活动地址:CSDN21天学习挑战赛
题目描述
英文版描述
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty). Implement the MyQueue class:
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
英文版地址
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
中文版描述
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty): 实现 MyQueue 类: void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾 int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素 int peek() 返回队列开头的元素 boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 说明: 你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例 1:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用 100 次 push、pop、peek 和 empty
假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)
中文版地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
解题思路
入栈:入栈前先将原先装有元素的栈中的全部取出,压入另一个栈中,然后将该元素也压入这个栈中,再将这个栈中的所有元素取出压入另一个栈 解决叻入栈问题(即将入栈顺序颠倒),然后就发现出栈以及其他操作则直接按照操作栈就好。。。 (不愧是我(。・ω・。)ノ)
解题方法
俺这版
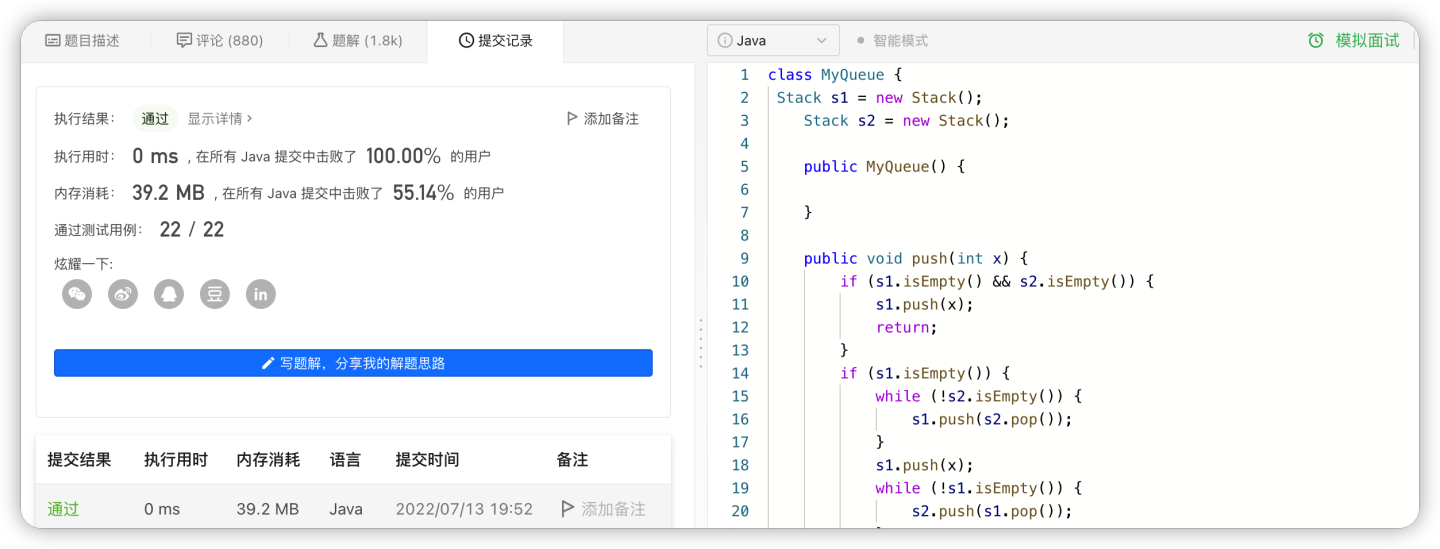
class MyQueue {
Stack s1 = new Stack();
Stack s2 = new Stack();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
if (s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty()) {
s1.push(x);
return;
}
if (s1.isEmpty()) {
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
s1.push(s2.pop());
}
s1.push(x);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return;
}
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
s2.push(x);
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
s1.push(s2.pop());
}
return;
}
}
public int pop() {
if (s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else if (s1.isEmpty()) {
return (int) s2.pop();
} else {
return (int) s1.pop();
}
}
public int peek() {
if (s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else if (s1.isEmpty()) {
return (int) s2.peek();
} else {
return (int) s1.peek();
}
}
public boolean empty() {
if (s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/官方版
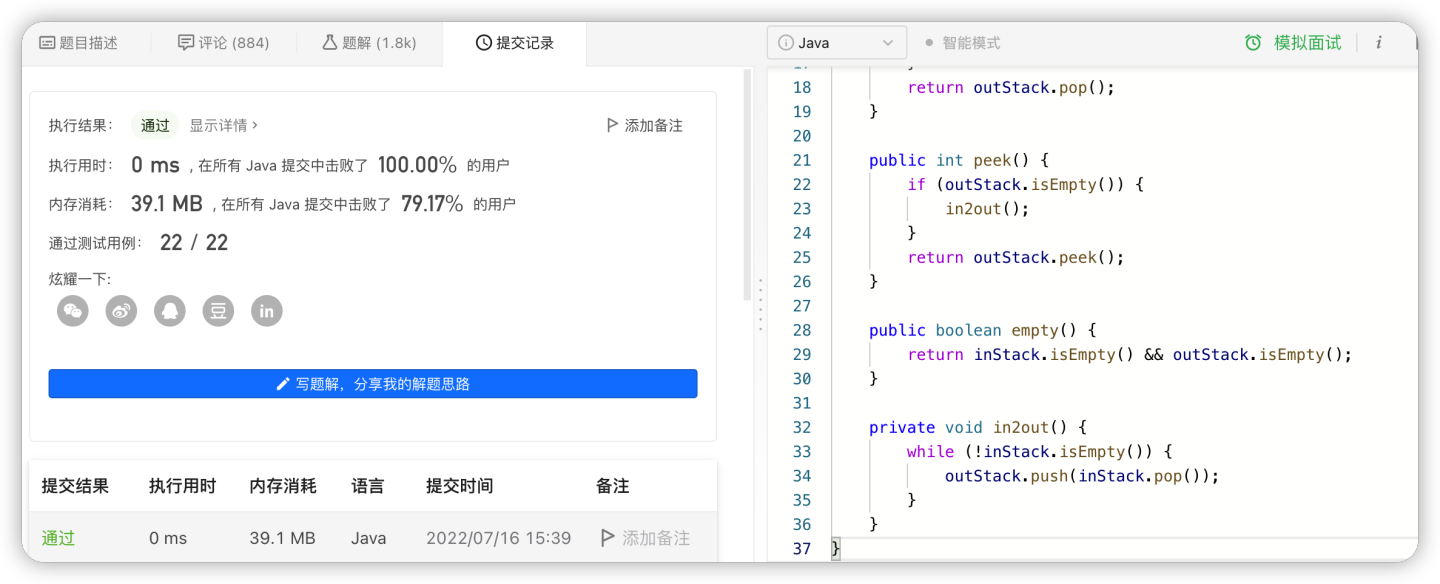
class MyQueue {
Deque<Integer> inStack;
Deque<Integer> outStack;
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
outStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return inStack.isEmpty() && outStack.isEmpty();
}
private void in2out() {
while (!inStack.isEmpty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
}总结
需要将先入后出的顺序改变为先入先出,则需要在每次插入或者每次删除处执行变换顺序的操作,就是将其中一个栈数据弹出,压入另一个栈,实现全部元素顺序的颠倒,这十分符合我在之前文章中提到的优化思路,即最先想到的"暴力破解"方法,于是有了上面👆我那版里的方法。
后面我思考有没有优化的空间,即这些操作中是否有重复,我发现其实是有很多重复的,就是如果用户连续执行n次入栈,用最开始的方法则会排序n次,但其实只需要在最后一次入栈结束后,执行一次重排序即可,在官网的提示下,我了解到了“均摊”的思想,于是尝试将我的代码进行优化,即将一个栈作用来弹出数据,一个栈用来压入数据,只有弹出数据的栈为空的情况下,才将压入栈的数据(不为空的情况下)全部放入弹出栈。 执行了下,果然,快很多(。・ω・。)ノ
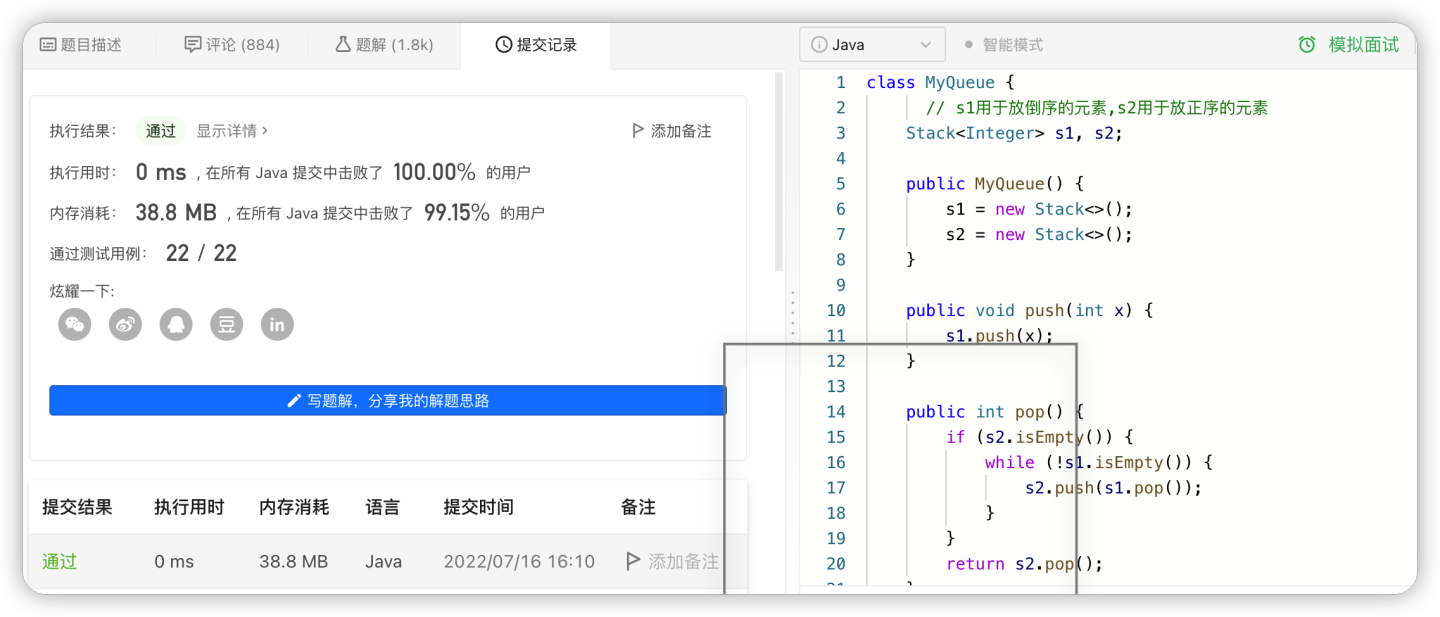
class MyQueue {
// s1用于放倒序的元素,s2用于放正序的元素
Stack<Integer> s1, s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}