一、Listener监听器
1、简介
Listener是Servlet规范中的一员
在Servlet中,所有的监听器接口都是以Listener结尾
监听器实际上是Servlet规范留给JavaWeb程序员的一些特殊时机
当在某些时机需要执行一段Java代码时,可以用对应的监听器
2、常用的监听器接口
(1)jakarta.servlet 包下:
ServletContextListener、ServletContextAttributeListener
ServletRequestListener、ServletRequestAttributeListener
(2)jakarta.servlet.http 包下:
HttpSessionListener
HttpSessionAttributeListener、HttpSessionBindingListener
HttpSessionIdListener、HttpSessionActivationListener
3、实现一个监听器的步骤
(1)以ServletContextListener为例
编写一个类实现ServletContextListener接口
这个监听器监听的是ServletContext对象的创建和销毁
监听器中的方法不需要程序员调用,在特定事件发生时由服务器调用
@WebListener
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
@override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
// 这个方法在ServletContext对象被创建时调用
}
@override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
// 这个方法在ServletContext对象被销毁时调用
}
}(2)在web.xml文件中配置这个监听器
也可以使用 @WebListener 注解
<listener>
<listener-class>自己实现的监听器类的全类名</listener-class>
</listener>4、其他监听器
(1)XxxxAttributeListener
监听的是某个域中的attribute被增加、修改、删除
只要域中的数据发生变化,就执行相应的方法
(2)XxxxBindingListener
例如,一个JavaBean实体类实现了HttpSessionBindingListener接口
那么当这个实体类的对象被放入session的attribute中触发bind事件,移除触发unbind事件
这个实体类不需要使用 @WebListener注解
(3)HttpSessionIdListener
监听Session对象的Id,当Id改变时调用类中的唯一的方法
(4)HttpSessionActivationListener
监听Session对象的钝化和活化
钝化:session对象从内存中存储到硬盘文件
活化:session对象从硬盘文件中恢复到内存
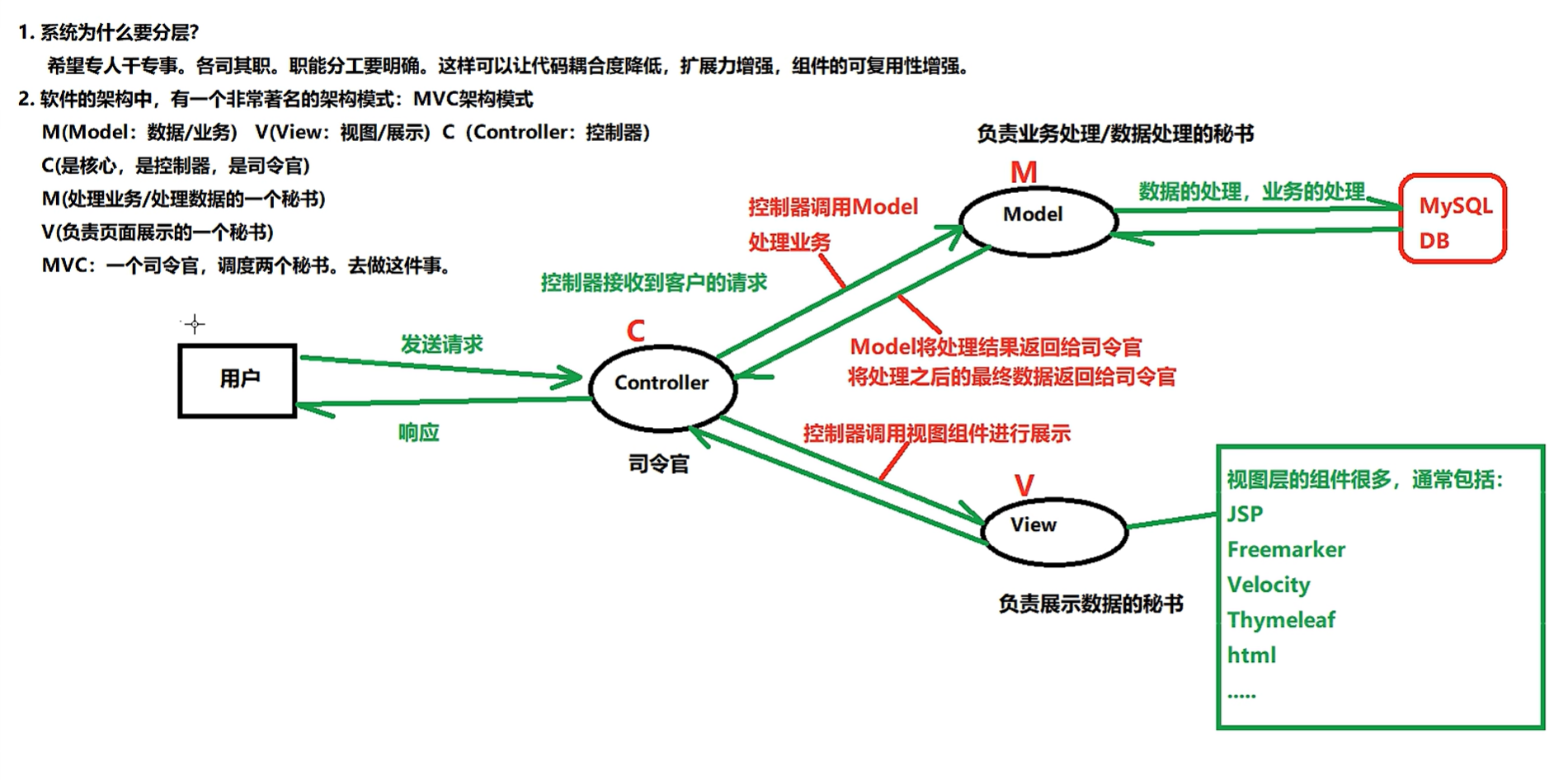
二、MVC架构模式
1、简介以及示意图
2、JDBC工具类的封装
public class DBUtil {
private static ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/jdbc");
private static String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
private static String url = bundle.getString("url");
private static String user = bundle.getString("user");
private static String password = bundle.getString("password");
// 工具类的所有方法都是静态的
// 将构造方法私有化,防止创建对象
private DBUtil() {}
static {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> local = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 没有使用数据库连接池,直接创建连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = local.get();
if (conn == null) {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
local.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
local.remove();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}3、MVC架构模式与三层架构的关系
三层架构:表现层、业务逻辑层、持久化层
表现层对应V和C
M包括了业务逻辑层和持久化层