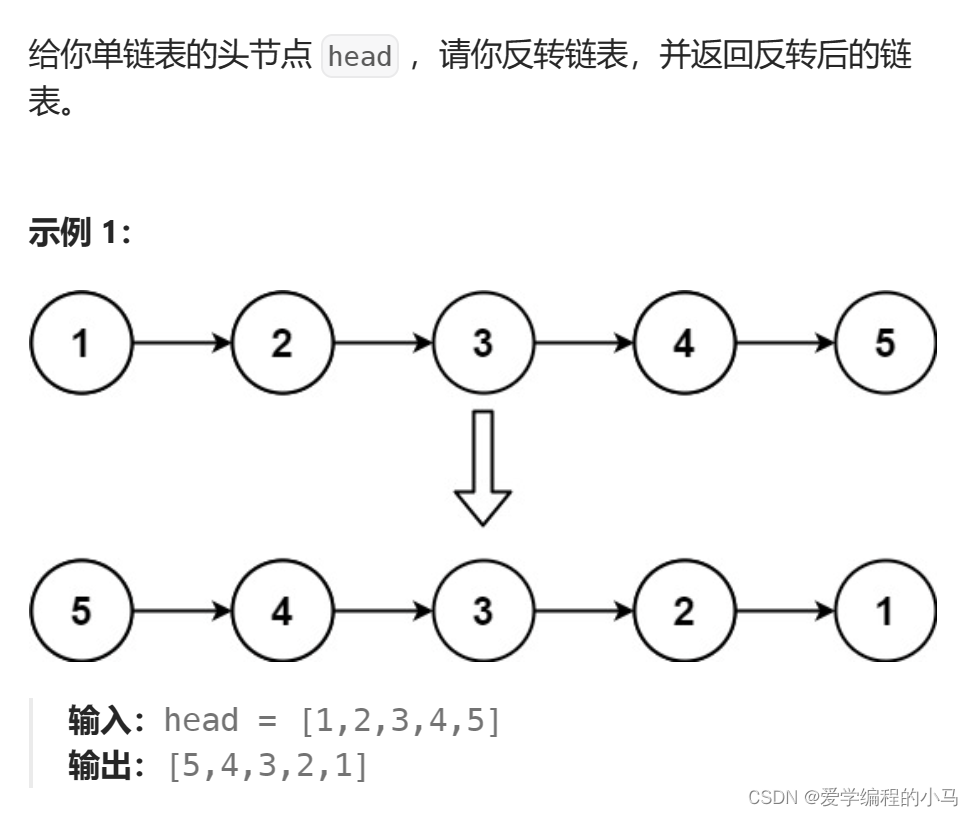
1.链表反转
typedef struct ListNode listnode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head == NULL)
{
return head;
}
listnode* p1 = NULL;
listnode* p2 = head;
listnode* p3 = head->next;
while(p2)
{
p2->next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p3;
if(p3)
p3 = p3->next;
}
return p1;
}核心思想:定义三个指针,第一个只想为空,第二个指向头节点,第三个指向头节点的下一个节点。之后让头节点的next指针反转180°,三个指针依次往后走。循环这一过程,直到p2为空。
要注意的是p3为空时不能解引用,否则编译器会报错。
2.移除链表元素

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* phead = NULL;
struct ListNode* ptail = NULL;
struct ListNode* pcur = head;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val != val)
{
if(phead == NULL)
{
phead = ptail = pcur;
}
else
{
ptail->next = pcur;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
if(ptail)
ptail->next = NULL;
return phead;
}核心思想: 遍历链表,把pcur->val = val的节点跳过。最后尾节点的next指针指向空。
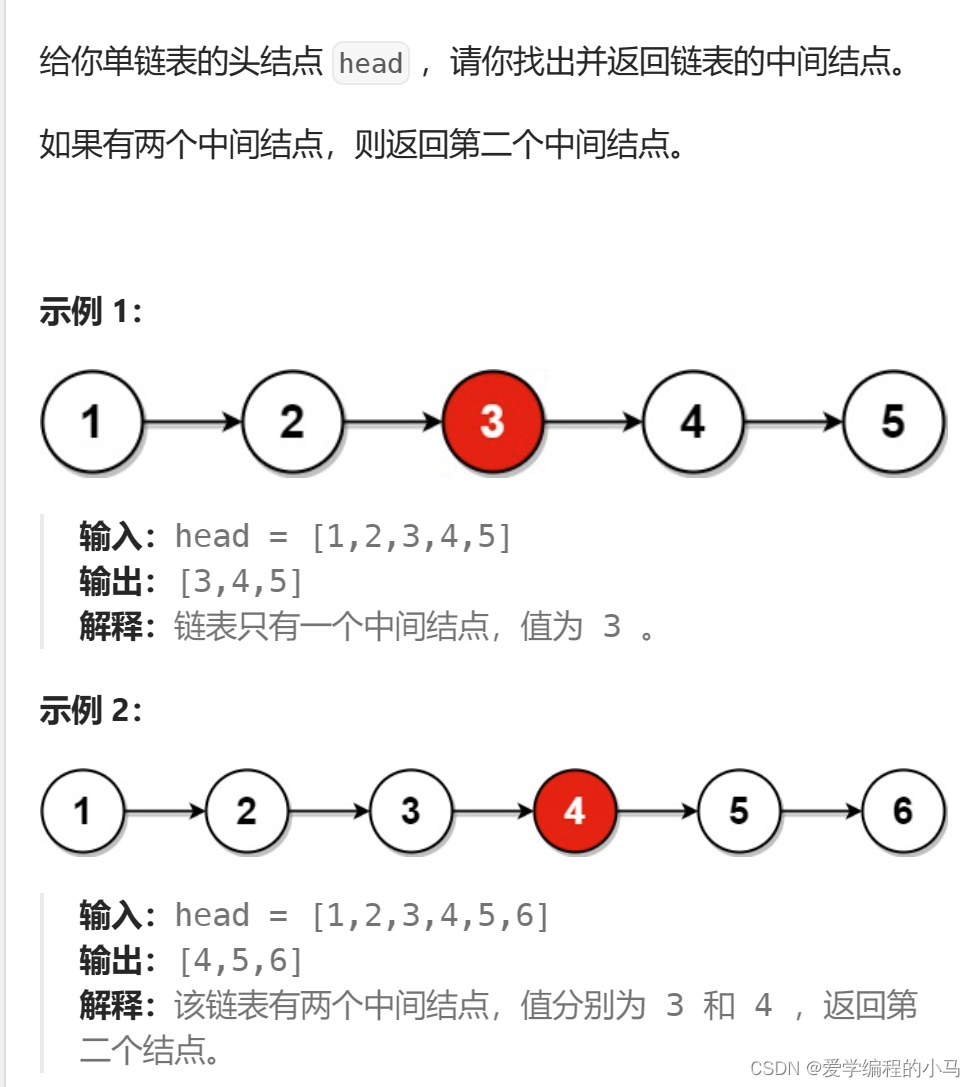
3.链表的中间节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode listnode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
listnode* man = head;
listnode* kuai = head;
while(kuai && kuai->next)
{
man = man->next;
kuai = kuai->next->next;
}
return man;
}核心思想:快慢指针
快指针每次移动两个单位,慢指针每次移动一个单位。这样,快指针指向空或者快指针的next指针指向空时。满指针指向的节点即为中间节点。
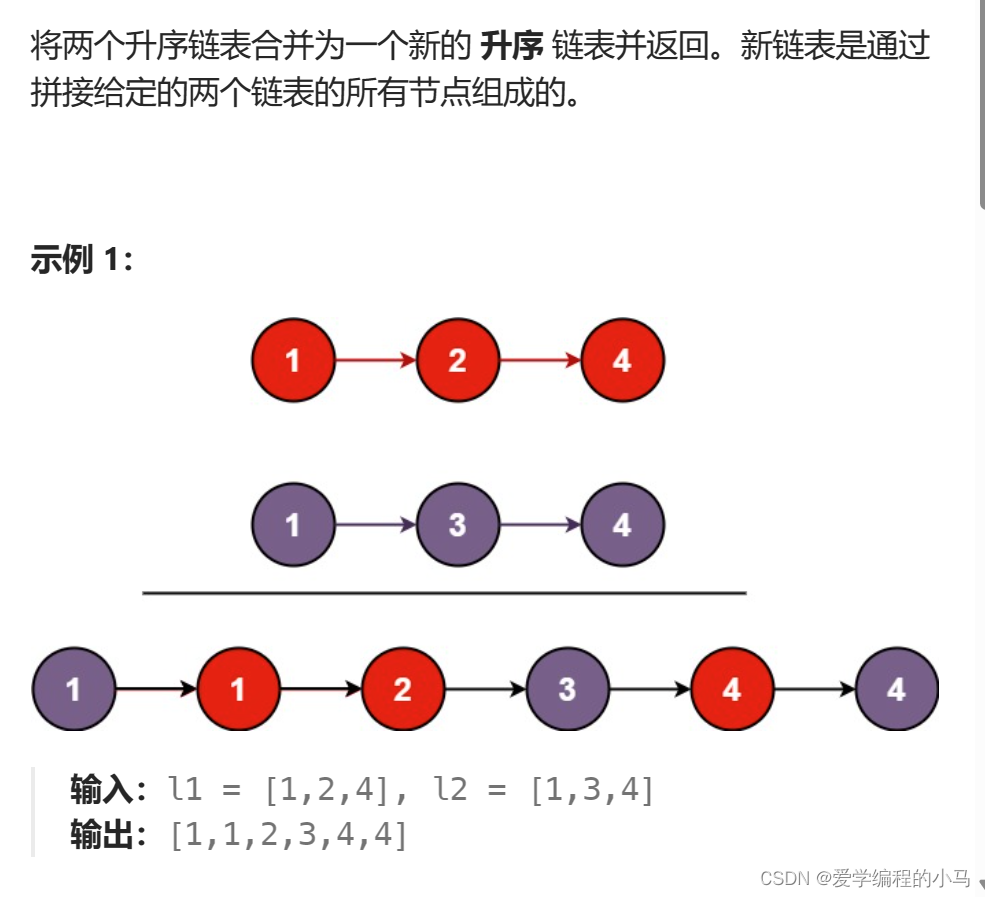
4.合并两个有序链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
if(l1 == NULL)
return l2;
if(l2 == NULL)
return l1;
ListNode* newhead = NULL;
ListNode* newtail = NULL;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val > l2->val)
{
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
}
if(l1)
newtail->next = l1;
if(l2)
newtail->next = l2;
return newhead;
}核心思想: 遍历两个链表,比较两链表节点的val值大小,将尾节点的next指针指向较小的节点,直到l1或者l2有一个为空时跳出循环。最后将没有走到空的链表尾插进来。
5.环形链表的约瑟夫问题

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* ByNode(int x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
ListNode* List(int n)
{
ListNode* phead = ByNode(1);
ListNode* ptail = phead;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
ptail->next = ByNode(i);
ptail = ptail->next;
}
ptail->next = phead;
return ptail;
}
int ysf(int m, int n)
{
ListNode* perv = List(n);
ListNode* pcur = perv->next;
int count = 1;
while (pcur->next != pcur)
{
if (count != m)
{
perv = pcur;
pcur = pcur->next;
count++;
}
else
{
perv->next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = perv->next;
count = 1;
}
}
return pcur->val;
}
int main()
{
int m, n;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
int ret = ysf(m, n);
printf("%d", ret);
return 0;
}主要思路:首先需要创建一个环形链表,然会创建一个指针pcur指向头节点,用pcur来遍历链表,如果count的值等于m,就需要把该节点释放,释放之前要将perv的next指针指向pcur的下一个节点。随后pcur向后移动,count重新置1。如果count的值不等于m,则不需要释放节点,只需把perv和pcur向后移动即可。同时count++。