今天是星期几?
void PrintWeekday();
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
二. 基本接口
🐋默认成员函数
🎨构造函数
通过之前的学习,我们知道日期类是不需要写析构和拷贝构造函数,用默认生成的即可,我们只需要完成构造函数
//检查正确的日期
bool checkDate()
{
if (_year >= 1
&& _month>0 && _month<13
&& _day>0 && _day <= GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//构造会频繁的调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline
Date(int year = 2022, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!checkDate())
{
Print();
cout << "刚构造的日期非法" << endl;
}
}
输入天数的同时还要判断是否为非法日期:2021年10月90日,为了判断天数是否合理,我们引入了下一个接口,来获取某年某月的天数 ——
🎨拷贝构造函数
日期类的可以不用写,系统自动生成的即可完成,不懂的回去看看这篇博客:复习跳转
🐋获取某年某月天数
我们用数组来储存每个月的天数,第几月就对于多少天
- 因为频繁的调用,数组设为
静态的,节省空间 - 只有2月的天数随着是否为闰年改变而改变
- 对闰年的处理,先来判断
month == 2(反过来就没这么好了,细节)
//获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
//静态:不用多次开空间
static int days[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int day = days[month];
//闰年:四年一闰、百年不闰、四百年再闰
if (month == 2
&& ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))//先判断是否2月
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
三.一系列运算符重载
⚡+=、+、++
🌍日期+=天数
2022年10月12日 +200天,但顺着我们正常的计算思维,列写几个例子,其实很简单。✅它其实就是一个不断进位的过程,天满了往月进;月满了往年进、月归1

//d2 += d1 += 100 连续加等,有返回值
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;//d1没销毁,可以传引用返回
}
- 注意我们这里改变了实现的是
+=,而不是+,因为改变了day ——
int i = 100;
i + 100;
此处i的值并不会变,那该怎么样实现+的重载呢,很简单给它来一个临时对象
🌍日期+天数
- 拷贝构造一个临时变量,避免对
d的改变 - 巧妙复用
+=
// d1 + 100 不能改变d1
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = (*this);//拷贝构造一个
tmp += day;// tmp.operator(&tmp,)
return tmp;
}
🌍前置++、后置++
前置++和后置++都是一元运算符,为了让前置++与后置++形成能正确重载
C++规定:后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器自动传递
- 🔥注意:判断是否是传引用返回or传值返回:是要根据实现逻辑的不同,看你返回的对象,出了作用域被没被销毁,分析出来加上的,当然熟练了就直接写了
🎨前置++
Date& Date::operator++() //前置++
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
🎨后置++
Date Date::operator++(int) //后置++
{
Date ret = *this;
*this += 1;
return ret;
}
他们在编译器眼里会转化成:
Date d1(2022,10,12)
++d1;//d1.operator(&d1)
d1++;//d2.operator(&d1, 1)
- 如果是对于自定义类型,建议使用前置++。这是因为前置++,我们可以传引用返回;后置++,拷贝构造临时对象加上传值返回,要拷贝构造两次(传参构造一次、返回值构造一次),效率低下
⚡+=、+、++
哎呀有了之前的知识铺垫,后面的不就信手拈来? 哈哈别太自信
🌍日期 -= 天数
怎么样减呢?根据加的思路差不多,不够找月借,再不够找年借

注:
- 天数 <= 0都不合法,要借位
- 注意我们借到的天数是上一个月的天数(这与“加”不同,“加”获取的是本月天数)
- 到达边界时,我们是先把月置12,再对天数处理
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
❌这时候问题就来了,万一我们输入的天数是负数怎么办?
我们则需要把它单独拿出来处理,-=day 等价于 +=(-day),加一个负数不就等于减一个整数
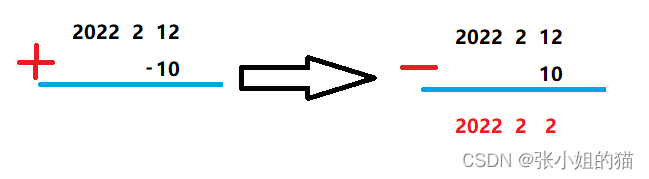
同样的刚刚我们实现的+=运算符重载函数也需要同样处理,代码如下 ——
//+=
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;//d1没销毁,可以传引用返回
}
//-=
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
🌍日期 - 天数
照常复用即可
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
🌍前置–、后置–
注意点和前置++一样
Date& Date::operator--() //前置
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int) //后置
{
Date ret = *this;
*this -= 1;
return ret;
}
⚡一堆比较== 、!=、>、>=、<、<=
任何一个类,只需要写一个 > == 重载 或者 < == 即可,剩下比较运算符复用即可
//d1 > d2
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if((_year>d._year)
||(_year==d._year &&_month > d._month)
||(_year==d._year && _month==d._month && _day>d._day))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// ==
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
下面开始疯狂的复用吧
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
//d1 >= d2
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
//d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
四.日期-日期
这里我们计算一个我们离实习的时间吧
//日期-日期
// offerDay - today =>offerDay.operator(&offerday,today);
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
int flag = 1;//防止天数为负
Date max = *this;//晚
Date min = d;//早
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int day = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++day;
}
return day* flag;
}
五、计算星期几
void Date::PrintWeekday()
{
Date start(1900, 1, 1); //查询得星期一
int count = *this - start;
cout << "星期" << ((count % 7) + 1) << endl;
}
六、const成员
举例:
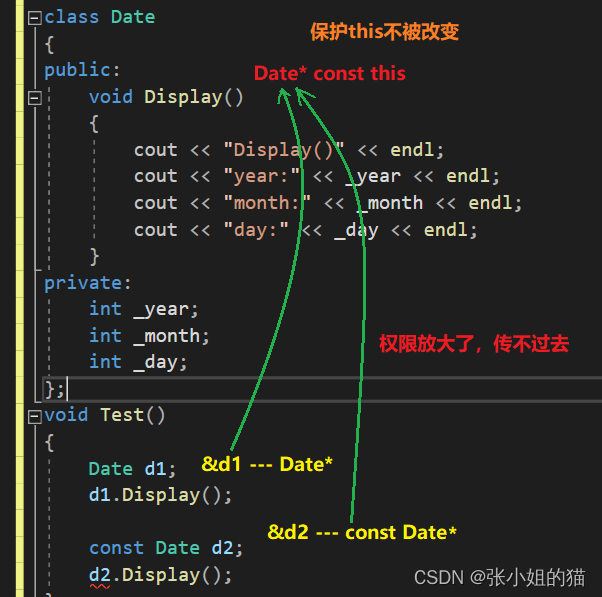
同理:d2 < d1 也会出错
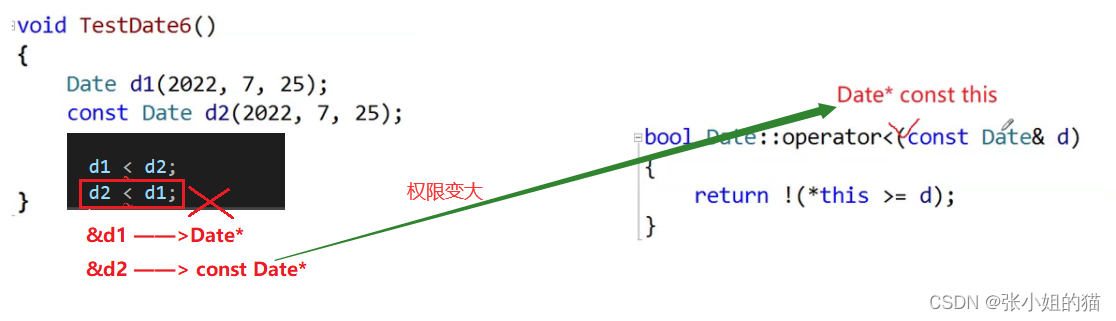
于是C++增加了const成员函数,实际修饰this指针,保护this指向的内容不被修改,即不能对任何类成员进行修改
class Date
{
public:
void Display() const
{
cout << "year:" << _year << endl;
cout << "month:" << _month << endl;
cout << "day:" << _day << endl << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1;
d1.Display(); //权限缩小
const Date d2;
d2.Display(); //权限不变
return 0;
}
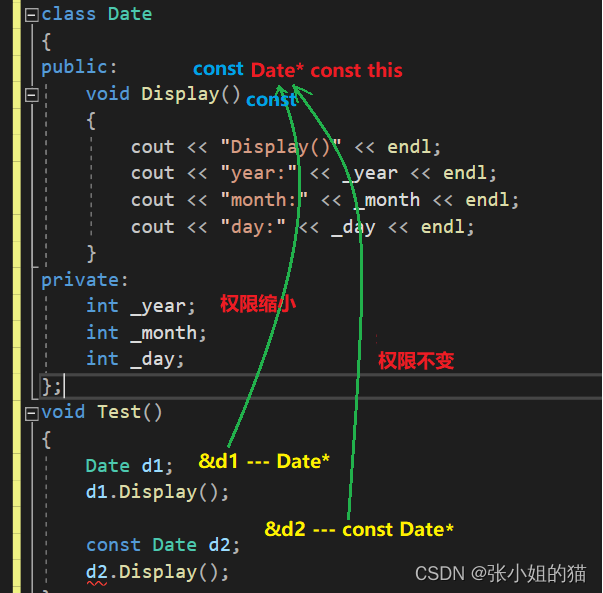
const Date* const this
- 第一个const修饰:this指针指向的内容
- 第二个const修饰:this指针本身不能被修改
也就是说const对象和非const对象都可以调用这个成员函数
七、取地址及const取地址操作符重载
这两个函数意义不大
这两个默认成员函数一般不用重新定义 ,编译器默认会生成的就足够用了
class Date
{
public :
Date* operator&()
{
return this ;
}
const Date* operator&()const
{
return this ;
}
private :
int _year ; // 年
int _month ; // 月
int _day ; // 日
};
这两个运算符一般不需要重载,使用编译器生成的默认取地址的重载即可,只有特殊情况,才需要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容
八、实现代码
🎉Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WAENINGS
#include "Date.h"
void Date::Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
//任何一个类,只需要写一个 > == 重载 或者 < == 即可,剩下比较运算符复用即可
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
//d1 > d2
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if((_year>d._year)
||(_year==d._year &&_month > d._month)
||(_year==d._year && _month==d._month && _day>d._day))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//尽可能的去复用
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = (*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
//d2 += d1 += 100 连续加等,有返回值
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;//d1没销毁,可以传引用返回
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date& Date::operator--() //前置
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int) //后置
{
Date ret = *this;
*this -= 1;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator++() //前置++
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int) //后置++
{
Date ret = *this;
*this += 1;
return ret;
}
//日期-日期
// offerDay - today =>offerDay.operator(&offerday,today);
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
//假设
int flag = 1;//防止天数为负
Date max = *this;//晚
Date min = d;//早
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int day = 0;
while (min < max)
{
++min;
++day;
}
return day* flag;
}
void Date::PrintWeekday()
{
Date start(1900, 1, 1); //查询得星期一
int count = *this - start;
cout << "星期" << ((count % 7) +1) << endl;
}
🎉Test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date.h"
void test1()
{
Date d1(2002, 3, 7);
d1.Print();
Date d2(2022, 2, 29);
}
//测试+、+=、++
void test2()
{
Date d1(2022, 1, 16);
/*Date ret = d1 + 100;
ret.Print();*/
//Date d2(2022, 1, 16);
//d2 += 100;
//d2.Print();
//++d1;
d1++;
}
//测试这一堆运算符重载函数
void test3()
{
Date d1(2002, 3, 7);
Date d2(2002, 2, 19); //missing lmyy
Date d3(2002, 3, 7);
cout << (d1 == d3) << endl;
cout << (d1 >= d2) << endl;
cout << (d1 < d3) << endl;
cout << (d1 <= d2) << endl;
cout << (d1 != d3) << endl;
}
// 测试-,-=,--
void test4()
{
Date d1(2022, 1, 10);
Date d2(2022, 2, 19);
Date ret2 = d2 - 60;
ret2.Print();
d1 -= 10;
d1.Print();
/*--d2;
d2--;*/
}
//测试日期 - 日期,星期几
void test5()
{
Date today(2022,1,23);
Date offerDay(2022, 9, 1);
cout << (offerDay - today) << endl;
today.PrintWeekday();
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
//test3();
//test4();
test5();
return 0;
}
📢写在最后
英雄联盟世界赛要准备开打了,有爱看的兄弟吗?

