系列文章目录
文章目录
1.Piorityqueue
定义:是一种优先级队列,底层使用了堆的数据结构。
堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
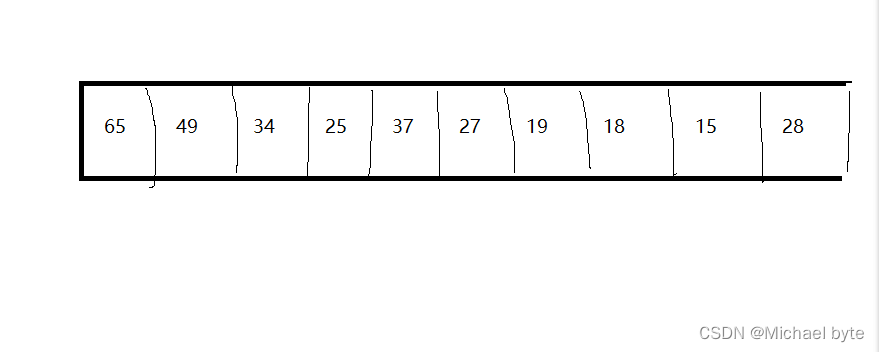
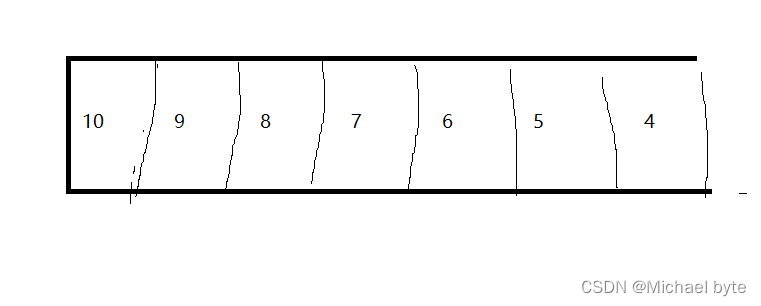
堆通常采用顺序表存储
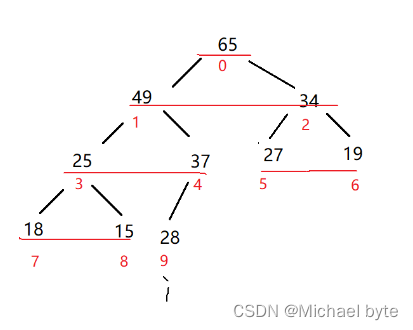
大根推:
根结点总是大于左右孩子结点。
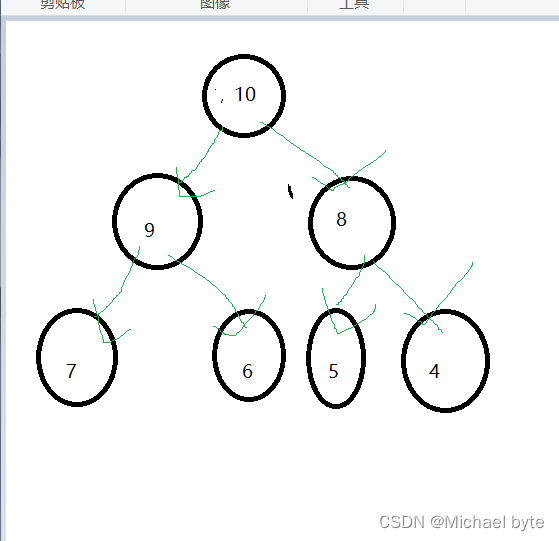
小根堆:
根结点总是小于左右孩子:
建立一个大根堆:
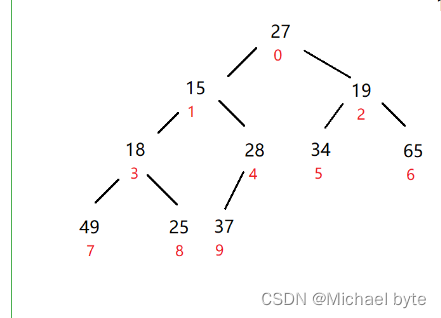
如图所示,我们如何建立一个大根堆呢?
那我们肯定是要从最后一个父亲结点倒着往前调,使它的根节点在这一棵树中是最大的值,那么最后有个父亲结点的下标又是什么呢?结点=(len-1-1)/2;
第二个问题是我们假设在调整一个父亲结点时,那么我们怎么确定这个父亲结点是否调整完了呢?
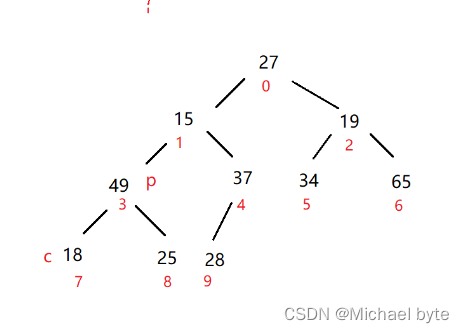
假设我们再调整15这个父亲结点
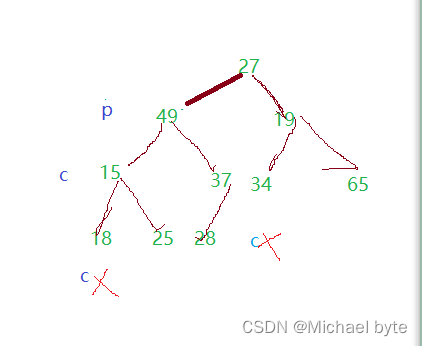
我们把49给换上去了,那么15这个结点又是一棵子树,我们需要对它进行再一次调整,以此类推,那么什么时候结束了,我们假设p是根节点坐标,c是孩子结点坐标,p=2*c+1,当c>=len 时,就调整完了。
class PriorityQueue
{
public static int[]elem;
public static int usesized;
public PriorityQueue()
{
elem=new int[10];
}
public static void ininum(int[]arry)
{
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<arry.length;i++)
{
elem[i]=arry[i];
usesized++;
}
}
public static void creat() //建立一个堆
{
for(int parent=(usesized-1-1)/2;parent>=0;parent--)
{
shit(usesized,parent);
}
}
public static void shit(int len,int parent)
{
int child=2*parent+1;
while(child<len)
{
if(child+1<len&&elem[child]<elem[child+1])
{
child++;
}
if(elem[child]>elem[parent])
{
int tmp=elem[child];
elem[child]=elem[parent];
elem[parent]=tmp;
parent=child;
child=2*parent+1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public static void offer(int num) //增加一元素,把它放在最后面,然后再进行调整
{
if(isfull())
{
elem= Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
elem[usesized]=num;
usesized++;
int child1=usesized-1;
int parent1=(child1-1)/2;
while(parent1>=0)
{
if(elem[child1]>elem[parent1])
{
int tmp=elem[child1];
elem[child1]=elem[parent1];
elem[parent1]=tmp;
child1=parent1;
parent1=(child1-1)/2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public static int peek()
{
return elem[0];
}
public static boolean isfull()
{
return usesized==10;
}
public static void shanchu() //删除元素只能删除最顶端的元素,做法是把最后的元素和最顶端的元素进行交换,然后再把祖先结点进行调整成大根堆,
// 不需要调整所有的结点,只有祖先结点需要调整
{
int tmp=elem[0];
elem[0]=elem[usesized-1];
elem[usesized-1]=tmp;
usesized--;
shit(usesized,0);
}
public static boolean empty()
{
return usesized==0;
}
}
2.我们先来观察一段代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> a=new PriorityQueue<>(new inum());
a.offer(10);
a.offer(20);
a.offer(30);
System.out.println(a.poll());
}
我们可以看到PriorityQueue底层其实是一个小根堆。
我们再来看一段代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<person>a=new PriorityQueue<>();
a.offer(new person(5));
a.offer(new person(10));
a.offer(new person(20));
System.out.println("ggag");
//System.out.println(a.poll());
}你像这段代码,person这个对象没有办法比较,这时候我们就需要使用Comparable,然后再重写一下compareTo这个方法。
class person implements Comparable<person>
{
int age;
public person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(person o) {
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<person> a=new PriorityQueue<>();
a.offer(new person(10));
a.offer(new person(5));
System.out.println(1);
}我们来看一下:
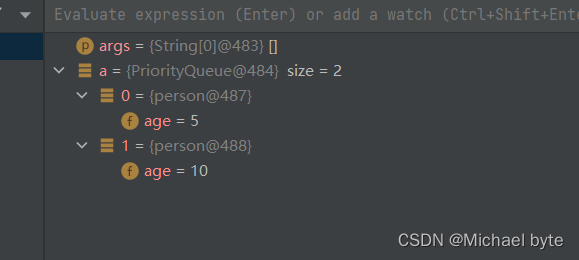
那么为什么底层是小根堆呢?
我们可以来看一下它底层的代码:
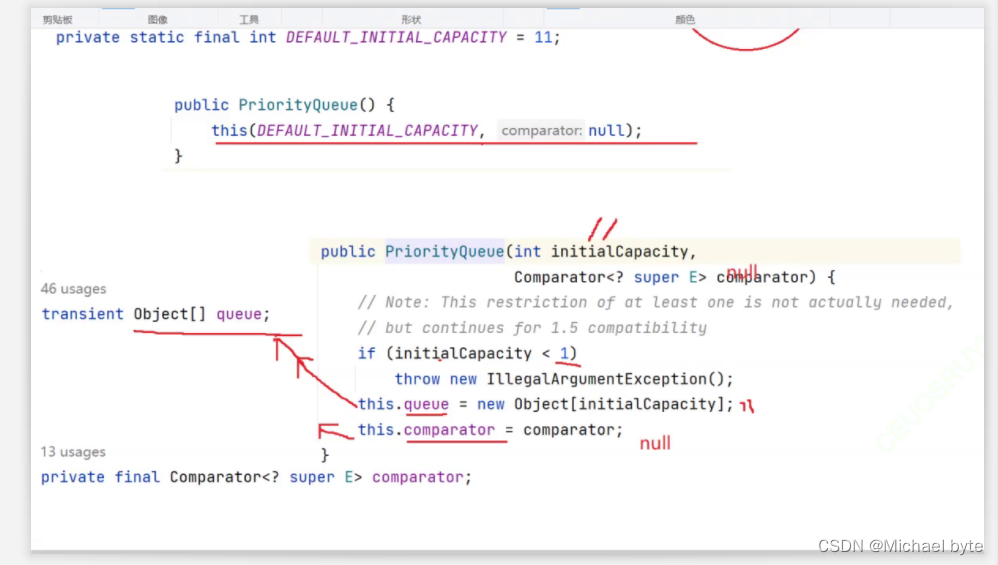
由这张源码,我们可以看到当没有传入比较器的时候,这一段代码其实是对底层的数组完成了初始化,开辟了11个空间。

当我们再加上new Student(5)时,
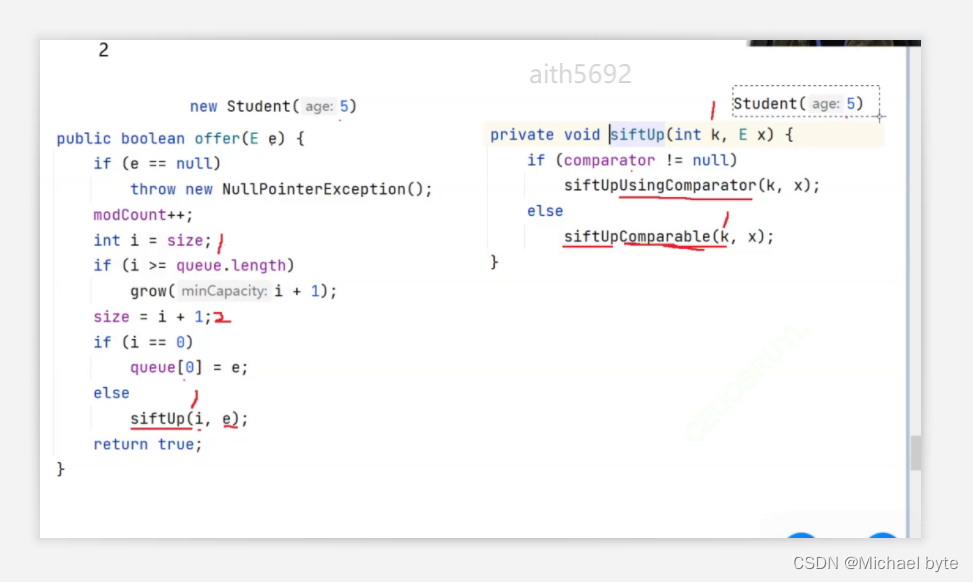
我们可以得出i=1,此时我们调用siftUp函数,因为我们没有传入比较器,所以我们再调用siftUpComparable函数,我们再来看源码
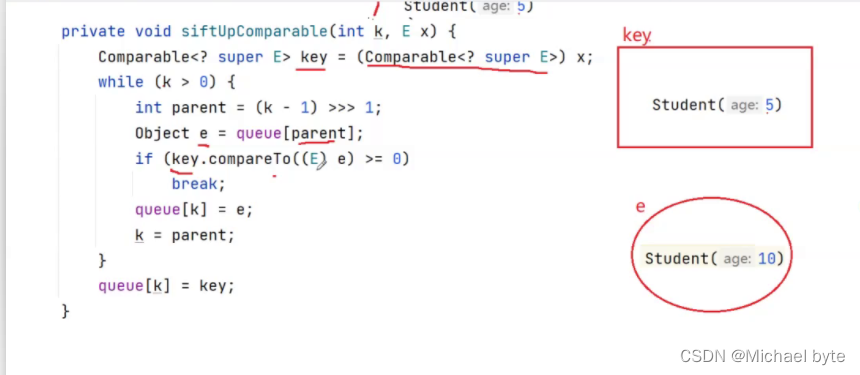
k=1,parent=0;我们可以看到key里存放的是Student(5),e里存放的是Student(10),if语句进不去
queue[1]=e;然后queue[0]=key就变成了
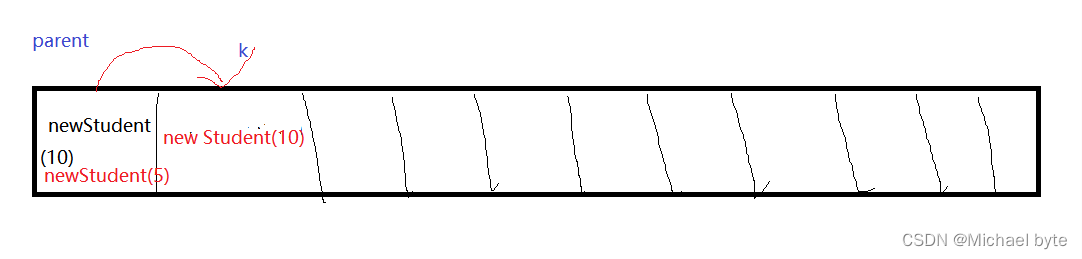
这时我们就应该明白了为什么是小根堆了把,只要后者比前者小,就交换位置。那么我们有没有办法让它变成大根堆呢?我们只需将key.compareTo(e)这个方法重写一下就可以了,其实就是将key和e换一下位置,此时就大于0了,queue[1]=5,queue[0]=10;
class person implements Comparable<person>
{
int age;
public person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(person o) {
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
public class text2
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<person>a=new PriorityQueue<>();
a.offer(new person(5));
a.offer(new person(10));
a.offer(new person(20));
System.out.println("ggag");
//System.out.println(a.poll());
}
}
这种情况下是小根堆。
将 this.age和o.age一换位置就成了大根堆
class person implements Comparable<person>
{
int age;
public person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(person o) {
return o.age-this.age;
}
}
这个题如果传比较器也是一样的思路,
当o1和o2没有换位置时,此时是小根堆。
class inum implements Comparator<Integer>
{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
}
public class text
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> a=new PriorityQueue<>(new inum());
a.offer(10);
a.offer(20);
a.offer(30);
System.out.println(a.poll());
}
}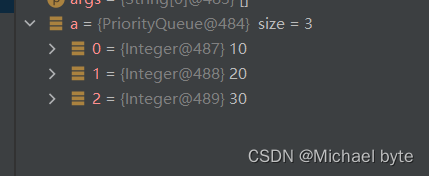
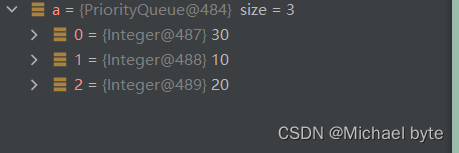
当o1和o2换位置时此时是大根堆
class inum implements Comparator<Integer>
{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
}
class inum implements Comparator<Integer>
{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
}
public class text
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> a=new PriorityQueue<>(new inum());//将比较器传进去
a.offer(10);
a.offer(20);
a.offer(30);
System.out.println(a.poll());
}
}
由这段代码我们可以知道我们建立了inum这个类,并实现了Comparator这个接口,并且重写了这个方法。
我们再来看一段代码:
PriorityQueue<Integer> a=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
这段代码和上一段代码其实是等价的,我们可以认为这是一个匿名内部类,实现了Comparator这个接口,并且重写了他的方法。
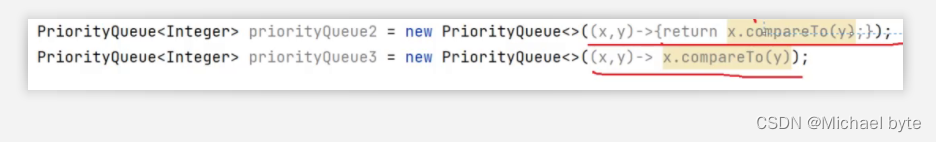
还有这两种写法也都和前两种实质上是一样的 。
四.优先级队列底层是如何扩容的
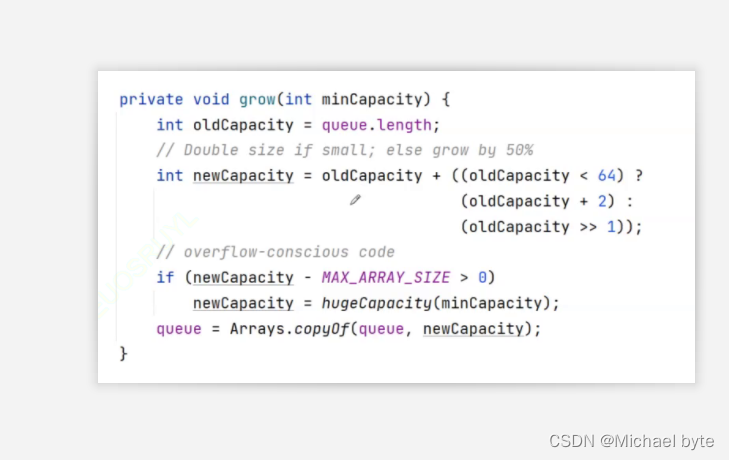
又原码可知:如果原来容量小于64,那么是2倍扩容,如果大于64,那么是1.5倍扩容,如果容量超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,按照MAX_ARRAY_SIZE扩容