1 复合高温干旱事件(compound dry-hot extremes)
1.1 归因(Attribution)
短时间尺度:静止反气旋(stationary anticyclones)
长时间尺度:强陆地-大气相互作用(land-atmosphere interactions)、大尺度变率模式
1.2 类型
1.2.1 类型1:高温和干旱同时发生
定义:
指标:
研究思路
- 利用多尺度标准化温度指数STI和标准化降雨指数SPI进行复合干热事件的监测和预测
- 指标:
①基于降水和温度的标准化复合事件指数(Standardized Compound Event Indicator, SCEI)
②标准化干热事件指数(Standardized Dry and Hot Index, SDHI)
③干热量级指数(Dry-hot Magnitude Index, DHMI)
1.2.2 类型2:高温和干旱连续发生
定义:
指标:
研究思路
2 复合干热指数
2.1 标准化干热事件指数(Standardized Dry and Hot Index, SDHI)
- J2018-Changes in the severity of compound drought and hot extremes over global land areas-首次提出SDHI指数
- 数据:日降水、日最大气温
2.1.1 指标原理

2.1.2 指标计算代码
2.2 干热量级指数(Dry-hot Magnitude Index, DHMI)
- J2019-Dry-hot magnitude index: a joint indicator for compound event analysis-首次提出DHMI指数
- 数据:日降水、日最大气温
2.2.1 指标原理
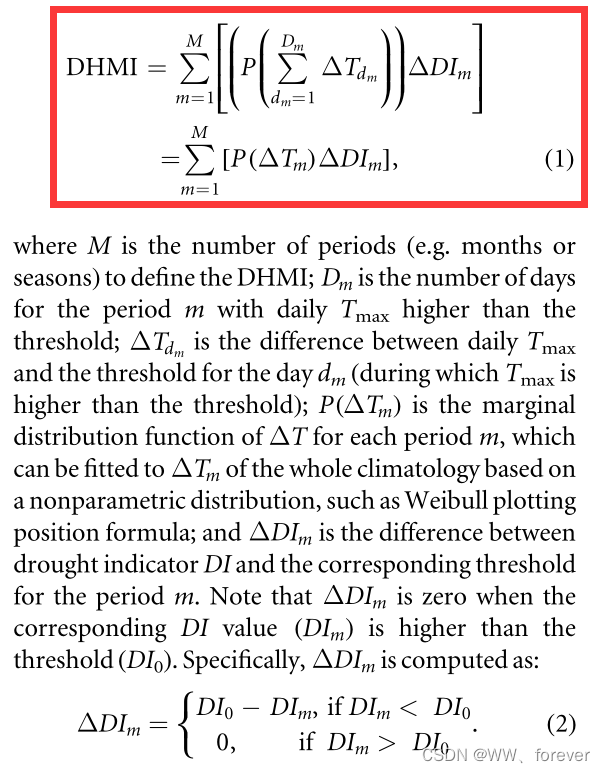
2.2.2 指标计算代码
2.3 基于降水和温度的标准化复合事件指数(Standardized Compound Event Indicator, SCEI)
- J2019-Statistical prediction of the severity of compound dry-hot events based on El Niño-Southern Oscillation-Journal of Hydrology-首次提出SCEI指数
- 数据:日降水、日最大气温
2.3.1 指标原理
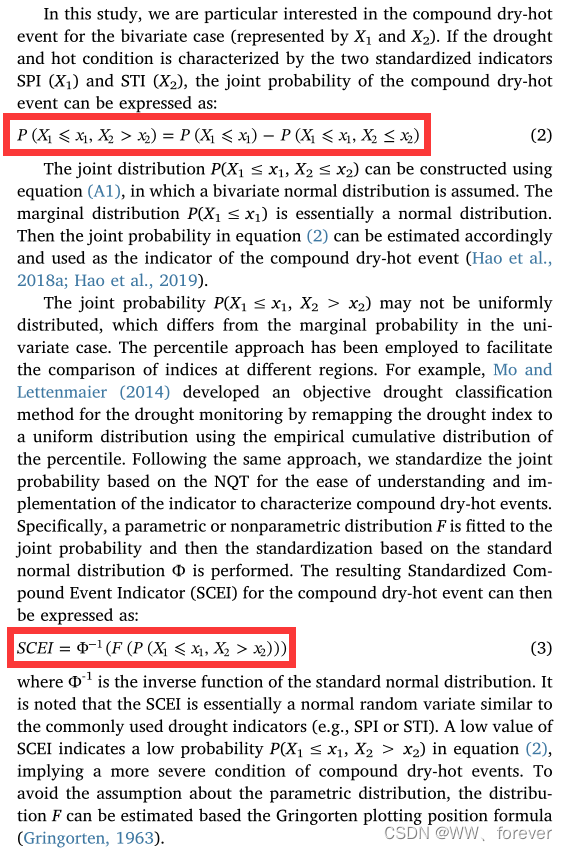

2.3.2 指标计算代码
3 总结
参考
- J2020-Evaluation of severity changes of compound dry and hot events in China based on a multivariate multi-index approach-Journal of Hydrolog
说明:基于降水和温度的标准化复合事件指数(Standardized Compound Event Indicator, SCEI)和标准化干热事件指数(Standardized Dry and Hot Index, SDHI)评价中国复合干热事件严重程度变化
本文含有隐藏内容,请 开通VIP 后查看