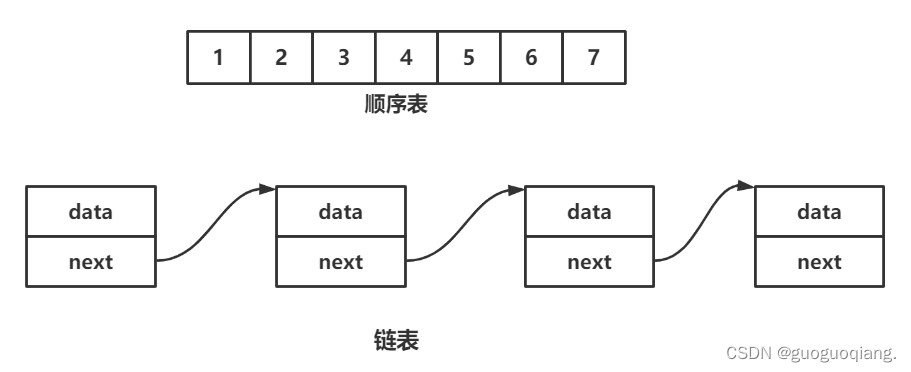
一、线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使
用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,
线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
二、顺序表的OJ题
1.原地移除数组中所有的元素val
27. 移除元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int scr=0,dst=0;
while(scr<numsSize){
if(nums[scr]==val){
scr++;
}
else{
nums[dst]=nums[scr];
scr++;
dst++;
}
}
return dst;
}在原数组上进行修改,等于val的跳过,不赋值。反之则赋值。
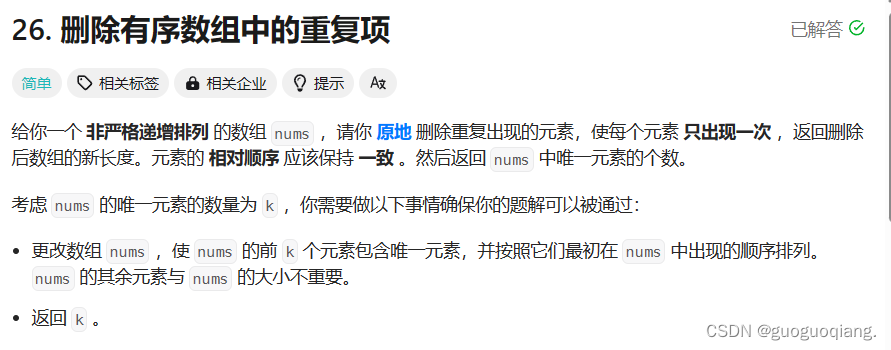
2.删除排序数组中的重复项
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize) {
if(numsSize==0){
return 0;
}
int fast=1,slow=1;
while(fast<numsSize){
if(nums[fast]!=nums[fast-1]){
nums[slow]=nums[fast];
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
return slow;
}对于这道题先处理特殊情况,如果numssize==0,则该数组没元素返回0。可以采用双指针法来实现,定义快慢指针,fast不等于fast-1对应下标的内容则让该fast对应的赋值给slow,再将slow++,
反之则就只让fast++,最后返回slow,slow前的数据都只出现了一次。
3.合并两个有序数组
88. 合并两个有序数组![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-sorted-array/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-sorted-array/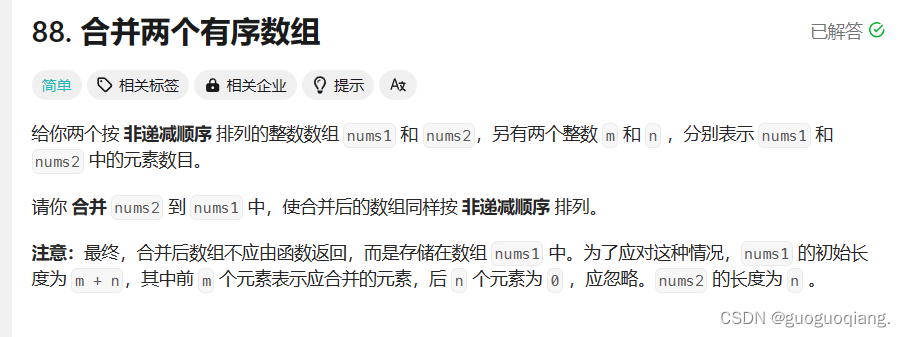
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
int l1=m-1,l2=n-1,l3=m+n-1;
while(l1>=0&&l2>=0){
if(nums1[l1]>nums2[l2]){
nums1[l3]=nums1[l1];
l3--;
l1--;
}
else{
nums1[l3]=nums2[l2];
l3--;
l2--;
}
}
while(l2>=0){
nums1[l3]=nums2[l2];
l3--;
l2--;
}
}按照题目要求本题本来就是要进行升序排序,对大的数据进行尾插操作,值得注意的是为什么需要对l2进行第二次循环呢?
因为&& 前真才会判断后面的,而如果前面就是假则直接判假跳过后面的了,所以需要对l2进行判断。
三、链表OJ题
在之前就已经写过一些有关链表的OJ题了,感兴趣的朋友可以去这个链接观看!!
学习c语言:单链表的应用-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读899次,点赞31次,收藏32次。单链表OJ题https://blog.csdn.net/bskmns/article/details/136591727?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501现在要对链表OJ题做些补充,准备发车了哦!!
1.链表分割
对于这个题,可以通过创建两个链表来进行分割,将小于x的数据尾插到less链表中,将大于x的数据尾插到great链表中。然后将less链表的未结点与great的头节点的next连接到一起,使链表连在一起,再将greattail置为空。返回lesshead->next.
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
struct ListNode*greatHead,*greattail,*lessHead,*lesstail,*cur;
greatHead=greattail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
lessHead=lesstail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur=pHead;
while(cur){
if(cur->val<x){
lesstail->next=cur;
lesstail=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
else{
greattail->next=cur;
greattail=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
lesstail->next=greatHead->next;
greattail->next=nullptr;
return lessHead->next;
}
};2.链表的回文结构
对于这个题,首先要找它的中间节点,使用快慢指针找中间节点,然后将slow后的链表进行逆置,然后将A与slow进行比较,以slow不等于A作为循环,如果值不相等就返回false,如果A的下一个等于slow就返回true,如果不是就将slow和A移到下一个。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// write code here
struct ListNode* slow=A;
struct ListNode* fast=A;
while(fast && fast->next){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
struct ListNode* head=slow;
while(head){
struct ListNode*next=head->next;
head->next=slow;
slow=head;
head=next;
}
head=A;
while(slow!=A){
if(A->val!=slow->val){
return false;
}
if(A->next==slow){
return true;
}
else{
slow=slow->next;
A=A->next;
}
}
return true;;
}
};三、相交链表
160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/两个链表找相交节点,如果一个链表为空则不存在相交节点,设置pa pb遍历链表,while循环如果pa不等于pb就进入循环,使pa和pb向后遍历,如果为空就返回headB headA,不为空就置为下一个。最后返回pa。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/两个链表找相交节点,如果一个链表为空则不存在相交节点,设置pa pb遍历链表,while循环如果pa不等于pb就进入循环,使pa和pb向后遍历,如果为空就返回headB headA,不为空就置为下一个。最后返回pa。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==NULL||headB==NULL){
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* pa=headA,*pb=headB;
while(pa!=pb){
pa=pa==NULL?headB:pa->next;
pb=pb==NULL?headA:pb->next;
}
return pa;
}四、环形链表
141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/在这个题中要判断该链表是否有环,可以通过快慢指针来进行实现,while循环fast&&fast->next
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/在这个题中要判断该链表是否有环,可以通过快慢指针来进行实现,while循环fast&&fast->next
fast=fast->next->next slow=slow->next,每次fast多走一步,所以链表只要有环就一定可以实现判断(当slow==fast时 返回true),否则返回false。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast &&fast ->next){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(slow==fast){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}好了,本期的内容到此结束,谢谢大家观看啊!!!
学习数据结构任重而道远,加油啊各位!!!