介绍一下常见的文本聚类Text Clustering方法
文本聚类(clustering)和文本分类(classification)的区别?
- 分类是事先定义好类别。分类器需要由人工标注的分类训练语料训练得到,属于有supervised learning。Classification uses predefined classes in which objects are assigned.
适用范围:分类适合类别已经确定的场合。例如按照国图分类法分类图书。
- 聚类则没有事先定义的类别。聚类不需要人工标注和预先训练分类器,类别在聚类过程中自动生成,属于unsupervised learning。Clustering identifies similarities between objects, which are grouped as "clusters" according to their common characteristics.
适用范围:聚类事先不知道要寻找的内容,没有预先设定好的目标变量。适合分类体系不确定的场合,比如搜索引擎结果后聚类(元搜素)。 【手心里的雪2017 知乎】Clustering is when you have no clue of what types there are, and you want an algorithm to discover what types there might be.
文本聚类的输入和输出是什么?
输入:词向量矩阵
输出:clusters向量矩阵
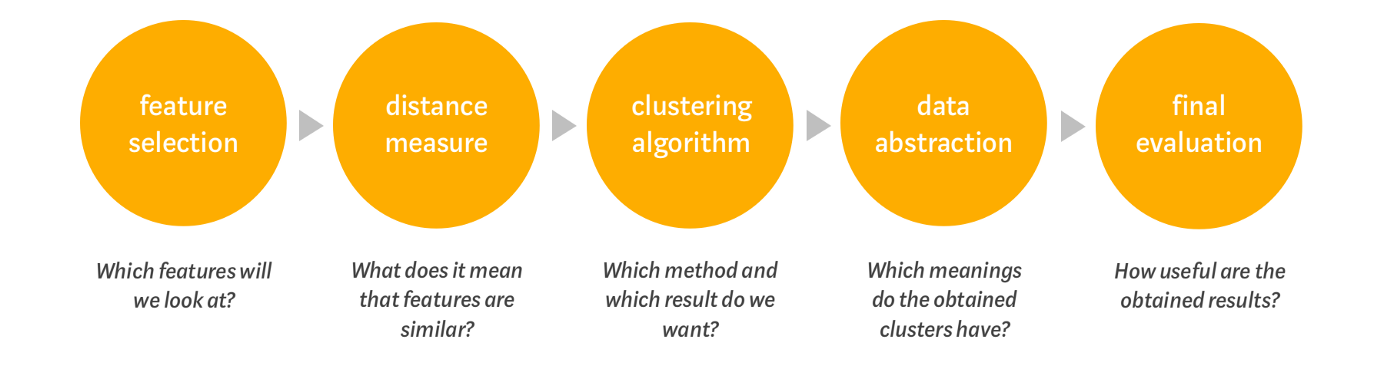
文本聚类的方法有哪些?
看以下思维导图。算法分为两种,一种是无监督学习, hard clustering,另一种是概率论,soft clustering。
Performance看下图:【神技圈子2019 CSDN】
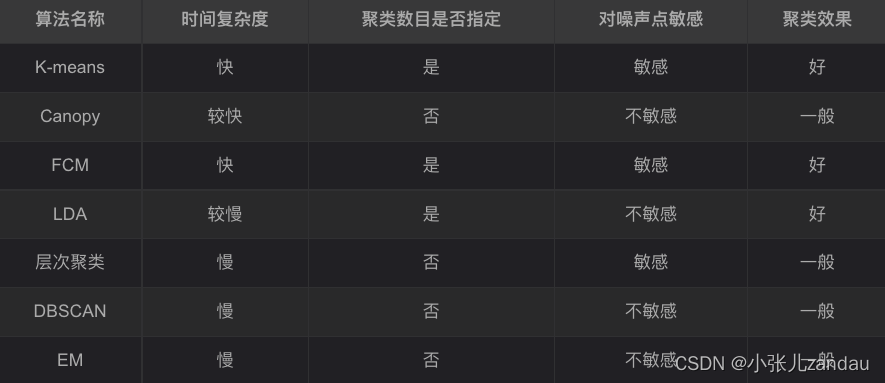
区分聚类方法的特点?
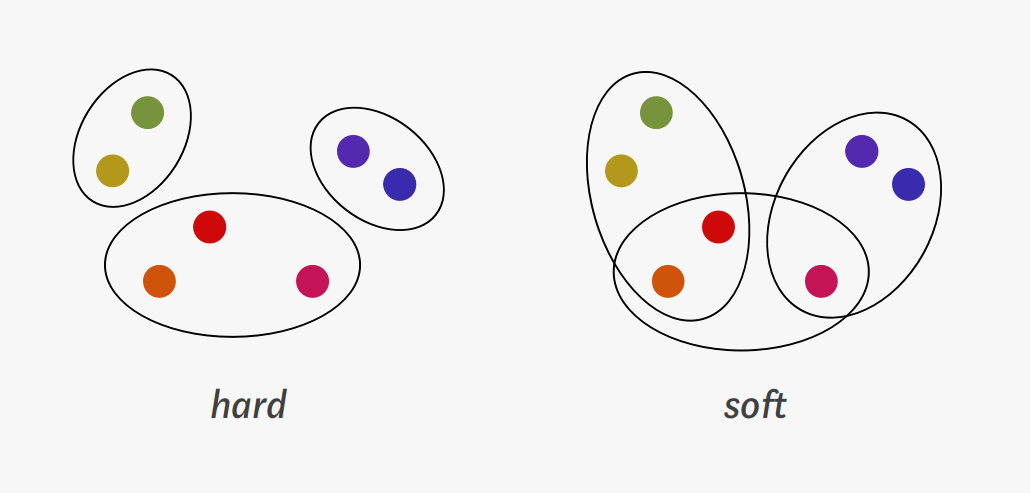
1. Hard clustering and soft clustering
In hard clustering, every object belongs to exactly one cluster. In soft clustering, an object can belong to one or more clusters. [Kosh2020 tds]
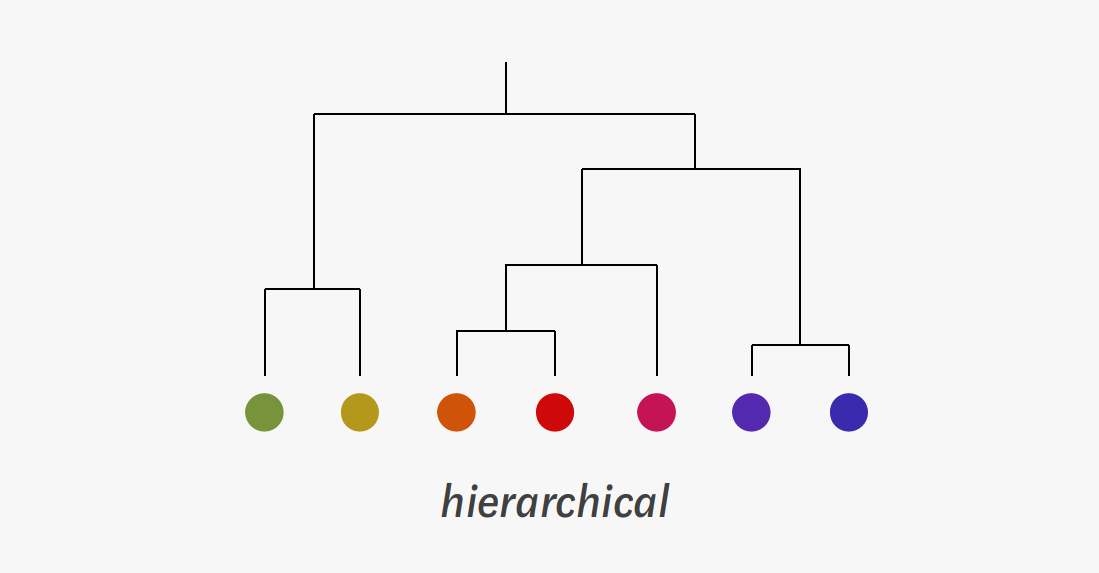
2. Hierarchical clustering and flat clustering
Hierarchical clustering can be viewed as a binary tree. Clusters are iteratively combined in a hierarchical manner, finally ending up in one root. [Kosh2020 tds]
--> Hierarchical methods can be futher divided into two subcategories. Agglomerative ("bottom up") methods start by putting each object into its own cluster and then keep unifying them. Divisive ("top down") methods start from the root and keep dividing it until only single objects are left.
All clustering methods not following this principle are described as flat clustering, which are cometimes called partitional. A hierarchical clustering can always be converted into a flat one by "cutting" the tree horizontally on a level of your choice. [Kosh2020 tds]
K-means
介绍:k-means是基于距离的聚类算法,采用的是”非此即彼”的硬聚类方式。
具体操作:
必须预先指定聚类的数目k,和指定算法迭代终止的条件(例如,迭代的次数,前后两次迭代中k个质心距离变化的综合小于一定阈值)。
1)k是需要指定的参数,即需要创建的簇的数目,继而空间中的点被划分为n簇。
2)k个簇的质心一开始通过随机的方式获得。在算法中,计算每个点到质心的距离,选择距离最小的质心对应的簇作为该数据点的划分。
3)分配过程后,更新簇的质心。重复上述过程,直至各个簇的质心不再变化为止。
英文版:
1) K random points are assinged in the vector space as initial, and each data point is then assigned to the nearest cluster mean.
2) Next, the the actual mean of each cluster is recalculated. Based on the shift of the means the data points are reassigned. This process repeats itself until the means of the clusters stop movinf around.

优点:- 适用于各个属性无关(e.g. nation, food),方差相等的类别,在二维空间类似球状分布。[ref]
- 算法快捷,容易理解。【ref】
- 相对有效率order of .. O(nkt),n是对象的总数,k是簇的个数 k<<n,t是迭代次数t<<n。[ref]
缺点:- 对初始聚类质心敏感,经常终止于局部最优解。
- 对噪声和离群点数据敏感
- 需要实现确定聚类个数
二分K-means
介绍:K-means算法的优化,有效解决k-means陷入局部最优解问题。
具体操作:
1)将所有数据点分为一个簇,使用k-means(k=2)对其进行划分
2)下一次迭代,选择使SSE下降程度最大的簇进行划分
3)重复该过程,直至簇的个数达到指定的数目位置
优点:有效解决k-means陷入局部最优解问题,聚类效果好于普通k-means算法。
缺点:..
DBSCAN
介绍:A method favouring densely populated clusters
EM
介绍:A method assumes an underlying probabilistic distribution for each cluster.
Canopy
介绍:不需要事先指定聚类数目的粗聚类方法。可以用它最为k-means, FCM或更精确聚类算法的预处理步骤,先获得k值。
优点:- 计算收敛速度快
- Canopy 算法选择的聚类中心点作为k-means算法的初始条件比较科学
缺点:- 精度较低
Brown Clustering
介绍:This is a agglomerative method relies on the distributional hypothesis.
具体做法:
A quality function is introduced, describing how well the surrounding context words predict the occurence of the words in the current cluster (so called mutual information).
1) Initialise by assigning every word to its own unique cluster
2) Merge the two clusters of which the produced union has the best quality function value. Repeat until only one cluster is left (i.e. only the root is left).
概率论类
假定数据的分布符合一系列的概率分布,用概率分布模型对数据进行聚类。因此,模型的好坏直接决定聚类效果的好坏。
PLSA
介绍:LDA的爸爸
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
介绍:PLSA的优化,在PLSA基础上加了Dirichlet先验分布。
基本操作:
假设:三层贝叶斯概率模型,分别为文档层,主体层和词层。
- 整个文档集合中存在k个相互独立的主题
- 每一个文档由k个主题的多项分布。
- 词袋假设,即在模型中不考虑词的顺序,只考虑他们的出现次数。
优点:相比PLSA,不容易产生过拟合现象。
- LDA算法具有完备的数据理论,和清晰的逻辑结构
- 适合大数据下的文本聚类。【神技圈子2019 CSDN】
缺点:- 收敛速度比较慢
- 预先人工确定主题数目