原创文章第93篇,专注“个人成长与财富自由、世界运作的逻辑, AI量化投资”。
今天要说说强化学习。
强化学习个人认为,是最契合金融投资的范式。它其实不是一个具体的算法,而是一种范式。
与监督学习不同,监督学习是“一次性”的,有明确的标签。而类比人类的学习,我们不会拿1万张猫的图片让孩子学习什么是猫,一个小朋友也许只见过几只猫,他几乎可以认出各种图片的,抽象的,卡通的猫。人脑的学习是激励-反馈机制。你做一个动作,得到一个正反馈就可以强化这个动作,如果得到负反馈,则弱化这个动作。
我们学骑自行车,并不会用物理学的公式,去计算,人体和地面的角度,手臂要如何发力,而是骑就是了,自行车和地面给你反馈,你随之调整。
简言之,智能体通过与环境交互,得到即时反馈,来调整自己的动作,直到学会某个技能。——这样的学习范式的通过的。所以有了alpha go, alpha master和alpha zero这样的围棋大师,然后它们的技能迁移的打战略游戏上,也是一等一的好手,都拜强化学习所赐。
昨天我们讲的DNN的模式,我们是让模型学习过去的因子“预测”当天的收盘价的“涨跌”。但现实交易过程中,我们就不会因为判断今天会涨就买入,而明天会跌就卖出吧。
投资是一个系列的决策,寻找是一段时间内的收益率,而不是某一天或某几天的涨与跌。这种多轮博弈,而且带有成本的多轮博弈,使用强化学习再适合不过了。
01 强化学习
导入一般常规配置:
import os
import math
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pylab import plt, mpl
plt.style.use('seaborn')
mpl.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 300
mpl.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'
np.set_printoptions(precision=4, suppress=True)
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = '0'
实现一个观察空间类,这是一个N维向量,n的维度等于我们因子的个数。
class observation_space:
def __init__(self, n):
self.shape = (n,)
动作空间,这里动作空间是2(买,卖)
class action_space:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
def seed(self, seed):
pass
def sample(self):
return random.randint(0, self.n - 1)
模似交易环境:
交易环境除了准备交易数据之外,最重要的就是step函数,我们这里的reward仍然与昨天的DNN类似,智能体猜中一次,则奖励加1分。
准确率低于47.5%时退出,或者一个episode结束时退出。
相当于我们做一个交易游戏,一个智能体进来“猜”,猜中加1分,计算准确率,低于47.5%直接出局。
class Finance:
url = 'http://hilpisch.com/aiif_eikon_eod_data.csv'
def __init__(self, symbol, features):
self.symbol = symbol
self.features = features
self.observation_space = observation_space(4)
self.osn = self.observation_space.shape[0]
self.action_space = action_space(2)
self.min_accuracy = 0.475
self._get_data()
self._prepare_data()
def _get_data(self):
self.raw = pd.read_csv(self.url, index_col=0,
parse_dates=True).dropna()
def _prepare_data(self):
self.data = pd.DataFrame(self.raw[self.symbol])
self.data['r'] = np.log(self.data / self.data.shift(1))
self.data.dropna(inplace=True)
self.data = (self.data - self.data.mean()) / self.data.std()
self.data['d'] = np.where(self.data['r'] > 0, 1, 0)
def _get_state(self):
return self.data[self.features].iloc[
self.bar - self.osn:self.bar].values
def seed(self, seed=None):
pass
def reset(self):
self.treward = 0
self.accuracy = 0
self.bar = self.osn
state = self.data[self.features].iloc[
self.bar - self.osn:self.bar]
return state.values
def step(self, action):
correct = action == self.data['d'].iloc[self.bar]
reward = 1 if correct else 0
self.treward += reward
self.bar += 1
self.accuracy = self.treward / (self.bar - self.osn)
if self.bar >= len(self.data):
done = True
elif reward == 1:
done = False
elif (self.accuracy < self.min_accuracy and
self.bar > self.osn + 10):
done = True
else:
done = False
state = self._get_state()
info = {}
return state, reward, done, info
智能体的实现DRL:
def set_seeds(seed=100):
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
env.seed(seed)
set_seeds(100)
from collections import deque
from keras.optimizers import Adam, RMSprop
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.optimizers import Adam, RMSprop
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from tensorflow.python.framework.ops import disable_eager_execution
disable_eager_execution()
class DQLAgent:
def __init__(self, gamma=0.95, hu=24, opt=Adam,
lr=0.001, finish=False):
self.finish = finish
self.epsilon = 1.0
self.epsilon_min = 0.01
self.epsilon_decay = 0.995
self.gamma = gamma
self.batch_size = 32
self.max_treward = 0
self.averages = list()
self.memory = deque(maxlen=2000)
self.osn = env.observation_space.shape[0]
self.model = self._build_model(hu, opt, lr)
def _build_model(self, hu, opt, lr):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(hu, input_dim=self.osn,
activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(hu, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(env.action_space.n, activation='linear'))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=opt(lr=lr))
return model
def act(self, state):
if random.random() <= self.epsilon:
return env.action_space.sample()
action = self.model.predict(state)[0]
return np.argmax(action)
def replay(self):
batch = random.sample(self.memory, self.batch_size)
for state, action, reward, next_state, done in batch:
if not done:
reward += self.gamma * np.amax(
self.model.predict(next_state)[0])
target = self.model.predict(state)
target[0, action] = reward
self.model.fit(state, target, epochs=1,
verbose=False)
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
def learn(self, episodes):
trewards = []
for e in range(1, episodes + 1):
state = env.reset()
state = np.reshape(state, [1, self.osn])
for _ in range(5000):
action = self.act(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_state = np.reshape(next_state,
[1, self.osn])
self.memory.append([state, action, reward,
next_state, done])
state = next_state
if done:
treward = _ + 1
trewards.append(treward)
av = sum(trewards[-25:]) / 25
self.averages.append(av)
self.max_treward = max(self.max_treward, treward)
templ = 'episode: {:4d}/{} | treward: {:4d} | '
templ += 'av: {:6.1f} | max: {:4d}'
print(templ.format(e, episodes, treward, av,
self.max_treward), end='\r')
break
if av > 195 and self.finish:
print()
break
if len(self.memory) > self.batch_size:
self.replay()
def test(self, episodes):
trewards = []
for e in range(1, episodes + 1):
state = env.reset()
for _ in range(5001):
state = np.reshape(state, [1, self.osn])
action = np.argmax(self.model.predict(state)[0])
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
state = next_state
if done:
treward = _ + 1
trewards.append(treward)
print('episode: {:4d}/{} | treward: {:4d}'
.format(e, episodes, treward), end='\r')
break
return trewards
重点关注learn函数:
每个episode跑5000次,遇到失败会退出。DRL有重放机制,这个我们系统讲强化学习算法的时候再说。
训练这个模型花了22分钟。

02 DRL应用于投资实战
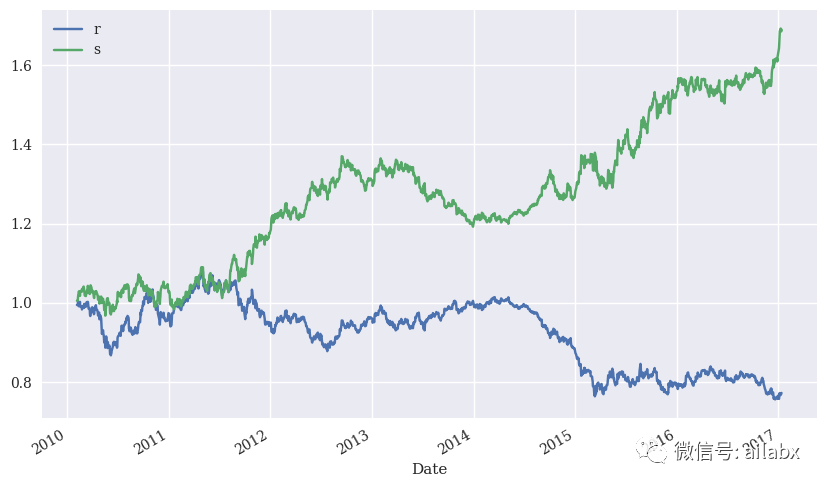
样本内的表现还是不错的,我们再来看样本外的表现情况:

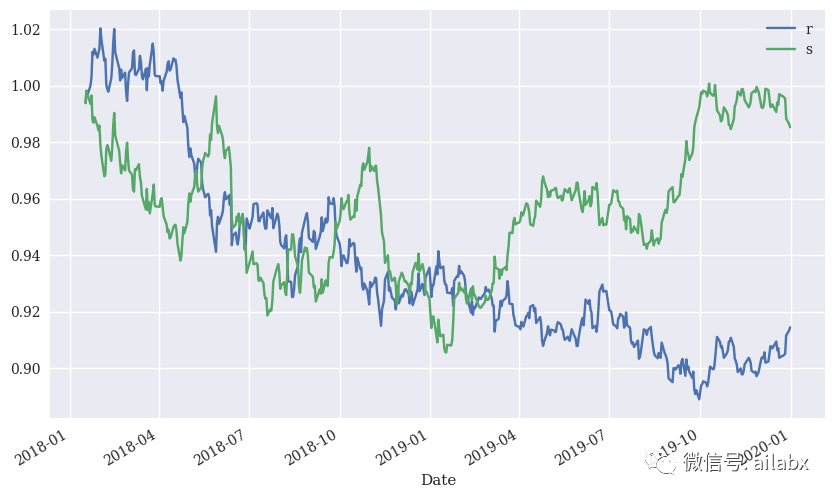
还可以,注意这里未考虑手续费。
小结:
本文重在演示强化学习如何作用于金融时间序列数据,这个方向一定是可行,而且应该深入探讨的。